Gundram Leifert
University of Rostock - CITlab
End-To-End Measure for Text Recognition
Aug 26, 2019
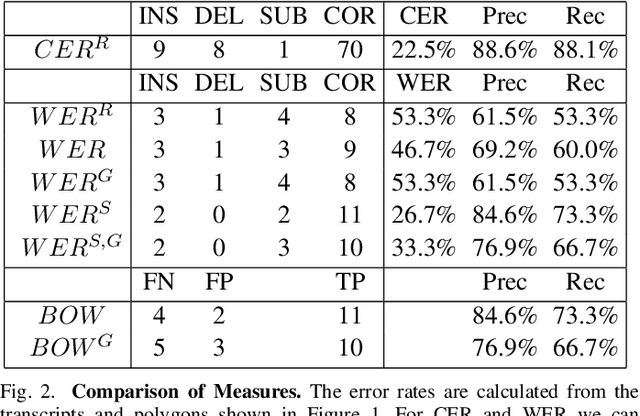
Abstract:Measuring the performance of text recognition and text line detection engines is an important step to objectively compare systems and their configuration. There exist well-established measures for both tasks separately. However, there is no sophisticated evaluation scheme to measure the quality of a combined text line detection and text recognition system. The F-measure on word level is a well-known methodology, which is sometimes used in this context. Nevertheless, it does not take into account the alignment of hypothesis and ground truth text and can lead to deceptive results. Since users of automatic information retrieval pipelines in the context of text recognition are mainly interested in the end-to-end performance of a given system, there is a strong need for such a measure. Hence, we present a measure to evaluate the quality of an end-to-end text recognition system. The basis for this measure is the well established and widely used character error rate, which is limited -- in its original form -- to aligned hypothesis and ground truth texts. The proposed measure is flexible in a way that it can be configured to penalize different reading orders between the hypothesis and ground truth and can take into account the geometric position of the text lines. Additionally, it can ignore over- and under- segmentation of text lines. With these parameters it is possible to get a measure fitting best to its own needs.
Bench-Marking Information Extraction in Semi-Structured Historical Handwritten Records
Jul 17, 2018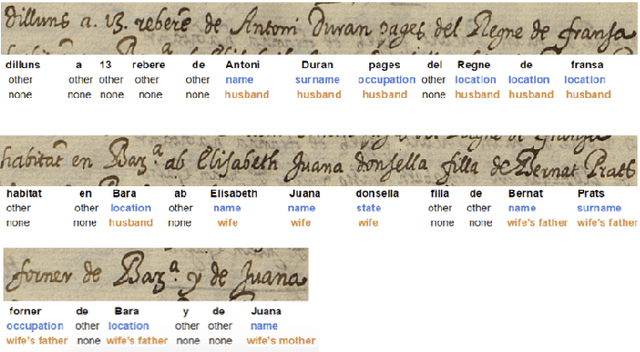
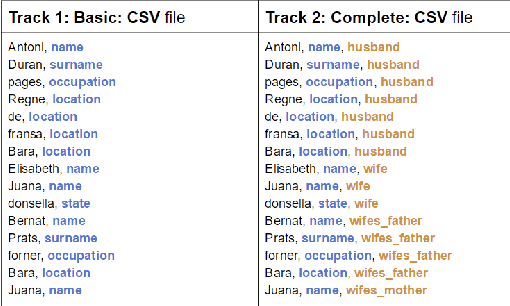
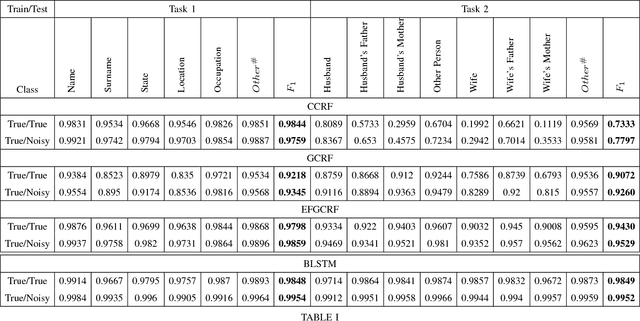
Abstract:In this report, we present our findings from benchmarking experiments for information extraction on historical handwritten marriage records Esposalles from IEHHR - ICDAR 2017 robust reading competition. The information extraction is modeled as semantic labeling of the sequence across 2 set of labels. This can be achieved by sequentially or jointly applying handwritten text recognition (HTR) and named entity recognition (NER). We deploy a pipeline approach where first we use state-of-the-art HTR and use its output as input for NER. We show that given low resource setup and simple structure of the records, high performance of HTR ensures overall high performance. We explore the various configurations of conditional random fields and neural networks to benchmark NER on given certain noisy input. The best model on 10-fold cross-validation as well as blind test data uses n-gram features with bidirectional long short-term memory.
A Two-Stage Method for Text Line Detection in Historical Documents
Feb 09, 2018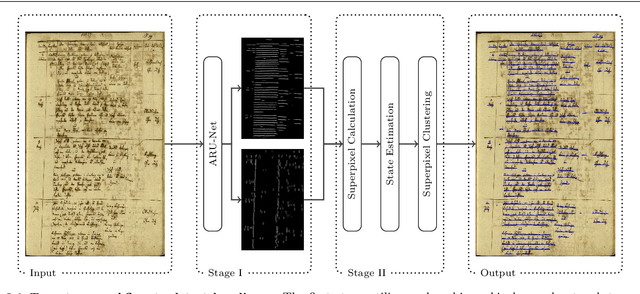
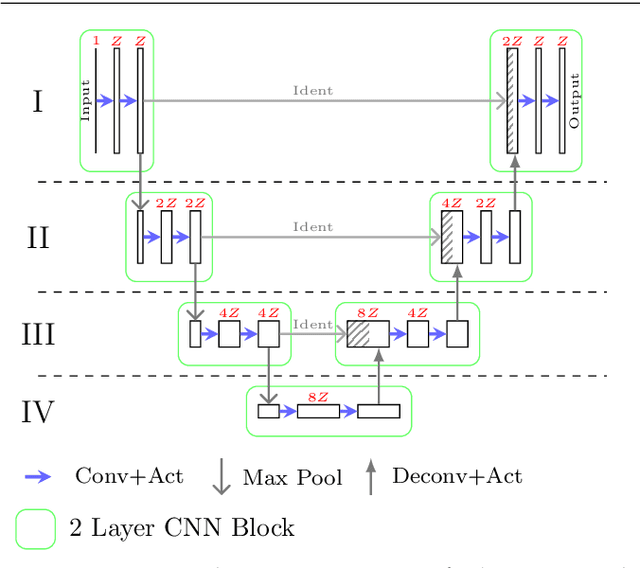
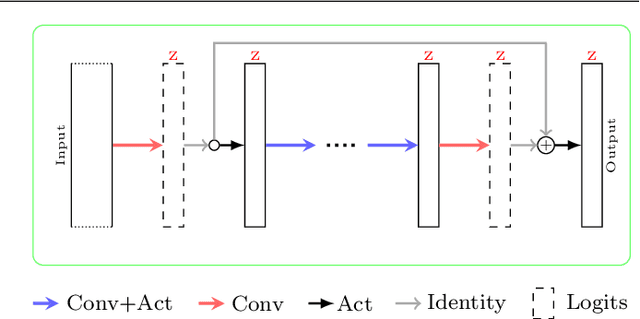
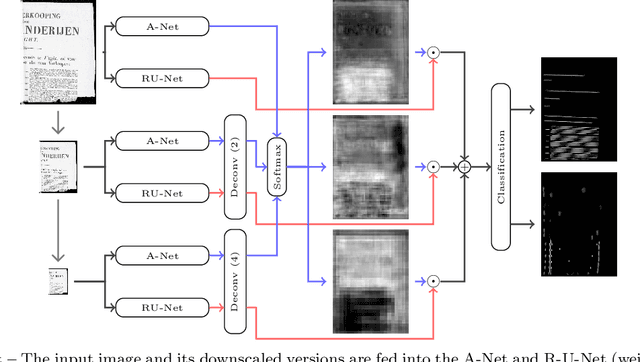
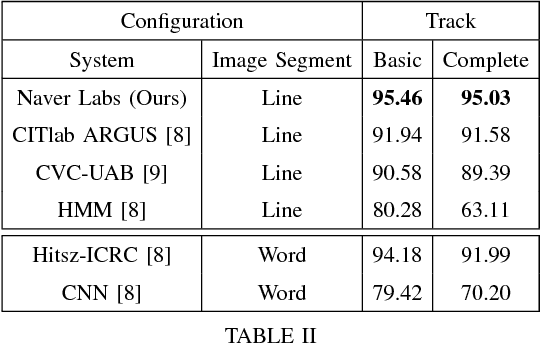
Abstract:This work presents a two-stage text line detection method for historical documents. In a first stage, a deep neural network called ARU-Net labels pixels to belong to one of the three classes: baseline, separator or other. The separator class marks beginning and end of each text line. The ARU-Net is trainable from scratch with manageably few manually annotated example images (less than 50). This is achieved by utilizing data augmentation strategies. The network predictions are used as input for the second stage which performs a bottom-up clustering to build baselines. The developed method is capable of handling complex layouts as well as curved and arbitrarily oriented text lines. It substantially outperforms current state-of-the-art approaches. For example, for the complex track of the cBAD: ICDAR2017 Competiton on Baseline Detection the F-value is increased from 0.859 to 0.922. The framework to train and run the ARU-Net is open source.
CITlab ARGUS for historical handwritten documents
May 26, 2016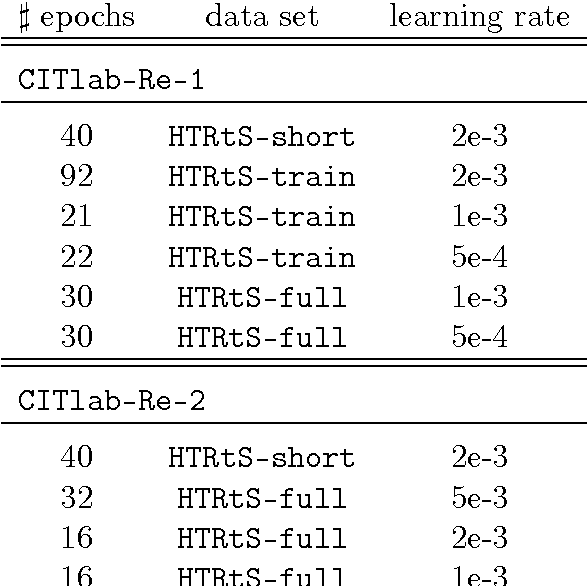


Abstract:We describe CITlab's recognition system for the HTRtS competition attached to the 13. International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, ICDAR 2015. The task comprises the recognition of historical handwritten documents. The core algorithms of our system are based on multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) and connectionist temporal classification (CTC). The software modules behind that as well as the basic utility technologies are essentially powered by PLANET's ARGUS framework for intelligent text recognition and image processing.
Regular expressions for decoding of neural network outputs
Feb 22, 2016
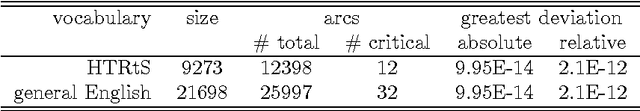
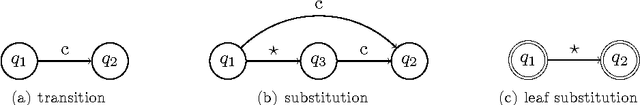
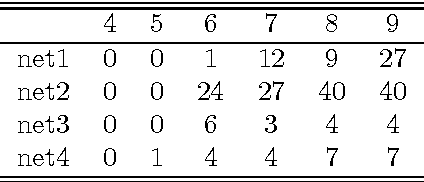
Abstract:This article proposes a convenient tool for decoding the output of neural networks trained by Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) for handwritten text recognition. We use regular expressions to describe the complex structures expected in the writing. The corresponding finite automata are employed to build a decoder. We analyze theoretically which calculations are relevant and which can be avoided. A great speed-up results from an approximation. We conclude that the approximation most likely fails if the regular expression does not match the ground truth which is not harmful for many applications since the low probability will be even underestimated. The proposed decoder is very efficient compared to other decoding methods. The variety of applications reaches from information retrieval to full text recognition. We refer to applications where we integrated the proposed decoder successfully.
CITlab ARGUS for Arabic Handwriting
Dec 15, 2014
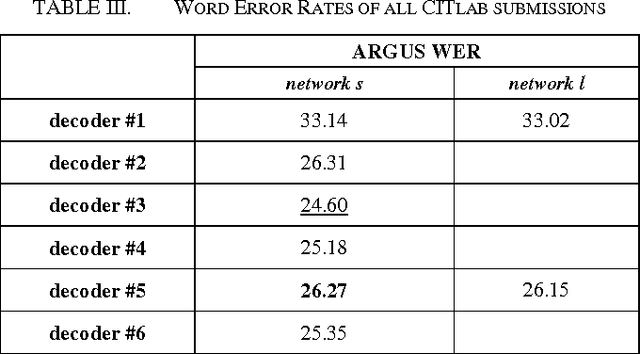
Abstract:In the recent years it turned out that multidimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) perform very well for offline handwriting recognition tasks like the OpenHaRT 2013 evaluation DIR. With suitable writing preprocessing and dictionary lookup, our ARGUS software completed this task with an error rate of 26.27% in its primary setup.
CITlab ARGUS for historical data tables
Dec 15, 2014


Abstract:We describe CITlab's recognition system for the ANWRESH-2014 competition attached to the 14. International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, ICFHR 2014. The task comprises word recognition from segmented historical documents. The core components of our system are based on multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) and connectionist temporal classification (CTC). The software modules behind that as well as the basic utility technologies are essentially powered by PLANET's ARGUS framework for intelligent text recognition and image processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge