Gabriela Zarzar Gandler
Frequency Matters: When Time Series Foundation Models Fail Under Spectral Shift
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Time series foundation models (TSFMs) have shown strong results on public benchmarks, prompting comparisons to a "BERT moment" for time series. Their effectiveness in industrial settings, however, remains uncertain. We examine why TSFMs often struggle to generalize and highlight spectral shift (a mismatch between the dominant frequency components in downstream tasks and those represented during pretraining) as a key factor. We present evidence from an industrial-scale player engagement prediction task in mobile gaming, where TSFMs underperform domain-adapted baselines. To isolate the mechanism, we design controlled synthetic experiments contrasting signals with seen versus unseen frequency bands, observing systematic degradation under spectral mismatch. These findings position frequency awareness as critical for robust TSFM deployment and motivate new pretraining and evaluation protocols that explicitly account for spectral diversity.
Are We Really Measuring Progress? Transferring Insights from Evaluating Recommender Systems to Temporal Link Prediction
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Recent work has questioned the reliability of graph learning benchmarks, citing concerns around task design, methodological rigor, and data suitability. In this extended abstract, we contribute to this discussion by focusing on evaluation strategies in Temporal Link Prediction (TLP). We observe that current evaluation protocols are often affected by one or more of the following issues: (1) inconsistent sampled metrics, (2) reliance on hard negative sampling often introduced as a means to improve robustness, and (3) metrics that implicitly assume equal base probabilities across source nodes by combining predictions. We support these claims through illustrative examples and connections to longstanding concerns in the recommender systems community. Our ongoing work aims to systematically characterize these problems and explore alternatives that can lead to more robust and interpretable evaluation. We conclude with a discussion of potential directions for improving the reliability of TLP benchmarks.
On the Power of Heuristics in Temporal Graphs
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Dynamic graph datasets often exhibit strong temporal patterns, such as recency, which prioritizes recent interactions, and popularity, which favors frequently occurring nodes. We demonstrate that simple heuristics leveraging only these patterns can perform on par or outperform state-of-the-art neural network models under standard evaluation protocols. To further explore these dynamics, we introduce metrics that quantify the impact of recency and popularity across datasets. Our experiments on BenchTemp and the Temporal Graph Benchmark show that our approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance across all datasets in the latter and secure top ranks on multiple datasets in the former. These results emphasize the importance of refined evaluation schemes to enable fair comparisons and promote the development of more robust temporal graph models. Additionally, they reveal that current deep learning methods often struggle to capture the key patterns underlying predictions in real-world temporal graphs. For reproducibility, we have made our code publicly available.
Expressivity of Representation Learning on Continuous-Time Dynamic Graphs: An Information-Flow Centric Review
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Graphs are ubiquitous in real-world applications, ranging from social networks to biological systems, and have inspired the development of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for learning expressive representations. While most research has centered on static graphs, many real-world scenarios involve dynamic, temporally evolving graphs, motivating the need for Continuous-Time Dynamic Graph (CTDG) models. This paper provides a comprehensive review of Graph Representation Learning (GRL) on CTDGs with a focus on Self-Supervised Representation Learning (SSRL). We introduce a novel theoretical framework that analyzes the expressivity of CTDG models through an Information-Flow (IF) lens, quantifying their ability to propagate and encode temporal and structural information. Leveraging this framework, we categorize existing CTDG methods based on their suitability for different graph types and application scenarios. Within the same scope, we examine the design of SSRL methods tailored to CTDGs, such as predictive and contrastive approaches, highlighting their potential to mitigate the reliance on labeled data. Empirical evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets validate our theoretical insights, demonstrating the strengths and limitations of various methods across long-range, bi-partite and community-based graphs. This work offers both a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for selecting and developing CTDG models, advancing the understanding of GRL in dynamic settings.
Text Annotation Handbook: A Practical Guide for Machine Learning Projects
Oct 18, 2023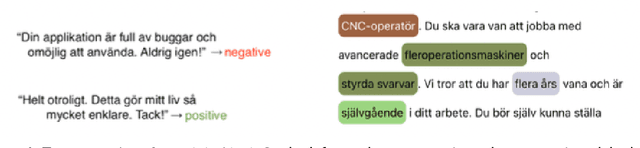
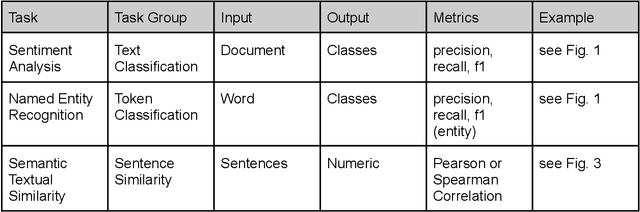
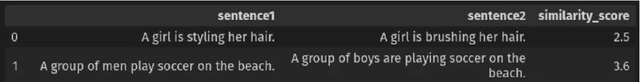
Abstract:This handbook is a hands-on guide on how to approach text annotation tasks. It provides a gentle introduction to the topic, an overview of theoretical concepts as well as practical advice. The topics covered are mostly technical, but business, ethical and regulatory issues are also touched upon. The focus lies on readability and conciseness rather than completeness and scientific rigor. Experience with annotation and knowledge of machine learning are useful but not required. The document may serve as a primer or reference book for a wide range of professions such as team leaders, project managers, IT architects, software developers and machine learning engineers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge