Fuyi Li
A Label-Free Heterophily-Guided Approach for Unsupervised Graph Fraud Detection
Feb 18, 2025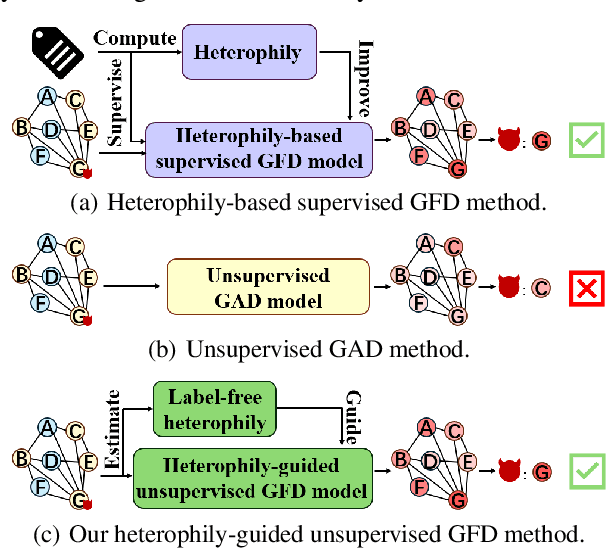

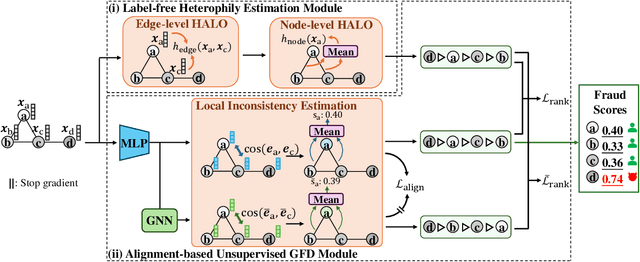
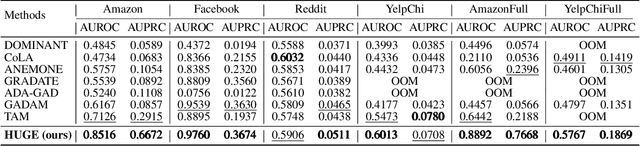
Abstract:Graph fraud detection (GFD) has rapidly advanced in protecting online services by identifying malicious fraudsters. Recent supervised GFD research highlights that heterophilic connections between fraudsters and users can greatly impact detection performance, since fraudsters tend to camouflage themselves by building more connections to benign users. Despite the promising performance of supervised GFD methods, the reliance on labels limits their applications to unsupervised scenarios; Additionally, accurately capturing complex and diverse heterophily patterns without labels poses a further challenge. To fill the gap, we propose a Heterophily-guided Unsupervised Graph fraud dEtection approach (HUGE) for unsupervised GFD, which contains two essential components: a heterophily estimation module and an alignment-based fraud detection module. In the heterophily estimation module, we design a novel label-free heterophily metric called HALO, which captures the critical graph properties for GFD, enabling its outstanding ability to estimate heterophily from node attributes. In the alignment-based fraud detection module, we develop a joint MLP-GNN architecture with ranking loss and asymmetric alignment loss. The ranking loss aligns the predicted fraud score with the relative order of HALO, providing an extra robustness guarantee by comparing heterophily among non-adjacent nodes. Moreover, the asymmetric alignment loss effectively utilizes structural information while alleviating the feature-smooth effects of GNNs.Extensive experiments on 6 datasets demonstrate that HUGE significantly outperforms competitors, showcasing its effectiveness and robustness. The source code of HUGE is at https://github.com/CampanulaBells/HUGE-GAD.
Contrastive Dual-Interaction Graph Neural Network for Molecular Property Prediction
May 04, 2024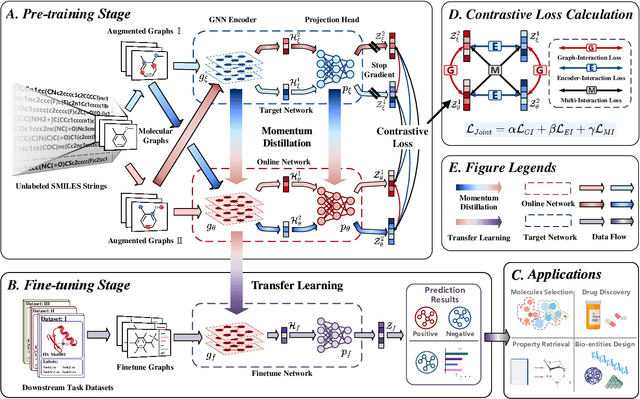
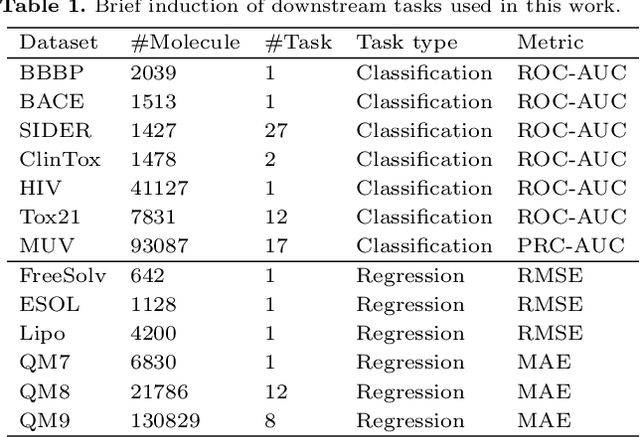
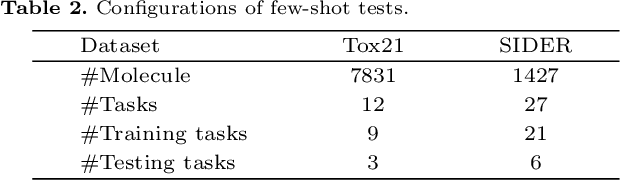
Abstract:Molecular property prediction is a key component of AI-driven drug discovery and molecular characterization learning. Despite recent advances, existing methods still face challenges such as limited ability to generalize, and inadequate representation of learning from unlabeled data, especially for tasks specific to molecular structures. To address these limitations, we introduce DIG-Mol, a novel self-supervised graph neural network framework for molecular property prediction. This architecture leverages the power of contrast learning with dual interaction mechanisms and unique molecular graph enhancement strategies. DIG-Mol integrates a momentum distillation network with two interconnected networks to efficiently improve molecular characterization. The framework's ability to extract key information about molecular structure and higher-order semantics is supported by minimizing loss of contrast. We have established DIG-Mol's state-of-the-art performance through extensive experimental evaluation in a variety of molecular property prediction tasks. In addition to demonstrating superior transferability in a small number of learning scenarios, our visualizations highlight DIG-Mol's enhanced interpretability and representation capabilities. These findings confirm the effectiveness of our approach in overcoming challenges faced by traditional methods and mark a significant advance in molecular property prediction.
Towards Self-Interpretable Graph-Level Anomaly Detection
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Graph-level anomaly detection (GLAD) aims to identify graphs that exhibit notable dissimilarity compared to the majority in a collection. However, current works primarily focus on evaluating graph-level abnormality while failing to provide meaningful explanations for the predictions, which largely limits their reliability and application scope. In this paper, we investigate a new challenging problem, explainable GLAD, where the learning objective is to predict the abnormality of each graph sample with corresponding explanations, i.e., the vital subgraph that leads to the predictions. To address this challenging problem, we propose a Self-Interpretable Graph aNomaly dETection model (SIGNET for short) that detects anomalous graphs as well as generates informative explanations simultaneously. Specifically, we first introduce the multi-view subgraph information bottleneck (MSIB) framework, serving as the design basis of our self-interpretable GLAD approach. This way SIGNET is able to not only measure the abnormality of each graph based on cross-view mutual information but also provide informative graph rationales by extracting bottleneck subgraphs from the input graph and its dual hypergraph in a self-supervised way. Extensive experiments on 16 datasets demonstrate the anomaly detection capability and self-interpretability of SIGNET.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge