Guy Blanc
Is nasty noise actually harder than malicious noise?
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:We consider the relative abilities and limitations of computationally efficient algorithms for learning in the presence of noise, under two well-studied and challenging adversarial noise models for learning Boolean functions: malicious noise, in which an adversary can arbitrarily corrupt a random subset of examples given to the learner; and nasty noise, in which an adversary can arbitrarily corrupt an adversarially chosen subset of examples given to the learner. We consider both the distribution-independent and fixed-distribution settings. Our main results highlight a dramatic difference between these two settings: For distribution-independent learning, we prove a strong equivalence between the two noise models: If a class ${\cal C}$ of functions is efficiently learnable in the presence of $η$-rate malicious noise, then it is also efficiently learnable in the presence of $η$-rate nasty noise. In sharp contrast, for the fixed-distribution setting we show an arbitrarily large separation: Under a standard cryptographic assumption, for any arbitrarily large value $r$ there exists a concept class for which there is a ratio of $r$ between the rate $η_{malicious}$ of malicious noise that polynomial-time learning algorithms can tolerate, versus the rate $η_{nasty}$ of nasty noise that such learning algorithms can tolerate. To offset the negative result for the fixed-distribution setting, we define a broad and natural class of algorithms, namely those that ignore contradictory examples (ICE). We show that for these algorithms, malicious noise and nasty noise are equivalent up to a factor of two in the noise rate: Any efficient ICE learner that succeeds with $η$-rate malicious noise can be converted to an efficient learner that succeeds with $η/2$-rate nasty noise. We further show that the above factor of two is necessary, again under a standard cryptographic assumption.
Computational-Statistical Tradeoffs from NP-hardness
Jul 17, 2025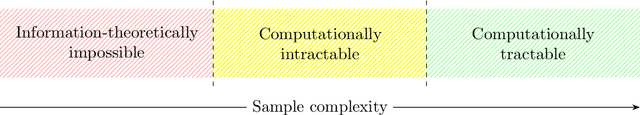


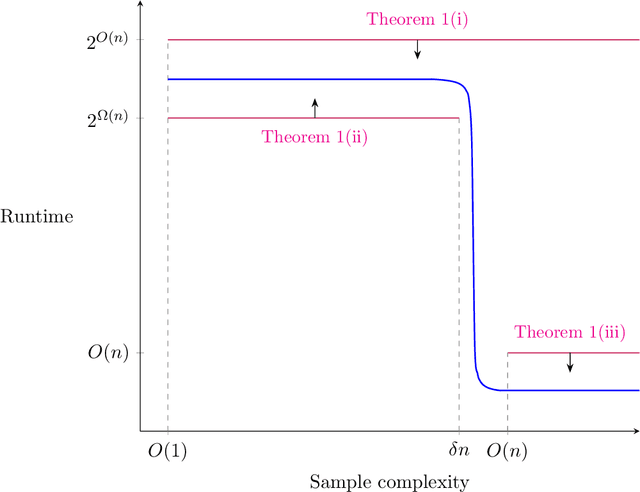
Abstract:A central question in computer science and statistics is whether efficient algorithms can achieve the information-theoretic limits of statistical problems. Many computational-statistical tradeoffs have been shown under average-case assumptions, but since statistical problems are average-case in nature, it has been a challenge to base them on standard worst-case assumptions. In PAC learning where such tradeoffs were first studied, the question is whether computational efficiency can come at the cost of using more samples than information-theoretically necessary. We base such tradeoffs on $\mathsf{NP}$-hardness and obtain: $\circ$ Sharp computational-statistical tradeoffs assuming $\mathsf{NP}$ requires exponential time: For every polynomial $p(n)$, there is an $n$-variate class $C$ with VC dimension $1$ such that the sample complexity of time-efficiently learning $C$ is $\Theta(p(n))$. $\circ$ A characterization of $\mathsf{RP}$ vs. $\mathsf{NP}$ in terms of learning: $\mathsf{RP} = \mathsf{NP}$ iff every $\mathsf{NP}$-enumerable class is learnable with $O(\mathrm{VCdim}(C))$ samples in polynomial time. The forward implication has been known since (Pitt and Valiant, 1988); we prove the reverse implication. Notably, all our lower bounds hold against improper learners. These are the first $\mathsf{NP}$-hardness results for improperly learning a subclass of polynomial-size circuits, circumventing formal barriers of Applebaum, Barak, and Xiao (2008).
Adaptive and oblivious statistical adversaries are equivalent
Oct 17, 2024
Abstract:We resolve a fundamental question about the ability to perform a statistical task, such as learning, when an adversary corrupts the sample. Such adversaries are specified by the types of corruption they can make and their level of knowledge about the sample. The latter distinguishes between sample-adaptive adversaries which know the contents of the sample when choosing the corruption, and sample-oblivious adversaries, which do not. We prove that for all types of corruptions, sample-adaptive and sample-oblivious adversaries are \emph{equivalent} up to polynomial factors in the sample size. This resolves the main open question introduced by \cite{BLMT22} and further explored in \cite{CHLLN23}. Specifically, consider any algorithm $A$ that solves a statistical task even when a sample-oblivious adversary corrupts its input. We show that there is an algorithm $A'$ that solves the same task when the corresponding sample-adaptive adversary corrupts its input. The construction of $A'$ is simple and maintains the computational efficiency of $A$: It requests a polynomially larger sample than $A$ uses and then runs $A$ on a uniformly random subsample. One of our main technical tools is a new structural result relating two distributions defined on sunflowers which may be of independent interest.
The Sample Complexity of Smooth Boosting and the Tightness of the Hardcore Theorem
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Smooth boosters generate distributions that do not place too much weight on any given example. Originally introduced for their noise-tolerant properties, such boosters have also found applications in differential privacy, reproducibility, and quantum learning theory. We study and settle the sample complexity of smooth boosting: we exhibit a class that can be weak learned to $\gamma$-advantage over smooth distributions with $m$ samples, for which strong learning over the uniform distribution requires $\tilde{\Omega}(1/\gamma^2)\cdot m$ samples. This matches the overhead of existing smooth boosters and provides the first separation from the setting of distribution-independent boosting, for which the corresponding overhead is $O(1/\gamma)$. Our work also sheds new light on Impagliazzo's hardcore theorem from complexity theory, all known proofs of which can be cast in the framework of smooth boosting. For a function $f$ that is mildly hard against size-$s$ circuits, the hardcore theorem provides a set of inputs on which $f$ is extremely hard against size-$s'$ circuits. A downside of this important result is the loss in circuit size, i.e. that $s' \ll s$. Answering a question of Trevisan, we show that this size loss is necessary and in fact, the parameters achieved by known proofs are the best possible.
Harnessing the Power of Choices in Decision Tree Learning
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:We propose a simple generalization of standard and empirically successful decision tree learning algorithms such as ID3, C4.5, and CART. These algorithms, which have been central to machine learning for decades, are greedy in nature: they grow a decision tree by iteratively splitting on the best attribute. Our algorithm, Top-$k$, considers the $k$ best attributes as possible splits instead of just the single best attribute. We demonstrate, theoretically and empirically, the power of this simple generalization. We first prove a {\sl greediness hierarchy theorem} showing that for every $k \in \mathbb{N}$, Top-$(k+1)$ can be dramatically more powerful than Top-$k$: there are data distributions for which the former achieves accuracy $1-\varepsilon$, whereas the latter only achieves accuracy $\frac1{2}+\varepsilon$. We then show, through extensive experiments, that Top-$k$ outperforms the two main approaches to decision tree learning: classic greedy algorithms and more recent "optimal decision tree" algorithms. On one hand, Top-$k$ consistently enjoys significant accuracy gains over greedy algorithms across a wide range of benchmarks. On the other hand, Top-$k$ is markedly more scalable than optimal decision tree algorithms and is able to handle dataset and feature set sizes that remain far beyond the reach of these algorithms.
Lifting uniform learners via distributional decomposition
Mar 30, 2023

Abstract:We show how any PAC learning algorithm that works under the uniform distribution can be transformed, in a blackbox fashion, into one that works under an arbitrary and unknown distribution $\mathcal{D}$. The efficiency of our transformation scales with the inherent complexity of $\mathcal{D}$, running in $\mathrm{poly}(n, (md)^d)$ time for distributions over $\{\pm 1\}^n$ whose pmfs are computed by depth-$d$ decision trees, where $m$ is the sample complexity of the original algorithm. For monotone distributions our transformation uses only samples from $\mathcal{D}$, and for general ones it uses subcube conditioning samples. A key technical ingredient is an algorithm which, given the aforementioned access to $\mathcal{D}$, produces an optimal decision tree decomposition of $\mathcal{D}$: an approximation of $\mathcal{D}$ as a mixture of uniform distributions over disjoint subcubes. With this decomposition in hand, we run the uniform-distribution learner on each subcube and combine the hypotheses using the decision tree. This algorithmic decomposition lemma also yields new algorithms for learning decision tree distributions with runtimes that exponentially improve on the prior state of the art -- results of independent interest in distribution learning.
Subsampling Suffices for Adaptive Data Analysis
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Ensuring that analyses performed on a dataset are representative of the entire population is one of the central problems in statistics. Most classical techniques assume that the dataset is independent of the analyst's query and break down in the common setting where a dataset is reused for multiple, adaptively chosen, queries. This problem of \emph{adaptive data analysis} was formalized in the seminal works of Dwork et al. (STOC, 2015) and Hardt and Ullman (FOCS, 2014). We identify a remarkably simple set of assumptions under which the queries will continue to be representative even when chosen adaptively: The only requirements are that each query takes as input a random subsample and outputs few bits. This result shows that the noise inherent in subsampling is sufficient to guarantee that query responses generalize. The simplicity of this subsampling-based framework allows it to model a variety of real-world scenarios not covered by prior work. In addition to its simplicity, we demonstrate the utility of this framework by designing mechanisms for two foundational tasks, statistical queries and median finding. In particular, our mechanism for answering the broadly applicable class of statistical queries is both extremely simple and state of the art in many parameter regimes.
Multitask Learning via Shared Features: Algorithms and Hardness
Sep 07, 2022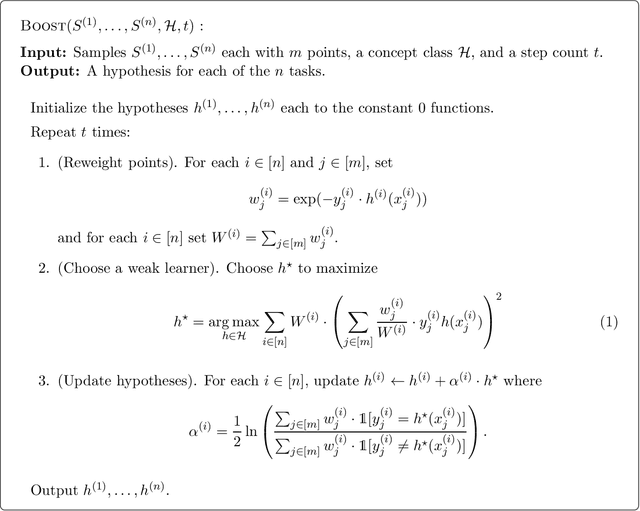
Abstract:We investigate the computational efficiency of multitask learning of Boolean functions over the $d$-dimensional hypercube, that are related by means of a feature representation of size $k \ll d$ shared across all tasks. We present a polynomial time multitask learning algorithm for the concept class of halfspaces with margin $\gamma$, which is based on a simultaneous boosting technique and requires only $\textrm{poly}(k/\gamma)$ samples-per-task and $\textrm{poly}(k\log(d)/\gamma)$ samples in total. In addition, we prove a computational separation, showing that assuming there exists a concept class that cannot be learned in the attribute-efficient model, we can construct another concept class such that can be learned in the attribute-efficient model, but cannot be multitask learned efficiently -- multitask learning this concept class either requires super-polynomial time complexity or a much larger total number of samples.
A Query-Optimal Algorithm for Finding Counterfactuals
Jul 14, 2022

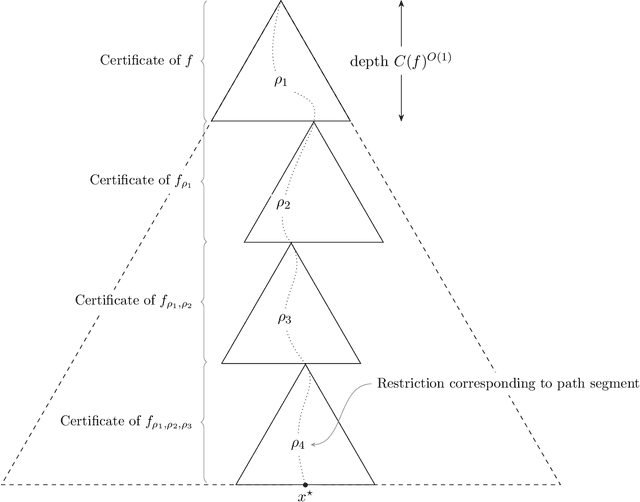
Abstract:We design an algorithm for finding counterfactuals with strong theoretical guarantees on its performance. For any monotone model $f : X^d \to \{0,1\}$ and instance $x^\star$, our algorithm makes \[ {S(f)^{O(\Delta_f(x^\star))}\cdot \log d}\] queries to $f$ and returns {an {\sl optimal}} counterfactual for $x^\star$: a nearest instance $x'$ to $x^\star$ for which $f(x')\ne f(x^\star)$. Here $S(f)$ is the sensitivity of $f$, a discrete analogue of the Lipschitz constant, and $\Delta_f(x^\star)$ is the distance from $x^\star$ to its nearest counterfactuals. The previous best known query complexity was $d^{\,O(\Delta_f(x^\star))}$, achievable by brute-force local search. We further prove a lower bound of $S(f)^{\Omega(\Delta_f(x^\star))} + \Omega(\log d)$ on the query complexity of any algorithm, thereby showing that the guarantees of our algorithm are essentially optimal.
Open Problem: Properly learning decision trees in polynomial time?
Jun 29, 2022
Abstract:The authors recently gave an $n^{O(\log\log n)}$ time membership query algorithm for properly learning decision trees under the uniform distribution (Blanc et al., 2021). The previous fastest algorithm for this problem ran in $n^{O(\log n)}$ time, a consequence of Ehrenfeucht and Haussler (1989)'s classic algorithm for the distribution-free setting. In this article we highlight the natural open problem of obtaining a polynomial-time algorithm, discuss possible avenues towards obtaining it, and state intermediate milestones that we believe are of independent interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge