Haeyeon Kim
RL4CO: an Extensive Reinforcement Learning for Combinatorial Optimization Benchmark
Jun 29, 2023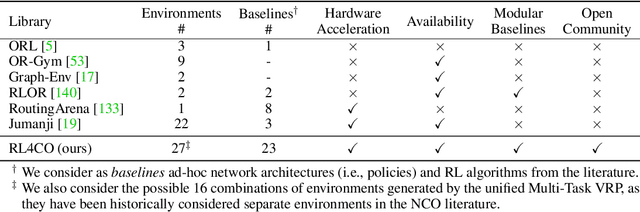
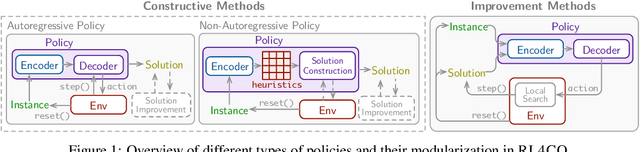

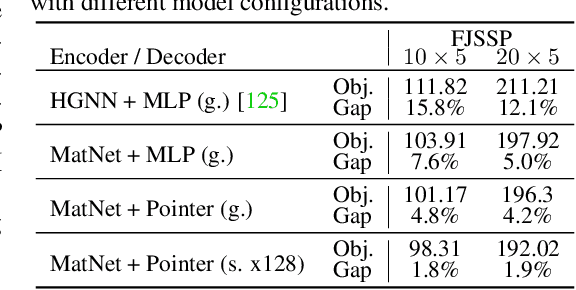
Abstract:We introduce RL4CO, an extensive reinforcement learning (RL) for combinatorial optimization (CO) benchmark. RL4CO employs state-of-the-art software libraries as well as best practices in implementation, such as modularity and configuration management, to be efficient and easily modifiable by researchers for adaptations of neural network architecture, environments, and algorithms. Contrary to the existing focus on specific tasks like the traveling salesman problem (TSP) for performance assessment, we underline the importance of scalability and generalization capabilities for diverse optimization tasks. We also systematically benchmark sample efficiency, zero-shot generalization, and adaptability to changes in data distributions of various models. Our experiments show that some recent state-of-the-art methods fall behind their predecessors when evaluated using these new metrics, suggesting the necessity for a more balanced view of the performance of neural CO solvers. We hope RL4CO will encourage the exploration of novel solutions to complex real-world tasks, allowing to compare with existing methods through a standardized interface that decouples the science from the software engineering. We make our library publicly available at https://github.com/kaist-silab/rl4co.
Collaborative Distillation Meta Learning for Simulation Intensive Hardware Design
May 26, 2022



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel collaborative distillation meta learning (CDML) framework for simulation intensive hardware design problems. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown promising performance in various hardware design problems. However, previous works on DRL-based hardware design only dealt with problems with simplified objectives, which are not practical. In fact, the objective evaluation of real-world electrical performance through simulation is costly in terms of both time and computation, making DRL scheme involving extensive reward calculations not suitable. In this paper, we apply the CDML framework to decoupling capacitor placement problem (DPP), one of the significant simulation intensive hardware design problems. The CDML framework consists of a context-based meta learner and collaborative distillation scheme to produce a reusable solver. The context-based meta learner captures the location of probing port (i.e., target circuit block) and improves generalization capability. The collaborative distillation scheme with equivariant label transformation imposes the action-permutation (AP)-equivariant nature of placement problems, which not only improves sample efficiency but also improves generalization capability. Extensive experimental results verified that our CDML outperforms both neural baselines and iterative conventional design methods in terms of real-world objective, power integrity, with zero-shot transfer-ability.
Transformer Network-based Reinforcement Learning Method for Power Distribution Network (PDN) Optimization of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)
Mar 29, 2022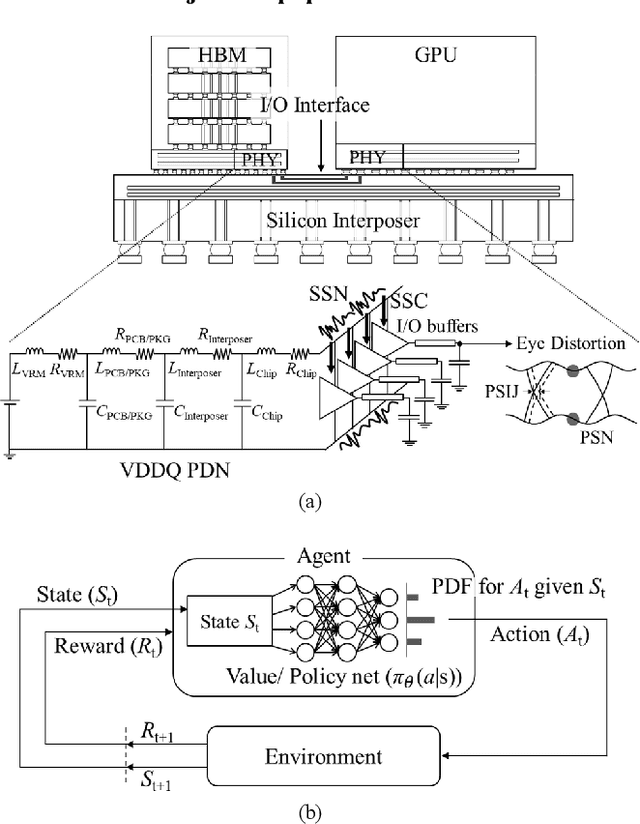
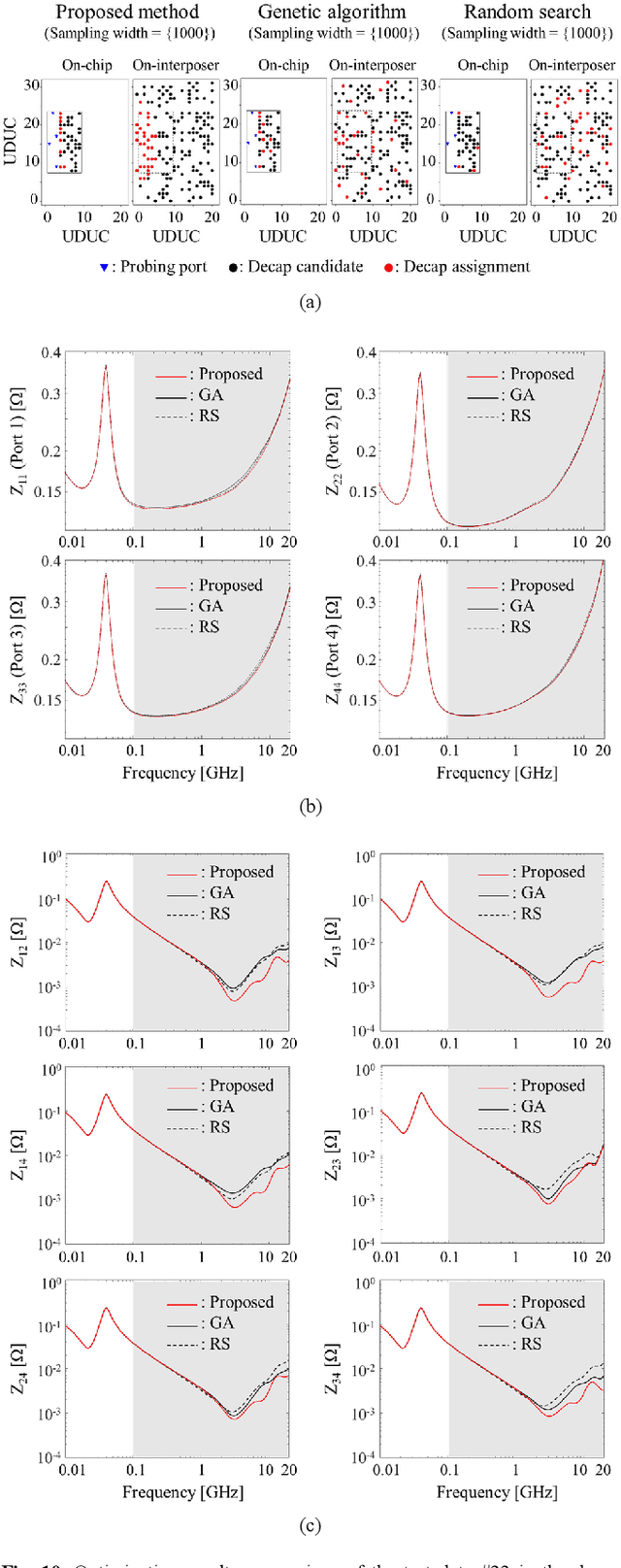
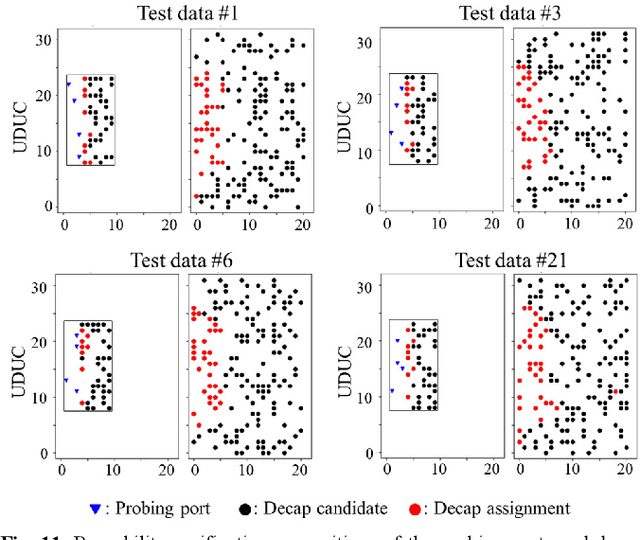
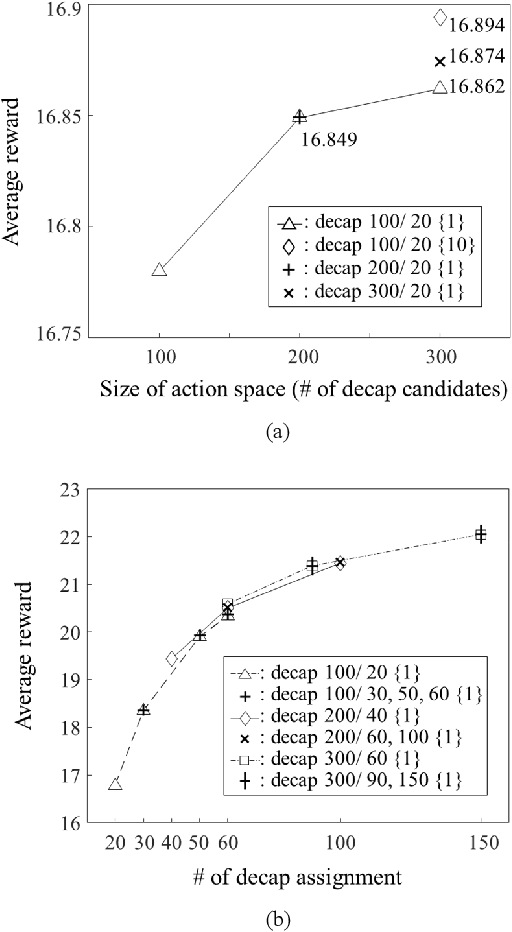
Abstract:In this article, for the first time, we propose a transformer network-based reinforcement learning (RL) method for power distribution network (PDN) optimization of high bandwidth memory (HBM). The proposed method can provide an optimal decoupling capacitor (decap) design to maximize the reduction of PDN self- and transfer impedance seen at multiple ports. An attention-based transformer network is implemented to directly parameterize decap optimization policy. The optimality performance is significantly improved since the attention mechanism has powerful expression to explore massive combinatorial space for decap assignments. Moreover, it can capture sequential relationships between the decap assignments. The computing time for optimization is dramatically reduced due to the reusable network on positions of probing ports and decap assignment candidates. This is because the transformer network has a context embedding process to capture meta-features including probing ports positions. In addition, the network is trained with randomly generated data sets. Therefore, without additional training, the trained network can solve new decap optimization problems. The computing time for training and data cost are critically decreased due to the scalability of the network. Thanks to its shared weight property, the network can adapt to a larger scale of problems without additional training. For verification, we compare the results with conventional genetic algorithm (GA), random search (RS), and all the previous RL-based methods. As a result, the proposed method outperforms in all the following aspects: optimality performance, computing time, and data efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge