Tobias Strauß
University of Rostock - CITlab
Exploring transfer learning for Deep NLP systems on rarely annotated languages
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) has experienced rapid advancements with the rise of deep learning, significantly outperforming traditional rule-based methods. By capturing hidden patterns and underlying structures within data, deep learning has improved performance across various NLP tasks, overcoming the limitations of rule-based systems. However, most research and development in NLP has been concentrated on a select few languages, primarily those with large numbers of speakers or financial significance, leaving many others underexplored. This lack of research is often attributed to the scarcity of adequately annotated datasets essential for training deep learning models. Despite this challenge, there is potential in leveraging the linguistic similarities between unexplored and well-studied languages, particularly those in close geographic and linguistic proximity. This thesis investigates the application of transfer learning for Part-of-Speech (POS) tagging between Hindi and Nepali, two highly similar languages belonging to the Indo-Aryan language family. Specifically, the work explores whether joint training of a POS tagging model for both languages enhances performance. Additionally, we assess whether multitask learning in Hindi, with auxiliary tasks such as gender and singular/plural tagging, can contribute to improved POS tagging accuracy. The deep learning architecture employed is the BLSTM-CNN-CRF model, trained under different conditions: monolingual word embeddings, vector-mapped embeddings, and jointly trained Hindi-Nepali word embeddings. Varying dropout rates (0.25 to 0.5) and optimizers (ADAM and AdaDelta) are also evaluated. Results indicate that jointly trained Hindi-Nepali word embeddings improve performance across all models compared to monolingual and vector-mapped embeddings.
A Two-Stage Method for Text Line Detection in Historical Documents
Feb 09, 2018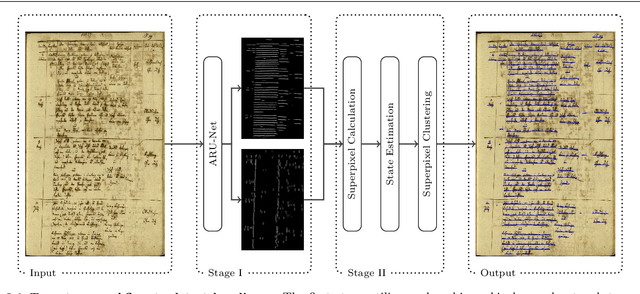
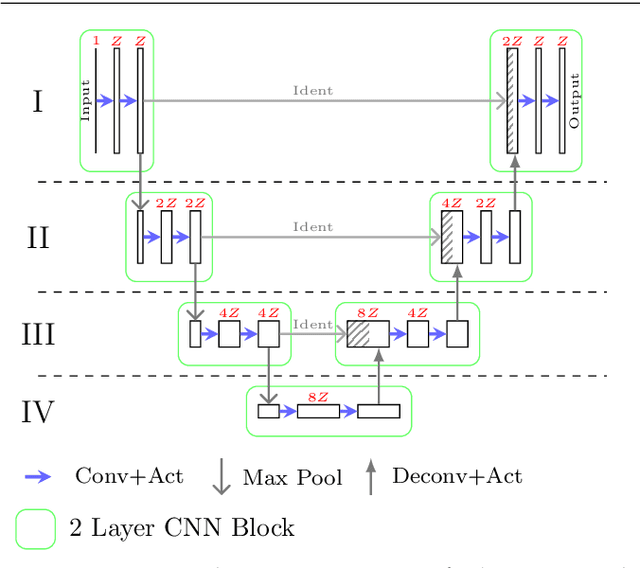
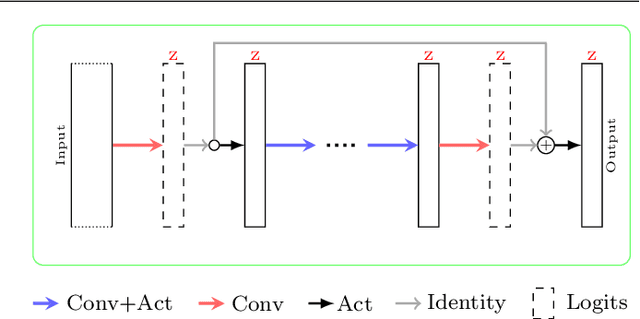
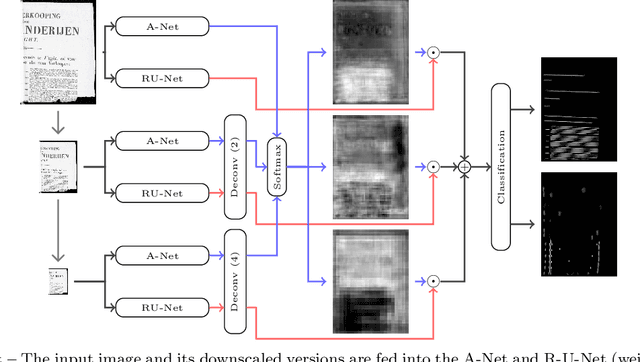
Abstract:This work presents a two-stage text line detection method for historical documents. In a first stage, a deep neural network called ARU-Net labels pixels to belong to one of the three classes: baseline, separator or other. The separator class marks beginning and end of each text line. The ARU-Net is trainable from scratch with manageably few manually annotated example images (less than 50). This is achieved by utilizing data augmentation strategies. The network predictions are used as input for the second stage which performs a bottom-up clustering to build baselines. The developed method is capable of handling complex layouts as well as curved and arbitrarily oriented text lines. It substantially outperforms current state-of-the-art approaches. For example, for the complex track of the cBAD: ICDAR2017 Competiton on Baseline Detection the F-value is increased from 0.859 to 0.922. The framework to train and run the ARU-Net is open source.
CITlab ARGUS for historical handwritten documents
May 26, 2016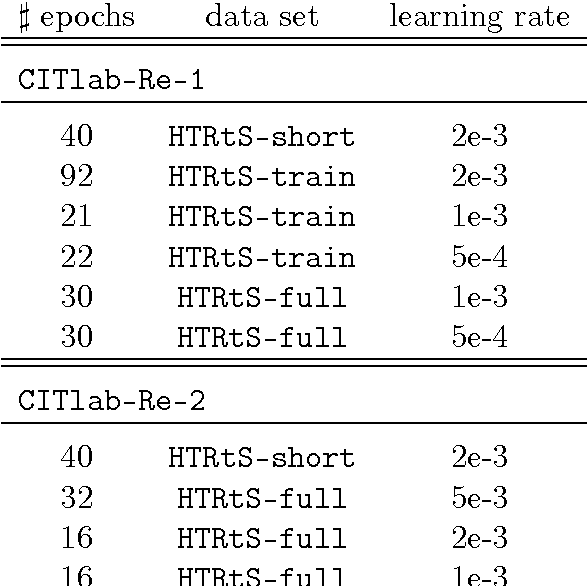


Abstract:We describe CITlab's recognition system for the HTRtS competition attached to the 13. International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, ICDAR 2015. The task comprises the recognition of historical handwritten documents. The core algorithms of our system are based on multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) and connectionist temporal classification (CTC). The software modules behind that as well as the basic utility technologies are essentially powered by PLANET's ARGUS framework for intelligent text recognition and image processing.
Regular expressions for decoding of neural network outputs
Feb 22, 2016
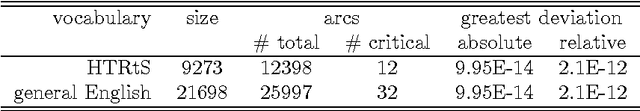
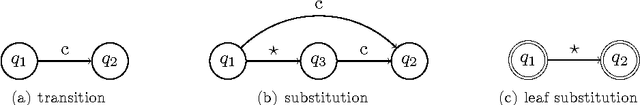
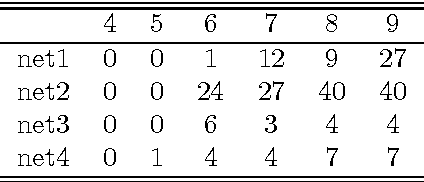
Abstract:This article proposes a convenient tool for decoding the output of neural networks trained by Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) for handwritten text recognition. We use regular expressions to describe the complex structures expected in the writing. The corresponding finite automata are employed to build a decoder. We analyze theoretically which calculations are relevant and which can be avoided. A great speed-up results from an approximation. We conclude that the approximation most likely fails if the regular expression does not match the ground truth which is not harmful for many applications since the low probability will be even underestimated. The proposed decoder is very efficient compared to other decoding methods. The variety of applications reaches from information retrieval to full text recognition. We refer to applications where we integrated the proposed decoder successfully.
CITlab ARGUS for Arabic Handwriting
Dec 15, 2014
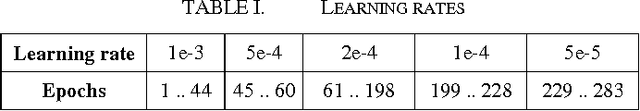
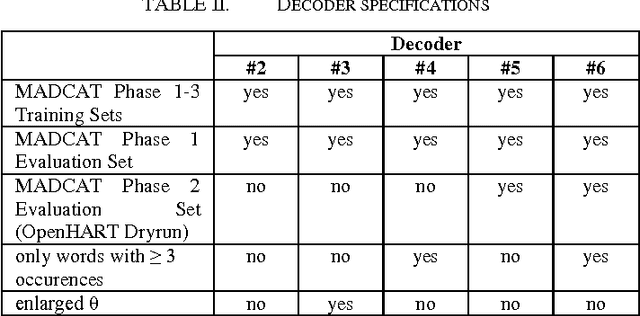
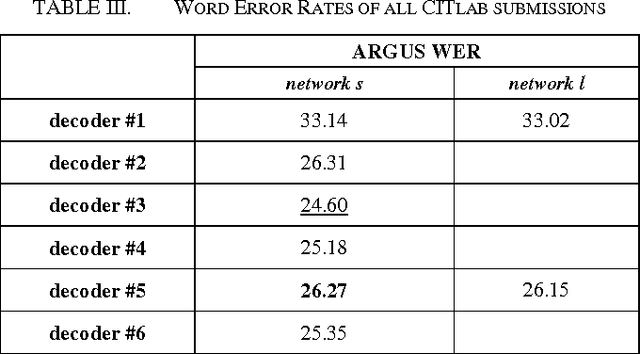
Abstract:In the recent years it turned out that multidimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) perform very well for offline handwriting recognition tasks like the OpenHaRT 2013 evaluation DIR. With suitable writing preprocessing and dictionary lookup, our ARGUS software completed this task with an error rate of 26.27% in its primary setup.
CITlab ARGUS for historical data tables
Dec 15, 2014

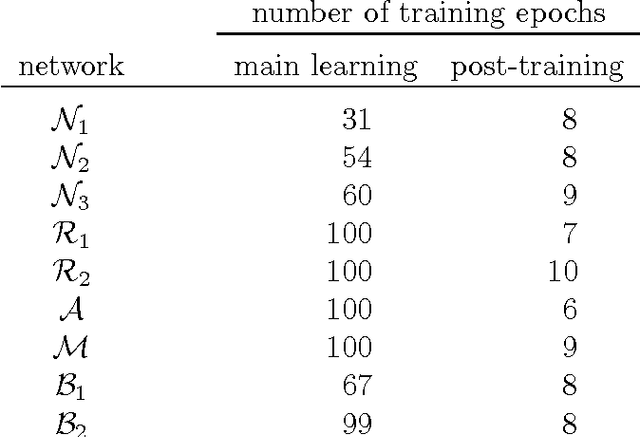

Abstract:We describe CITlab's recognition system for the ANWRESH-2014 competition attached to the 14. International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, ICFHR 2014. The task comprises word recognition from segmented historical documents. The core components of our system are based on multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks (MDRNN) and connectionist temporal classification (CTC). The software modules behind that as well as the basic utility technologies are essentially powered by PLANET's ARGUS framework for intelligent text recognition and image processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge