Gleb Shevchuk
Learning Reward Functions from Diverse Sources of Human Feedback: Optimally Integrating Demonstrations and Preferences
Jun 24, 2020

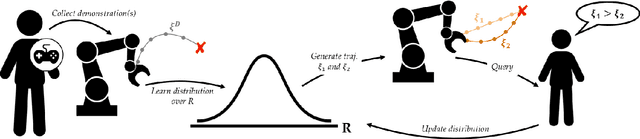

Abstract:Reward functions are a common way to specify the objective of a robot. As designing reward functions can be extremely challenging, a more promising approach is to directly learn reward functions from human teachers. Importantly, humans provide data in a variety of forms: these include instructions (e.g., natural language), demonstrations, (e.g., kinesthetic guidance), and preferences (e.g., comparative rankings). Prior research has independently applied reward learning to each of these different data sources. However, there exist many domains where some of these information sources are not applicable or inefficient -- while multiple sources are complementary and expressive. Motivated by this general problem, we present a framework to integrate multiple sources of information, which are either passively or actively collected from human users. In particular, we present an algorithm that first utilizes user demonstrations to initialize a belief about the reward function, and then proactively probes the user with preference queries to zero-in on their true reward. This algorithm not only enables us combine multiple data sources, but it also informs the robot when it should leverage each type of information. Further, our approach accounts for the human's ability to provide data: yielding user-friendly preference queries which are also theoretically optimal. Our extensive simulated experiments and user studies on a Fetch mobile manipulator demonstrate the superiority and the usability of our integrated framework.
Learning Reward Functions by Integrating Human Demonstrations and Preferences
Jun 21, 2019


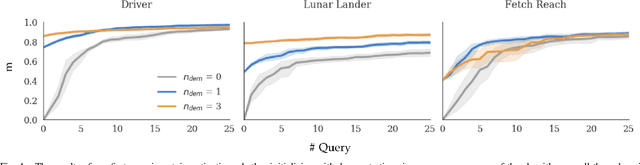
Abstract:Our goal is to accurately and efficiently learn reward functions for autonomous robots. Current approaches to this problem include inverse reinforcement learning (IRL), which uses expert demonstrations, and preference-based learning, which iteratively queries the user for her preferences between trajectories. In robotics however, IRL often struggles because it is difficult to get high-quality demonstrations; conversely, preference-based learning is very inefficient since it attempts to learn a continuous, high-dimensional function from binary feedback. We propose a new framework for reward learning, DemPref, that uses both demonstrations and preference queries to learn a reward function. Specifically, we (1) use the demonstrations to learn a coarse prior over the space of reward functions, to reduce the effective size of the space from which queries are generated; and (2) use the demonstrations to ground the (active) query generation process, to improve the quality of the generated queries. Our method alleviates the efficiency issues faced by standard preference-based learning methods and does not exclusively depend on (possibly low-quality) demonstrations. In numerical experiments, we find that DemPref is significantly more efficient than a standard active preference-based learning method. In a user study, we compare our method to a standard IRL method; we find that users rated the robot trained with DemPref as being more successful at learning their desired behavior, and preferred to use the DemPref system (over IRL) to train the robot.
Unsupervised Visuomotor Control through Distributional Planning Networks
Feb 14, 2019



Abstract:While reinforcement learning (RL) has the potential to enable robots to autonomously acquire a wide range of skills, in practice, RL usually requires manual, per-task engineering of reward functions, especially in real world settings where aspects of the environment needed to compute progress are not directly accessible. To enable robots to autonomously learn skills, we instead consider the problem of reinforcement learning without access to rewards. We aim to learn an unsupervised embedding space under which the robot can measure progress towards a goal for itself. Our approach explicitly optimizes for a metric space under which action sequences that reach a particular state are optimal when the goal is the final state reached. This enables learning effective and control-centric representations that lead to more autonomous reinforcement learning algorithms. Our experiments on three simulated environments and two real-world manipulation problems show that our method can learn effective goal metrics from unlabeled interaction, and use the learned goal metrics for autonomous reinforcement learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge