Guanyi Mou
Semantically Encoding Activity Labels for Context-Aware Human Activity Recognition
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Prior work has primarily formulated CA-HAR as a multi-label classification problem, where model inputs are time-series sensor data and target labels are binary encodings representing whether a given activity or context occurs. These CA-HAR methods either predicted each label independently or manually imposed relationships using graphs. However, both strategies often neglect an essential aspect: activity labels have rich semantic relationships. For instance, walking, jogging, and running activities share similar movement patterns but differ in pace and intensity, indicating that they are semantically related. Consequently, prior CA-HAR methods often struggled to accurately capture these inherent and nuanced relationships, particularly on datasets with noisy labels typically used for CA-HAR or situations where the ideal sensor type is unavailable (e.g., recognizing speech without audio sensors). To address this limitation, we propose SEAL, which leverage LMs to encode CA-HAR activity labels to capture semantic relationships. LMs generate vector embeddings that preserve rich semantic information from natural language. Our SEAL approach encodes input-time series sensor data from smart devices and their associated activity and context labels (text) as vector embeddings. During training, SEAL aligns the sensor data representations with their corresponding activity/context label embeddings in a shared embedding space. At inference time, SEAL performs a similarity search, returning the CA-HAR label with the embedding representation closest to the input data. Although LMs have been widely explored in other domains, surprisingly, their potential in CA-HAR has been underexplored, making our approach a novel contribution to the field. Our research opens up new possibilities for integrating more advanced LMs into CA-HAR tasks.
Deep Heterogeneous Contrastive Hyper-Graph Learning for In-the-Wild Context-Aware Human Activity Recognition
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is a challenging, multi-label classification problem as activities may co-occur and sensor signals corresponding to the same activity may vary in different contexts (e.g., different device placements). This paper proposes a Deep Heterogeneous Contrastive Hyper-Graph Learning (DHC-HGL) framework that captures heterogenous Context-Aware HAR (CA-HAR) hypergraph properties in a message-passing and neighborhood-aggregation fashion. Prior work only explored homogeneous or shallow-node-heterogeneous graphs. DHC-HGL handles heterogeneous CA-HAR data by innovatively 1) Constructing three different types of sub-hypergraphs that are each passed through different custom HyperGraph Convolution (HGC) layers designed to handle edge-heterogeneity and 2) Adopting a contrastive loss function to ensure node-heterogeneity. In rigorous evaluation on two CA-HAR datasets, DHC-HGL significantly outperformed state-of-the-art baselines by 5.8% to 16.7% on Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) and 3.0% to 8.4% on Macro F1 scores. UMAP visualizations of learned CA-HAR node embeddings are also presented to enhance model explainability.
* IMWUT 2023
Reducing and Exploiting Data Augmentation Noise through Meta Reweighting Contrastive Learning for Text Classification
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Data augmentation has shown its effectiveness in resolving the data-hungry problem and improving model's generalization ability. However, the quality of augmented data can be varied, especially compared with the raw/original data. To boost deep learning models' performance given augmented data/samples in text classification tasks, we propose a novel framework, which leverages both meta learning and contrastive learning techniques as parts of our design for reweighting the augmented samples and refining their feature representations based on their quality. As part of the framework, we propose novel weight-dependent enqueue and dequeue algorithms to utilize augmented samples' weight/quality information effectively. Through experiments, we show that our framework can reasonably cooperate with existing deep learning models (e.g., RoBERTa-base and Text-CNN) and augmentation techniques (e.g., Wordnet and Easydata) for specific supervised learning tasks. Experiment results show that our framework achieves an average of 1.6%, up to 4.3% absolute improvement on Text-CNN encoders and an average of 1.4%, up to 4.4% absolute improvement on RoBERTa-base encoders on seven GLUE benchmark datasets compared with the best baseline. We present an indepth analysis of our framework design, revealing the non-trivial contributions of our network components. Our code is publicly available for better reproducibility.
* IEEE BigData 2021
Heterogeneous Hyper-Graph Neural Networks for Context-aware Human Activity Recognition
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Context-aware Human Activity Recognition (CHAR) is challenging due to the need to recognize the user's current activity from signals that vary significantly with contextual factors such as phone placements and the varied styles with which different users perform the same activity. In this paper, we argue that context-aware activity visit patterns in realistic in-the-wild data can equivocally be considered as a general graph representation learning task. We posit that exploiting underlying graphical patterns in CHAR data can improve CHAR task performance and representation learning. Building on the intuition that certain activities are frequently performed with the phone placed in certain positions, we focus on the context-aware human activity problem of recognizing the <Activity, Phone Placement> tuple. We demonstrate that CHAR data has an underlying graph structure that can be viewed as a heterogenous hypergraph that has multiple types of nodes and hyperedges (an edge connecting more than two nodes). Subsequently, learning <Activity, Phone Placement> representations becomes a graph node representation learning problem. After task transformation, we further propose a novel Heterogeneous HyperGraph Neural Network architecture for Context-aware Human Activity Recognition (HHGNN-CHAR), with three types of heterogeneous nodes (user, phone placement, and activity). Connections between all types of nodes are represented by hyperedges. Rigorous evaluation demonstrated that on an unscripted, in-the-wild CHAR dataset, our proposed framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines including CHAR models that do not exploit graphs, and GNN variants that do not incorporate heterogeneous nodes or hyperedges with overall improvements 14.04% on Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) and 7.01% on Macro F1 scores.
* PerCom 2023
SWE2: SubWord Enriched and Significant Word Emphasized Framework for Hate Speech Detection
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Hate speech detection on online social networks has become one of the emerging hot topics in recent years. With the broad spread and fast propagation speed across online social networks, hate speech makes significant impacts on society by increasing prejudice and hurting people. Therefore, there are aroused attention and concern from both industry and academia. In this paper, we address the hate speech problem and propose a novel hate speech detection framework called SWE2, which only relies on the content of messages and automatically identifies hate speech. In particular, our framework exploits both word-level semantic information and sub-word knowledge. It is intuitively persuasive and also practically performs well under a situation with/without character-level adversarial attack. Experimental results show that our proposed model achieves 0.975 accuracy and 0.953 macro F1, outperforming 7 state-of-the-art baselines under no adversarial attack. Our model robustly and significantly performed well under extreme adversarial attack (manipulation of 50% messages), achieving 0.967 accuracy and 0.934 macro F1.
* Published in CIKM 2020
An Effective, Robust and Fairness-aware Hate Speech Detection Framework
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:With the widespread online social networks, hate speeches are spreading faster and causing more damage than ever before. Existing hate speech detection methods have limitations in several aspects, such as handling data insufficiency, estimating model uncertainty, improving robustness against malicious attacks, and handling unintended bias (i.e., fairness). There is an urgent need for accurate, robust, and fair hate speech classification in online social networks. To bridge the gap, we design a data-augmented, fairness addressed, and uncertainty estimated novel framework. As parts of the framework, we propose Bidirectional Quaternion-Quasi-LSTM layers to balance effectiveness and efficiency. To build a generalized model, we combine five datasets collected from three platforms. Experiment results show that our model outperforms eight state-of-the-art methods under both no attack scenario and various attack scenarios, indicating the effectiveness and robustness of our model. We share our code along with combined dataset for better future research
* IEEE BigData 2021
Wildlife Product Trading in Online Social Networks: A Case Study on Ivory-Related Product Sales Promotion Posts
Sep 25, 2024
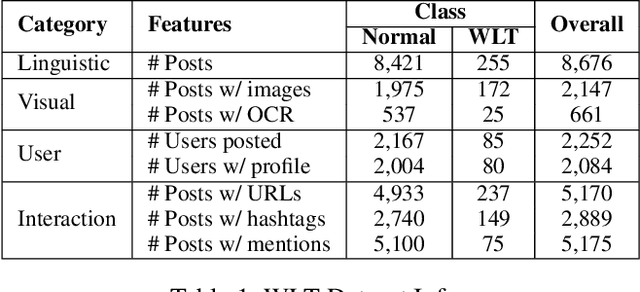
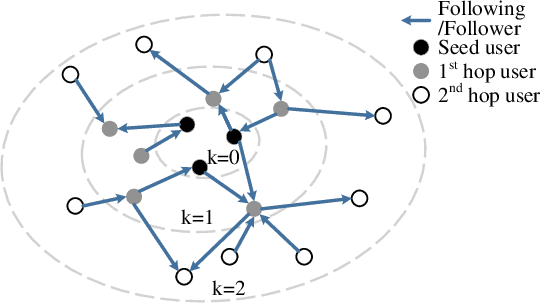
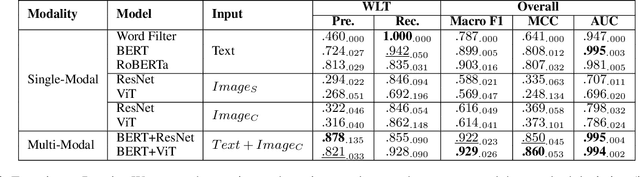
Abstract:Wildlife trafficking (WLT) has emerged as a global issue, with traffickers expanding their operations from offline to online platforms, utilizing e-commerce websites and social networks to enhance their illicit trade. This paper addresses the challenge of detecting and recognizing wildlife product sales promotion behaviors in online social networks, a crucial aspect in combating these environmentally harmful activities. To counter these environmentally damaging illegal operations, in this research, we focus on wildlife product sales promotion behaviors in online social networks. Specifically, 1) A scalable dataset related to wildlife product trading is collected using a network-based approach. This dataset is labeled through a human-in-the-loop machine learning process, distinguishing positive class samples containing wildlife product selling posts and hard-negatives representing normal posts misclassified as potential WLT posts, subsequently corrected by human annotators. 2) We benchmark the machine learning results on the proposed dataset and build a practical framework that automatically identifies suspicious wildlife selling posts and accounts, sufficiently leveraging the multi-modal nature of online social networks. 3) This research delves into an in-depth analysis of trading posts, shedding light on the systematic and organized selling behaviors prevalent in the current landscape. We provide detailed insights into the nature of these behaviors, contributing valuable information for understanding and countering illegal wildlife product trading.
* ICWSM 2024
Understanding Hyperbolic Metric Learning through Hard Negative Sampling
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:In recent years, there has been a growing trend of incorporating hyperbolic geometry methods into computer vision. While these methods have achieved state-of-the-art performance on various metric learning tasks using hyperbolic distance measurements, the underlying theoretical analysis supporting this superior performance remains under-exploited. In this study, we investigate the effects of integrating hyperbolic space into metric learning, particularly when training with contrastive loss. We identify a need for a comprehensive comparison between Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces regarding the temperature effect in the contrastive loss within the existing literature. To address this gap, we conduct an extensive investigation to benchmark the results of Vision Transformers (ViTs) using a hybrid objective function that combines loss from Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. Additionally, we provide a theoretical analysis of the observed performance improvement. We also reveal that hyperbolic metric learning is highly related to hard negative sampling, providing insights for future work. This work will provide valuable data points and experience in understanding hyperbolic image embeddings. To shed more light on problem-solving and encourage further investigation into our approach, our code is available online (https://github.com/YunYunY/HypMix).
Extracting and Visualizing Wildlife Trafficking Events from Wildlife Trafficking Reports
Jul 17, 2022



Abstract:Experts combating wildlife trafficking manually sift through articles about seizures and arrests, which is time consuming and make identifying trends difficult. We apply natural language processing techniques to automatically extract data from reports published by the Eco Activists for Governance and Law Enforcement (EAGLE). We expanded Python spaCy's pre-trained pipeline and added a custom named entity ruler, which identified 15 fully correct and 36 partially correct events in 15 reports against an existing baseline, which did not identify any fully correct events. The extracted wildlife trafficking events were inserted to a database. Then, we created visualizations to display trends over time and across regions to support domain experts. These are accessible on our website, Wildlife Trafficking in Africa (https://wildlifemqp.github.io/Visualizations/).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge