Gongping Huang
CoCoEmo: Composable and Controllable Human-Like Emotional TTS via Activation Steering
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Emotional expression in human speech is nuanced and compositional, often involving multiple, sometimes conflicting, affective cues that may diverge from linguistic content. In contrast, most expressive text-to-speech systems enforce a single utterance-level emotion, collapsing affective diversity and suppressing mixed or text-emotion-misaligned expression. While activation steering via latent direction vectors offers a promising solution, it remains unclear whether emotion representations are linearly steerable in TTS, where steering should be applied within hybrid TTS architectures, and how such complex emotion behaviors should be evaluated. This paper presents the first systematic analysis of activation steering for emotional control in hybrid TTS models, introducing a quantitative, controllable steering framework, and multi-rater evaluation protocols that enable composable mixed-emotion synthesis and reliable text-emotion mismatch synthesis. Our results demonstrate, for the first time, that emotional prosody and expressive variability are primarily synthesized by the TTS language module instead of the flow-matching module, and also provide a lightweight steering approach for generating natural, human-like emotional speech.
A Unified Neural Codec Language Model for Selective Editable Text to Speech Generation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Neural codec language models achieve impressive zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) by fully imitating the acoustic characteristics of a short speech prompt, including timbre, prosody, and paralinguistic information. However, such holistic imitation limits their ability to isolate and control individual attributes. In this paper, we present a unified codec language model SpeechEdit that extends zero-shot TTS with a selective control mechanism. By default, SpeechEdit reproduces the complete acoustic profile inferred from the speech prompt, but it selectively overrides only the attributes specified by explicit control instructions. To enable controllable modeling, SpeechEdit is trained on our newly constructed LibriEdit dataset, which provides delta (difference-aware) training pairs derived from LibriHeavy. Experimental results show that our approach maintains naturalness and robustness while offering flexible and localized control over desired attributes. Audio samples are available at https://speech-editing.github.io/speech-editing/.
Robust Online Overdetermined Independent Vector Analysis Based on Bilinear Decomposition
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Online blind source separation is essential for both speech communication and human-machine interaction. Among existing approaches, overdetermined independent vector analysis (OverIVA) delivers strong performance by exploiting the statistical independence of source signals and the orthogonality between source and noise subspaces. However, when applied to large microphone arrays, the number of parameters grows rapidly, which can degrade online estimation accuracy. To overcome this challenge, we propose decomposing each long separation filter into a bilinear form of two shorter filters, thereby reducing the number of parameters. Because the two filters are closely coupled, we design an alternating iterative projection algorithm to update them in turn. Simulation results show that, with far fewer parameters, the proposed method achieves improved performance and robustness.
TTMBA: Towards Text To Multiple Sources Binaural Audio Generation
Jul 22, 2025



Abstract:Most existing text-to-audio (TTA) generation methods produce mono outputs, neglecting essential spatial information for immersive auditory experiences. To address this issue, we propose a cascaded method for text-to-multisource binaural audio generation (TTMBA) with both temporal and spatial control. First, a pretrained large language model (LLM) segments the text into a structured format with time and spatial details for each sound event. Next, a pretrained mono audio generation network creates multiple mono audios with varying durations for each event. These mono audios are transformed into binaural audios using a binaural rendering neural network based on spatial data from the LLM. Finally, the binaural audios are arranged by their start times, resulting in multisource binaural audio. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in terms of both audio generation quality and spatial perceptual accuracy.
Spatial-Filter-Bank-Based Neural Method for Multichannel Speech Enhancement
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The performance of deep learning-based multi-channel speech enhancement methods often deteriorates when the geometric parameters of the microphone array change. Traditional approaches to mitigate this issue typically involve training on multiple microphone arrays, which can be costly. To address this challenge, we focus on uniform circular arrays and propose the use of a spatial filter bank to extract features that are approximately invariant to geometric parameters. These features are then processed by a two-stage conformer-based model (TSCBM) to enhance speech quality. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method can be trained on a fixed microphone array while maintaining effective performance across uniform circular arrays with unseen geometric configurations during applications.
LMFCA-Net: A Lightweight Model for Multi-Channel Speech Enhancement with Efficient Narrow-Band and Cross-Band Attention
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Deep learning based end-to-end multi-channel speech enhancement methods have achieved impressive performance by leveraging sub-band, cross-band, and spatial information. However, these methods often demand substantial computational resources, limiting their practicality on terminal devices. This paper presents a lightweight multi-channel speech enhancement network with decoupled fully connected attention (LMFCA-Net). The proposed LMFCA-Net introduces time-axis decoupled fully-connected attention (T-FCA) and frequency-axis decoupled fully-connected attention (F-FCA) mechanisms to effectively capture long-range narrow-band and cross-band information without recurrent units. Experimental results show that LMFCA-Net performs comparably to state-of-the-art methods while significantly reducing computational complexity and latency, making it a promising solution for practical applications.
Advances in Microphone Array Processing and Multichannel Speech Enhancement
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:This paper reviews pioneering works in microphone array processing and multichannel speech enhancement, highlighting historical achievements, technological evolution, commercialization aspects, and key challenges. It provides valuable insights into the progression and future direction of these areas. The paper examines foundational developments in microphone array design and optimization, showcasing innovations that improved sound acquisition and enhanced speech intelligibility in noisy and reverberant environments. It then introduces recent advancements and cutting-edge research in the field, particularly the integration of deep learning techniques such as all-neural beamformers. The paper also explores critical applications, discussing their evolution and current state-of-the-art technologies that significantly impact user experience. Finally, the paper outlines future research directions, identifying challenges and potential solutions that could drive further innovation in these fields. By providing a comprehensive overview and forward-looking perspective, this paper aims to inspire ongoing research and contribute to the sustained growth and development of microphone arrays and multichannel speech enhancement.
Noro: A Noise-Robust One-shot Voice Conversion System with Hidden Speaker Representation Capabilities
Nov 29, 2024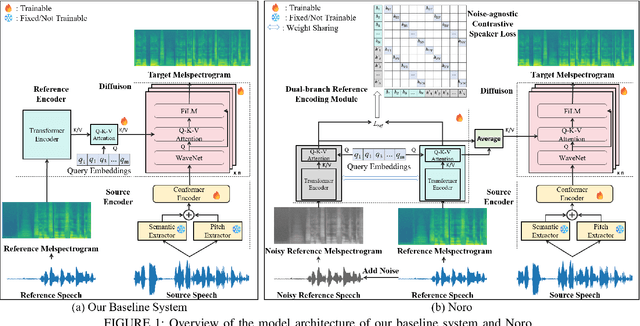
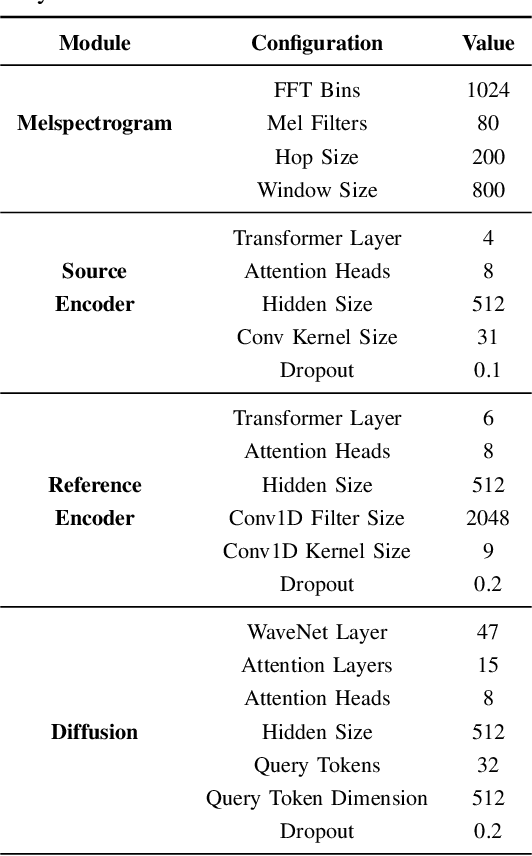
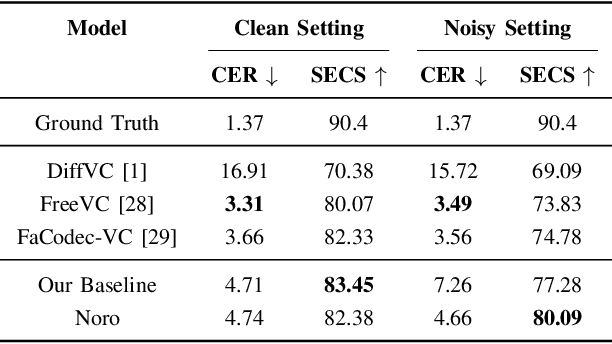
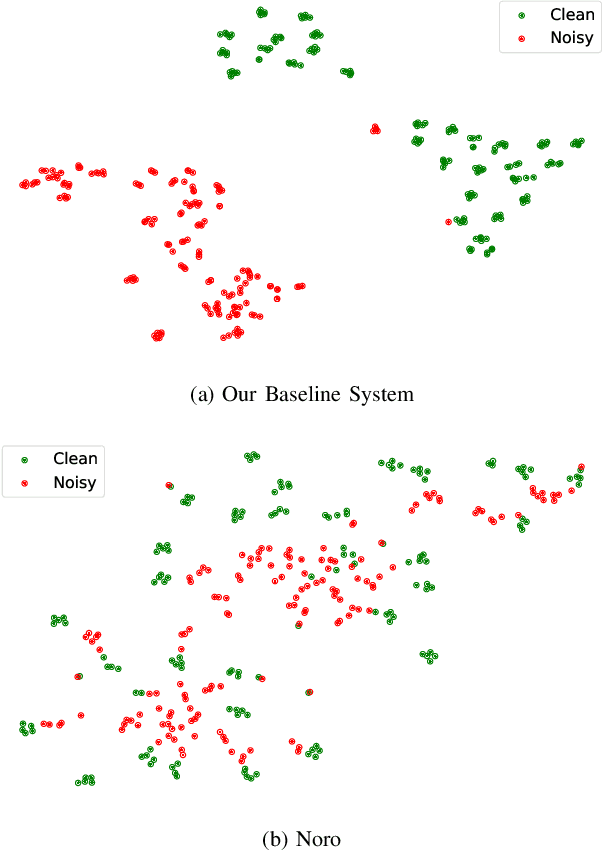
Abstract:One-shot voice conversion (VC) aims to alter the timbre of speech from a source speaker to match that of a target speaker using just a single reference speech from the target, while preserving the semantic content of the original source speech. Despite advancements in one-shot VC, its effectiveness decreases in real-world scenarios where reference speeches, often sourced from the internet, contain various disturbances like background noise. To address this issue, we introduce Noro, a Noise Robust One-shot VC system. Noro features innovative components tailored for VC using noisy reference speeches, including a dual-branch reference encoding module and a noise-agnostic contrastive speaker loss. Experimental results demonstrate that Noro outperforms our baseline system in both clean and noisy scenarios, highlighting its efficacy for real-world applications. Additionally, we investigate the hidden speaker representation capabilities of our baseline system by repurposing its reference encoder as a speaker encoder. The results shows that it is competitive with several advanced self-supervised learning models for speaker representation under the SUPERB settings, highlighting the potential for advancing speaker representation learning through one-shot VC task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge