Ghyslain Gagnon
WiP: Towards a Secure SECP256K1 for Crypto Wallets: Hardware Architecture and Implementation
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:The SECP256K1 elliptic curve algorithm is fundamental in cryptocurrency wallets for generating secure public keys from private keys, thereby ensuring the protection and ownership of blockchain-based digital assets. However, the literature highlights several successful side-channel attacks on hardware wallets that exploit SECP256K1 to extract private keys. This work proposes a novel hardware architecture for SECP256K1, optimized for side-channel attack resistance and efficient resource utilization. The architecture incorporates complete addition formulas, temporary registers, and parallel processing techniques, making elliptic curve point addition and doubling operations indistinguishable. Implementation results demonstrate an average reduction of 45% in LUT usage compared to similar works, emphasizing the design's resource efficiency.
Improvement Of Audiovisual Quality Estimation Using A Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Neural Network And Bitstream Parameters
Feb 28, 2024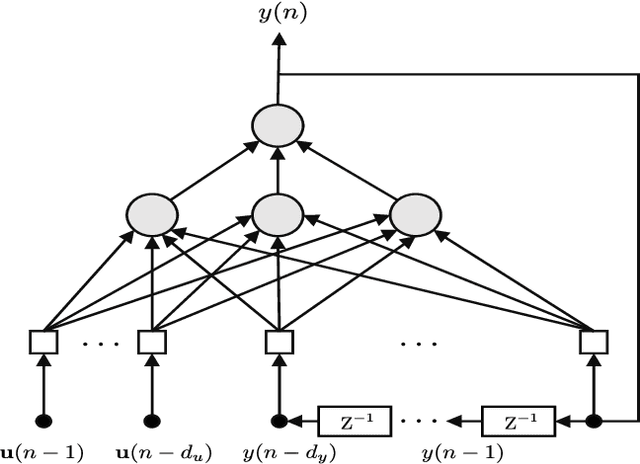
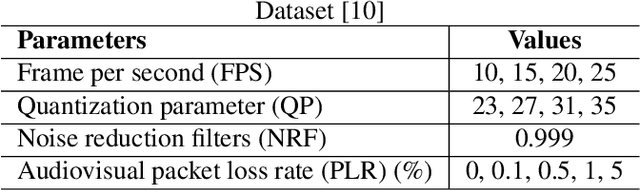
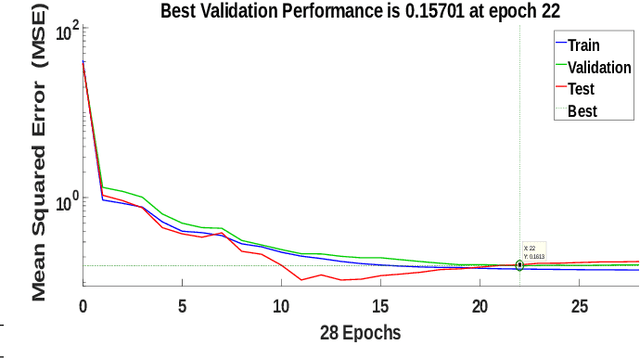
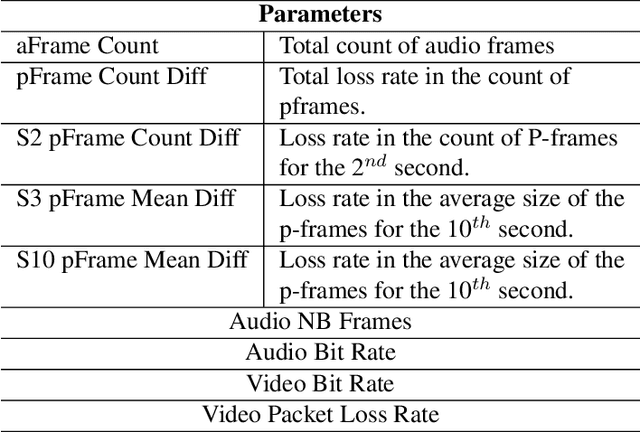
Abstract:With the increasing demand for audiovisual services, telecom service providers and application developers are compelled to ensure that their services provide the best possible user experience. Particularly, services such as videoconferencing are very sensitive to network conditions. Therefore, their performance should be monitored in real time in order to adjust parameters to any network perturbation. In this paper, we developed a parametric model for estimating the perceived audiovisual quality in videoconference services. Our model is developed with the nonlinear autoregressive exogenous (NARX) recurrent neural network and estimates the perceived quality in terms of mean opinion score (MOS). We validate our model using the publicly available INRS bitstream audiovisual quality dataset. This dataset contains bitstream parameters such as loss per frame, bit rate and video duration. We compare the proposed model against state-of-the-art methods based on machine learning and show our model to outperform these methods in terms of mean square error (MSE=0.150) and Pearson correlation coefficient (R=0.931)
Energy Disaggregation using Variational Autoencoders
Mar 22, 2021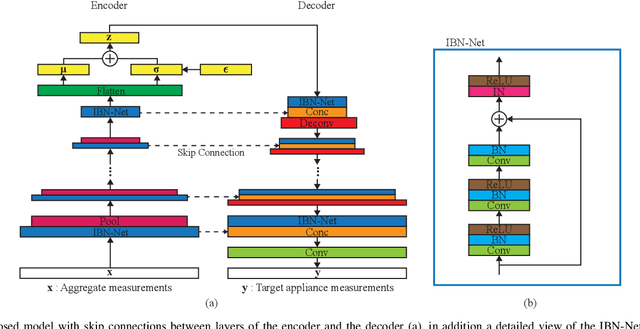
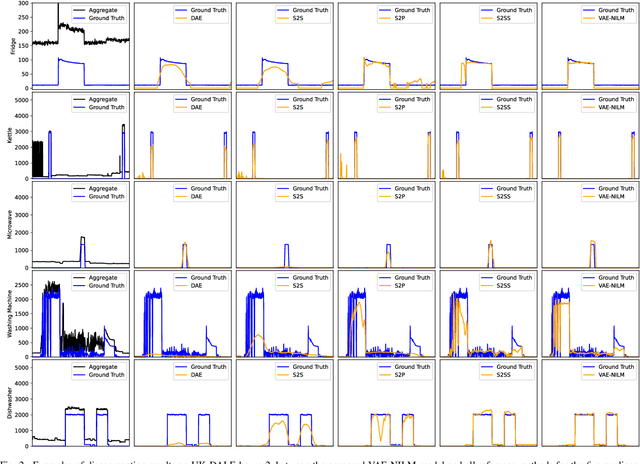
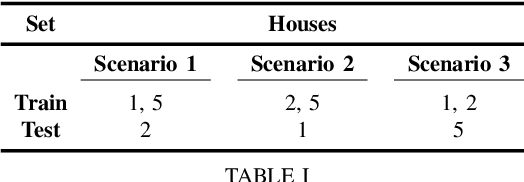
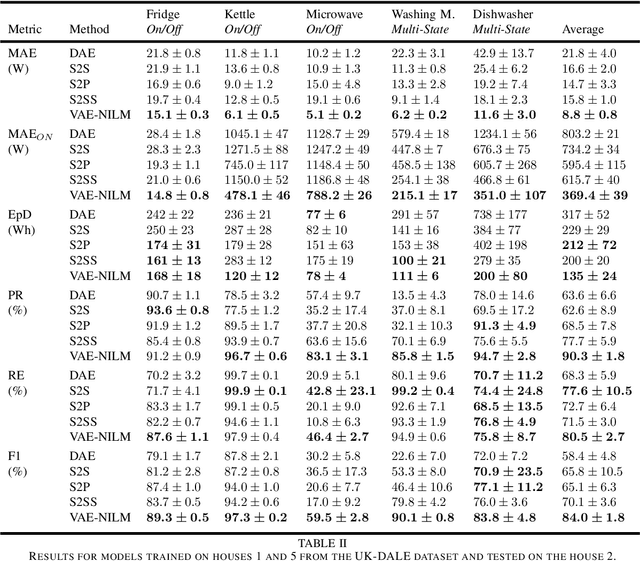
Abstract:Non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) is a technique that uses a single sensor to measure the total power consumption of a building. Using an energy disaggregation method, the consumption of individual appliances can be estimated from the aggregate measurement. Recent disaggregation algorithms have significantly improved the performance of NILM systems. However, the generalization capability of these methods to different houses as well as the disaggregation of multi-state appliances are still major challenges. In this paper we address these issues and propose an energy disaggregation approach based on the variational autoencoders (VAE) framework. The probabilistic encoder makes this approach an efficient model for encoding information relevant to the reconstruction of the target appliance consumption. In particular, the proposed model accurately generates more complex load profiles, thus improving the power signal reconstruction of multi-state appliances. Moreover, its regularized latent space improves the generalization capabilities of the model across different houses. The proposed model is compared to state-of-the-art NILM approaches on the UK-DALE dataset, and yields competitive results. The mean absolute error reduces by 18% on average across all appliances compared to the state-of-the-art. The F1-Score increases by more than 11%, showing improvements for the detection of the target appliance in the aggregate measurement.
Measuring Disentanglement: A Review of Metrics
Jan 05, 2021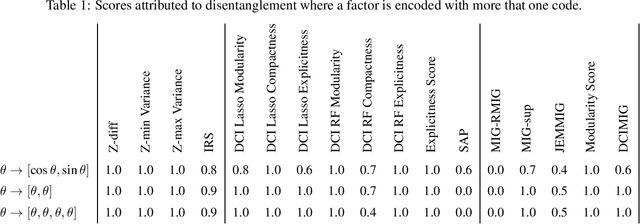
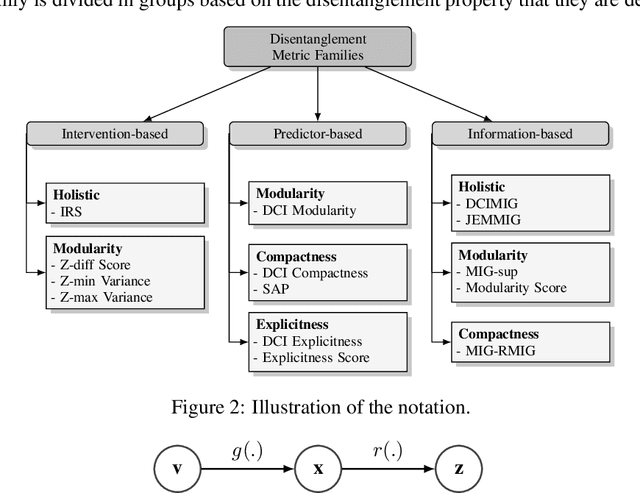
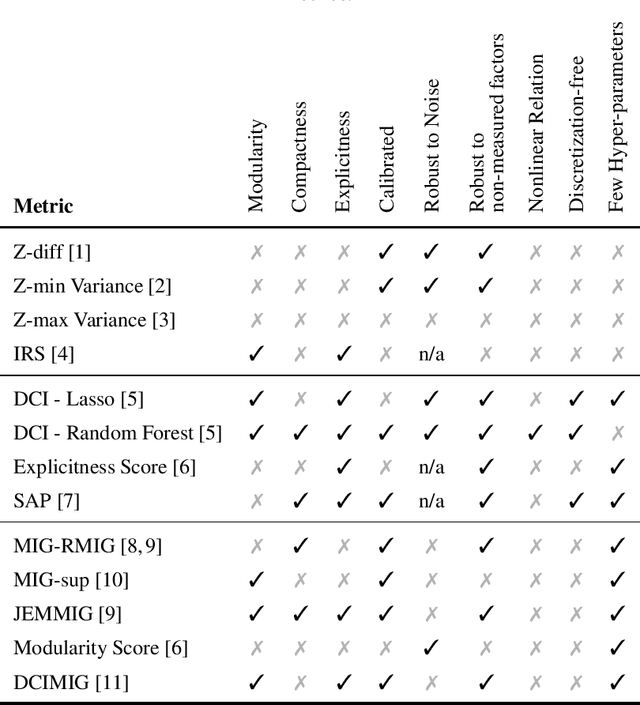
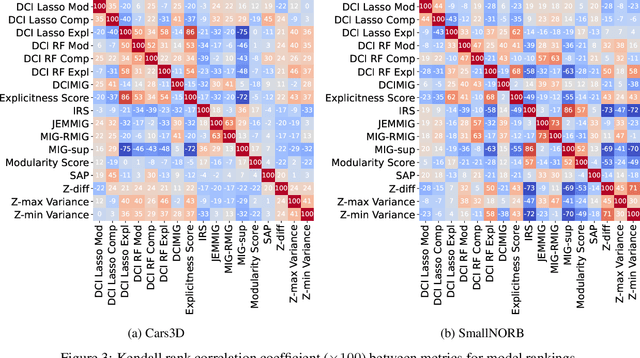
Abstract:Learning to disentangle and represent factors of variation in data is an important problem in AI. While many advances are made to learn these representations, it is still unclear how to quantify disentanglement. Several metrics exist, however little is known on their implicit assumptions, what they truly measure and their limits. As a result, it is difficult to interpret results when comparing different representations. In this work, we survey supervised disentanglement metrics and thoroughly analyze them. We propose a new taxonomy in which all metrics fall into one of three families: intervention-based, predictor-based and information-based. We conduct extensive experiments, where we isolate representation properties to compare all metrics on many aspects. From experiment results and analysis, we provide insights on relations between disentangled representation properties. Finally, we provide guidelines on how to measure disentanglement and report the results.
Multi-stage Jamming Attacks Detection using Deep Learning Combined with Kernelized Support Vector Machine in 5G Cloud Radio Access Networks
Apr 14, 2020
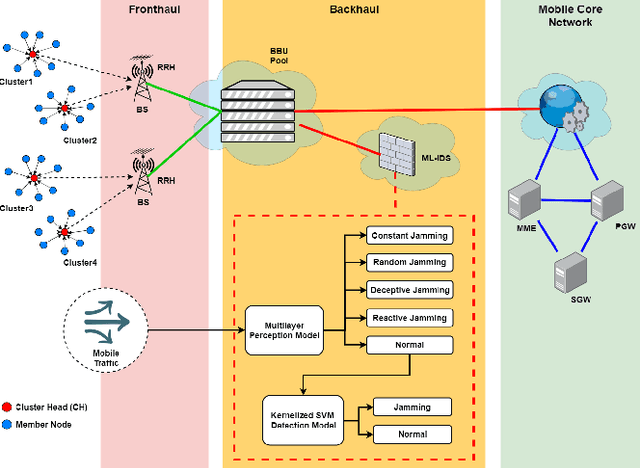
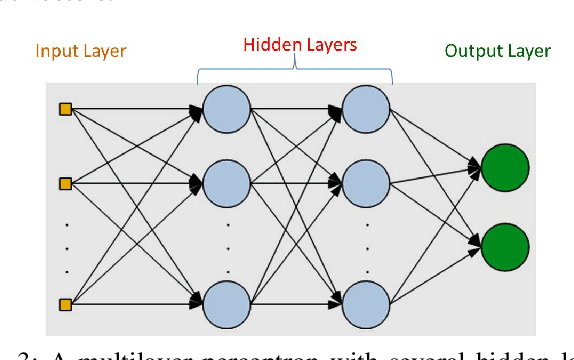
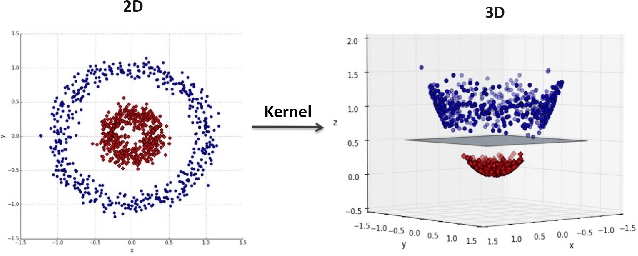
Abstract:In 5G networks, the Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN) is considered a promising future architecture in terms of minimizing energy consumption and allocating resources efficiently by providing real-time cloud infrastructures, cooperative radio, and centralized data processing. Recently, given their vulnerability to malicious attacks, the security of C-RAN networks has attracted significant attention. Among various anomaly-based intrusion detection techniques, the most promising one is the machine learning-based intrusion detection as it learns without human assistance and adjusts actions accordingly. In this direction, many solutions have been proposed, but they show either low accuracy in terms of attack classification or they offer just a single layer of attack detection. This research focuses on deploying a multi-stage machine learning-based intrusion detection (ML-IDS) in 5G C-RAN that can detect and classify four types of jamming attacks: constant jamming, random jamming, deceptive jamming, and reactive jamming. This deployment enhances security by minimizing the false negatives in C-RAN architectures. The experimental evaluation of the proposed solution is carried out using WSN-DS (Wireless Sensor Networks DataSet), which is a dedicated wireless dataset for intrusion detection. The final classification accuracy of attacks is 94.51\% with a 7.84\% false negative rate.
Bag-Level Aggregation for Multiple Instance Active Learning in Instance Classification Problems
Oct 06, 2017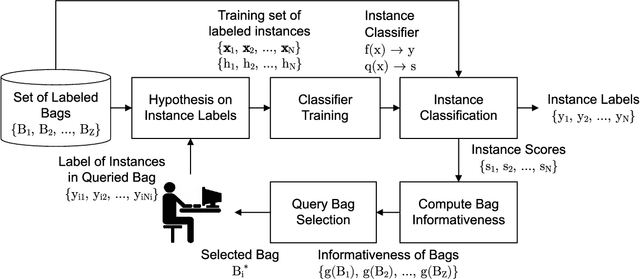
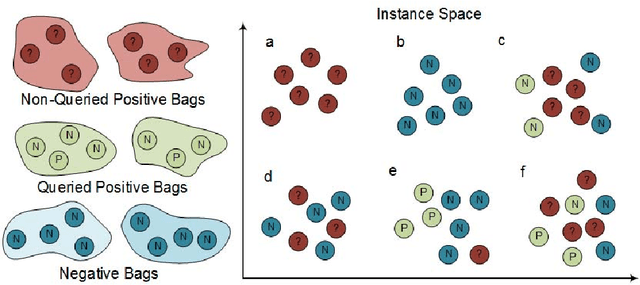
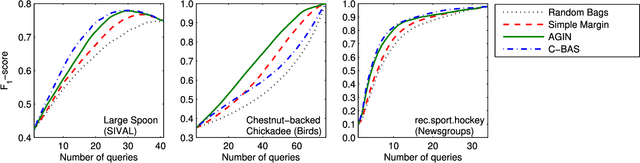
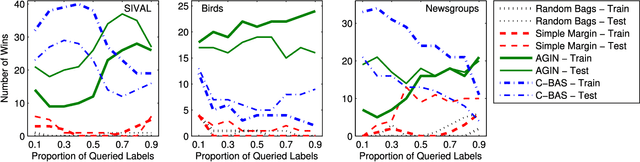
Abstract:A growing number of applications, e.g. video surveillance and medical image analysis, require training recognition systems from large amounts of weakly annotated data while some targeted interactions with a domain expert are allowed to improve the training process. In such cases, active learning (AL) can reduce labeling costs for training a classifier by querying the expert to provide the labels of most informative instances. This paper focuses on AL methods for instance classification problems in multiple instance learning (MIL), where data is arranged into sets, called bags, that are weakly labeled. Most AL methods focus on single instance learning problems. These methods are not suitable for MIL problems because they cannot account for the bag structure of data. In this paper, new methods for bag-level aggregation of instance informativeness are proposed for multiple instance active learning (MIAL). The \textit{aggregated informativeness} method identifies the most informative instances based on classifier uncertainty, and queries bags incorporating the most information. The other proposed method, called \textit{cluster-based aggregative sampling}, clusters data hierarchically in the instance space. The informativeness of instances is assessed by considering bag labels, inferred instance labels, and the proportion of labels that remain to be discovered in clusters. Both proposed methods significantly outperform reference methods in extensive experiments using benchmark data from several application domains. Results indicate that using an appropriate strategy to address MIAL problems yields a significant reduction in the number of queries needed to achieve the same level of performance as single instance AL methods.
Multiple Instance Learning: A Survey of Problem Characteristics and Applications
Dec 11, 2016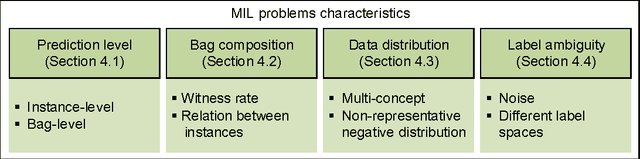
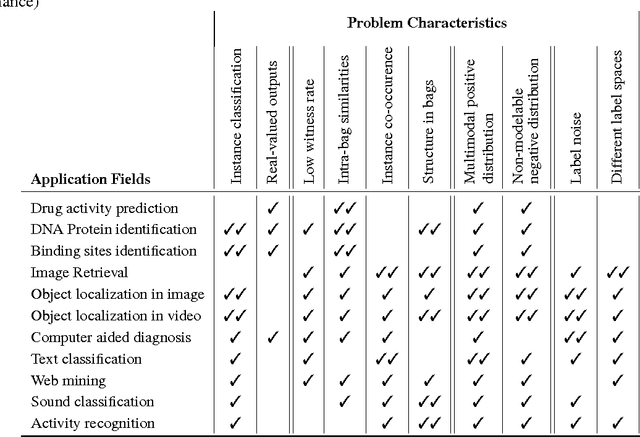
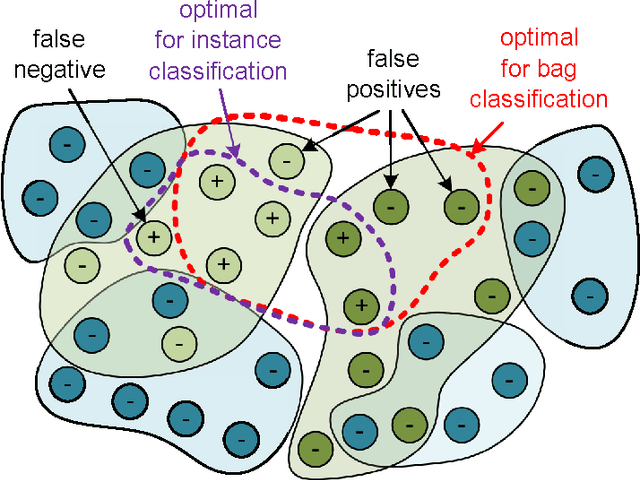
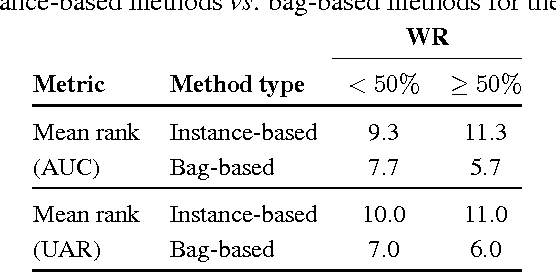
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a form of weakly supervised learning where training instances are arranged in sets, called bags, and a label is provided for the entire bag. This formulation is gaining interest because it naturally fits various problems and allows to leverage weakly labeled data. Consequently, it has been used in diverse application fields such as computer vision and document classification. However, learning from bags raises important challenges that are unique to MIL. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the characteristics which define and differentiate the types of MIL problems. Until now, these problem characteristics have not been formally identified and described. As a result, the variations in performance of MIL algorithms from one data set to another are difficult to explain. In this paper, MIL problem characteristics are grouped into four broad categories: the composition of the bags, the types of data distribution, the ambiguity of instance labels, and the task to be performed. Methods specialized to address each category are reviewed. Then, the extent to which these characteristics manifest themselves in key MIL application areas are described. Finally, experiments are conducted to compare the performance of 16 state-of-the-art MIL methods on selected problem characteristics. This paper provides insight on how the problem characteristics affect MIL algorithms, recommendations for future benchmarking and promising avenues for research.
Feature Learning from Spectrograms for Assessment of Personality Traits
Oct 04, 2016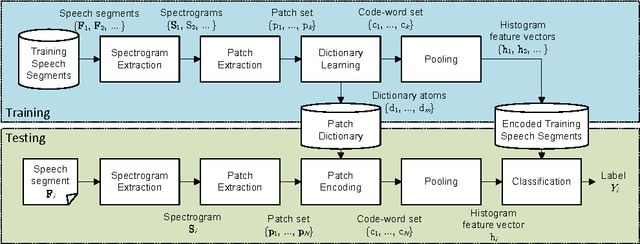
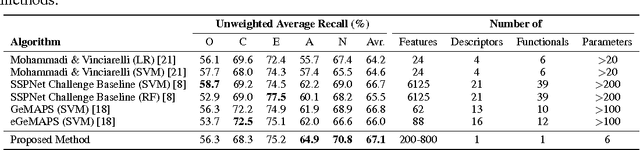
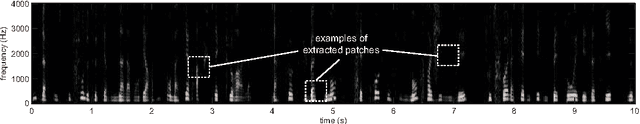

Abstract:Several methods have recently been proposed to analyze speech and automatically infer the personality of the speaker. These methods often rely on prosodic and other hand crafted speech processing features extracted with off-the-shelf toolboxes. To achieve high accuracy, numerous features are typically extracted using complex and highly parameterized algorithms. In this paper, a new method based on feature learning and spectrogram analysis is proposed to simplify the feature extraction process while maintaining a high level of accuracy. The proposed method learns a dictionary of discriminant features from patches extracted in the spectrogram representations of training speech segments. Each speech segment is then encoded using the dictionary, and the resulting feature set is used to perform classification of personality traits. Experiments indicate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results with a significant reduction in complexity when compared to the most recent reference methods. The number of features, and difficulties linked to the feature extraction process are greatly reduced as only one type of descriptors is used, for which the 6 parameters can be tuned automatically. In contrast, the simplest reference method uses 4 types of descriptors to which 6 functionals are applied, resulting in over 20 parameters to be tuned.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge