Gabriel Gomes
Industrial Robot Motion Planning with GPUs: Integration of cuRobo for Extended DOF Systems
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Efficient motion planning remains a key challenge in industrial robotics, especially for multi-axis systems operating in complex environments. This paper addresses that challenge by integrating GPU-accelerated motion planning through NVIDIA's cuRobo library into Vention's modular automation platform. By leveraging accurate CAD-based digital twins and real-time parallel optimization, our system enables rapid trajectory generation and dynamic collision avoidance for pick-and-place tasks. We demonstrate this capability on robots equipped with additional degrees of freedom, including a 7th-axis gantry, and benchmark performance across various scenarios. The results show significant improvements in planning speed and robustness, highlighting the potential of GPU-based planning pipelines for scalable, adaptable deployment in modern industrial workflows.
Efficient Online Hyperparameter Optimization for Kernel Ridge Regression with Applications to Traffic Time Series Prediction
Nov 01, 2018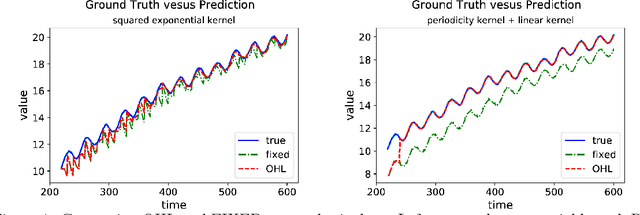
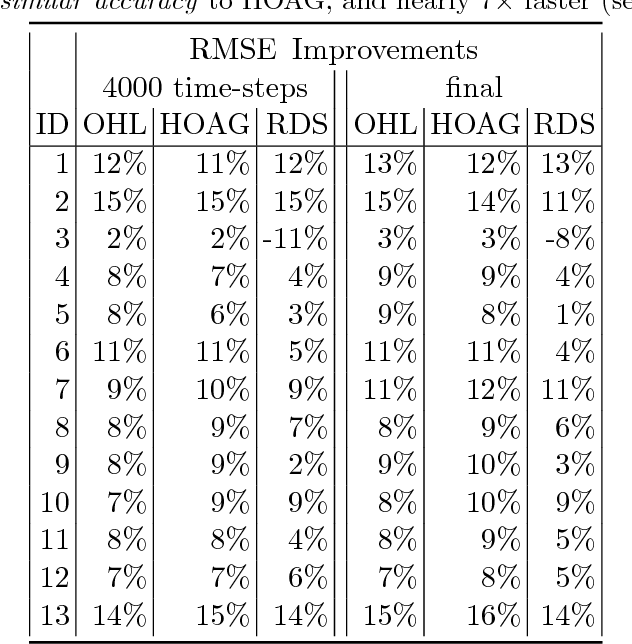
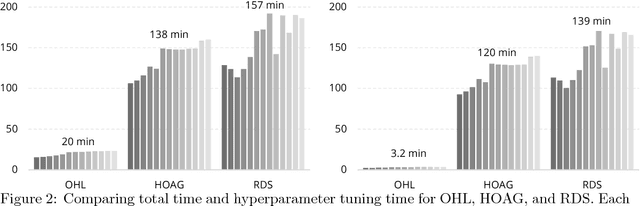
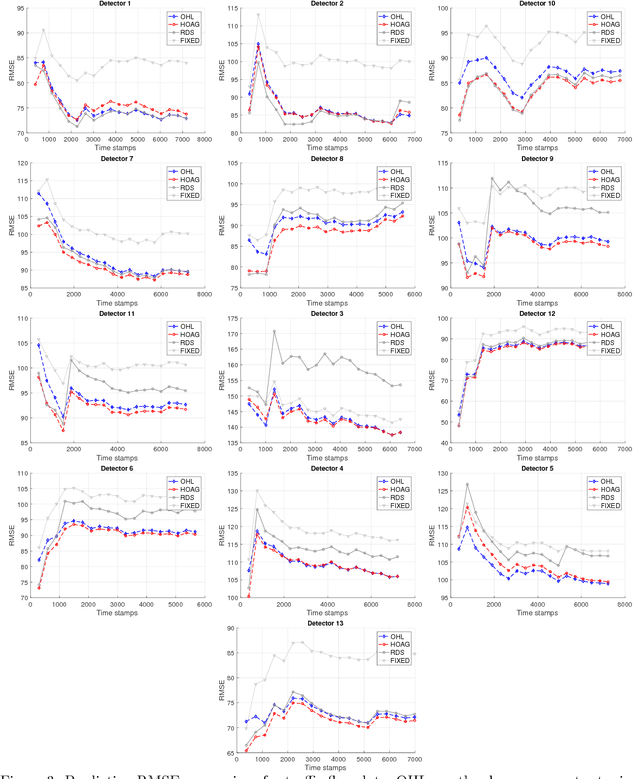
Abstract:Computational efficiency is an important consideration for deploying machine learning models for time series prediction in an online setting. Machine learning algorithms adjust model parameters automatically based on the data, but often require users to set additional parameters, known as hyperparameters. Hyperparameters can significantly impact prediction accuracy. Traffic measurements, typically collected online by sensors, are serially correlated. Moreover, the data distribution may change gradually. A typical adaptation strategy is periodically re-tuning the model hyperparameters, at the cost of computational burden. In this work, we present an efficient and principled online hyperparameter optimization algorithm for Kernel Ridge regression applied to traffic prediction problems. In tests with real traffic measurement data, our approach requires as little as one-seventh of the computation time of other tuning methods, while achieving better or similar prediction accuracy.
* An extended version of "Efficient Online Hyperparameter Learning for Traffic Flow Prediction" published in The 21st IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC 2018)
Expert Level control of Ramp Metering based on Multi-task Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 30, 2017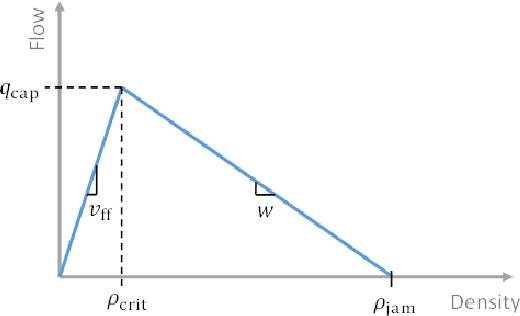
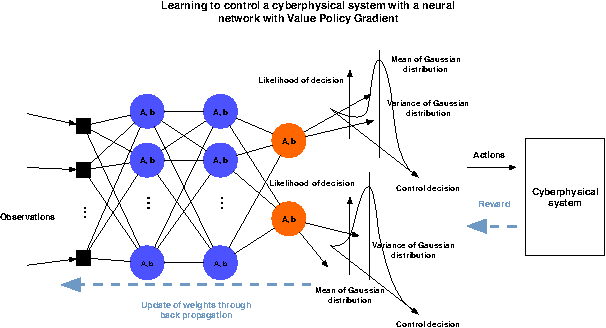
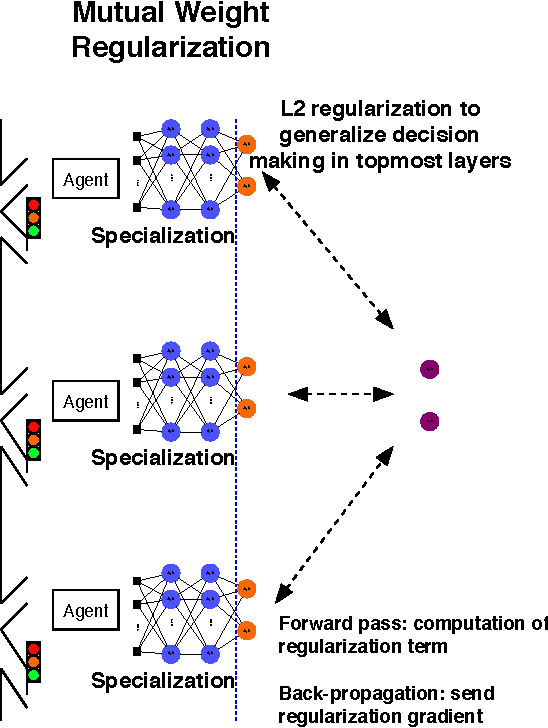
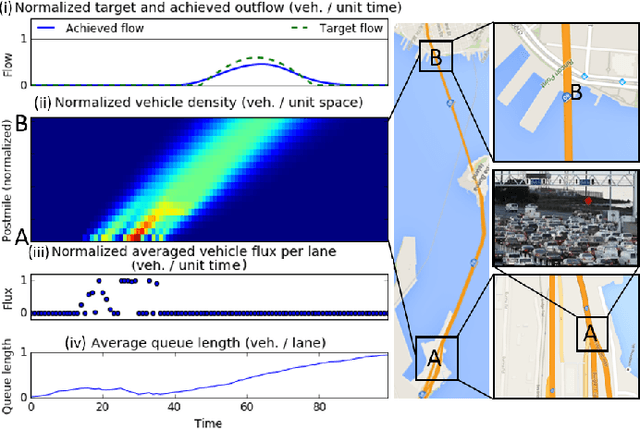
Abstract:This article shows how the recent breakthroughs in Reinforcement Learning (RL) that have enabled robots to learn to play arcade video games, walk or assemble colored bricks, can be used to perform other tasks that are currently at the core of engineering cyberphysical systems. We present the first use of RL for the control of systems modeled by discretized non-linear Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) and devise a novel algorithm to use non-parametric control techniques for large multi-agent systems. We show how neural network based RL enables the control of discretized PDEs whose parameters are unknown, random, and time-varying. We introduce an algorithm of Mutual Weight Regularization (MWR) which alleviates the curse of dimensionality of multi-agent control schemes by sharing experience between agents while giving each agent the opportunity to specialize its action policy so as to tailor it to the local parameters of the part of the system it is located in.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge