Francesco Linsalata
Autonomous Sensing UAV for Accurate Multi-User Identification and Localization in Cellular Networks
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an autonomous sensing frame- work for identifying and localizing multiple users in Fifth Generation (5G) networks using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) that is not part of the serving access network. Unlike conventional aerial serving nodes, the proposed UAV operates passively and is dedicated solely to sensing. It captures Uplink (UL) Sounding Reference Signals (SRS), and requires virtually no coordination with the network infrastructure. A complete signal processing chain is proposed and developed, encompassing synchronization, user identification, and localization, all executed onboard UAV during flight. The system autonomously plans and adapts its mission workflow to estimate multiple user positions within a single deployment, integrating flight control with real-time sensing. Extensive simulations and a full-scale low- altitude experimental campaign validate the approach, showing localization errors below 3 m in rural field tests and below 8 m in urban simulation scenarios, while reliably identifying each user. The results confirm the feasibility of infrastructure-independent sensing UAVs as a core element of the emerging Low Altitude Economy (LAE), supporting situational awareness and rapid deployment in emergency or connectivity-limited environments.
Chartwin: a Case Study on Channel Charting-aided Localization in Dynamic Digital Network Twins
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Wireless communication systems can significantly benefit from the availability of spatially consistent representations of the wireless channel to efficiently perform a wide range of communication tasks. Towards this purpose, channel charting has been introduced as an effective unsupervised learning technique to achieve both locally and globally consistent radio maps. In this letter, we propose Chartwin, a case study on the integration of localization-oriented channel charting with dynamic Digital Network Twins (DNTs). Numerical results showcase the significant performance of semi-supervised channel charting in constructing a spatially consistent chart of the considered extended urban environment. The considered method results in $\approx$ 4.5 m localization error for the static DNT and $\approx$ 6 m in the dynamic DNT, fostering DNT-aided channel charting and localization.
AI-empowered Real-Time Line-of-Sight Identification via Network Digital Twins
May 21, 2025
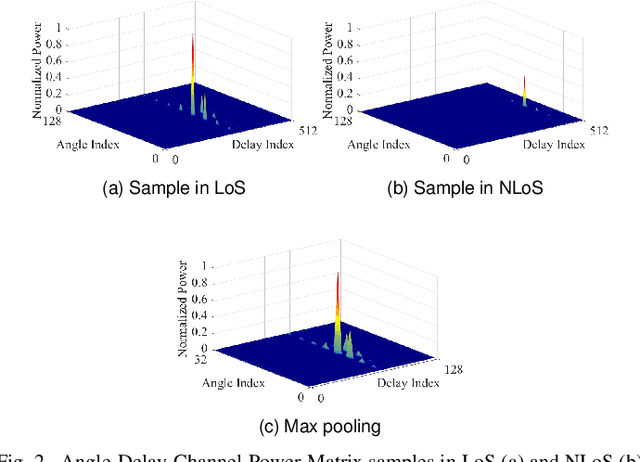
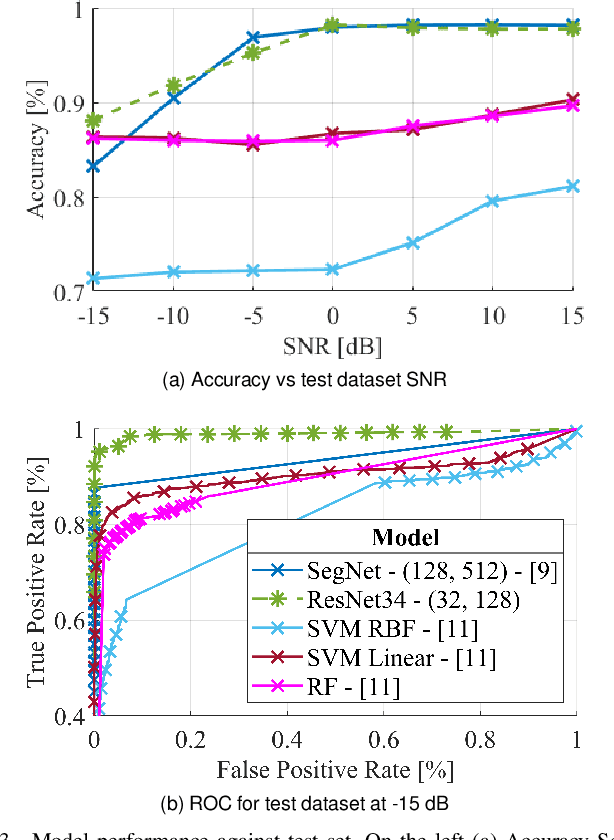
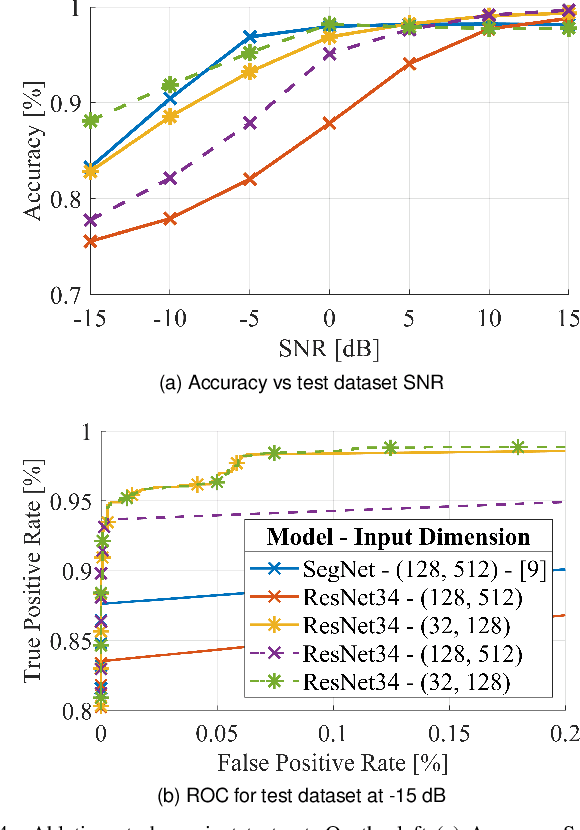
Abstract:The identification of Line-of-Sight (LoS) conditions is critical for ensuring reliable high-frequency communication links, which are particularly vulnerable to blockages and rapid channel variations. Network Digital Twins (NDTs) and Ray-Tracing (RT) techniques can significantly automate the large-scale collection and labeling of channel data, tailored to specific wireless environments. This paper examines the quality of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models trained on data generated by Network Digital Twins. We propose and evaluate training strategies for a general-purpose Deep Learning model, demonstrating superior performance compared to the current state-of-the-art. In terms of classification accuracy, our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art Deep Learning model by 5% in very low SNR conditions and by approximately 10% in medium-to-high SNR scenarios. Additionally, the proposed strategies effectively reduce the input size to the Deep Learning model while preserving its performance. The computational cost, measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPs) during inference, is reduced by 98.55% relative to state-of-the-art solutions, making it ideal for real-time applications.
Exploiting Age of Information in Network Digital Twins for AI-driven Real-Time Link Blockage Detection
May 21, 2025Abstract:The Line-of-Sight (LoS) identification is crucial to ensure reliable high-frequency communication links, especially those vulnerable to blockages. Network Digital Twins and Artificial Intelligence are key technologies enabling blockage detection (LoS identification) for high-frequency wireless systems, e.g., 6>GHz. In this work, we enhance Network Digital Twins by incorporating Age of Information (AoI) metrics, a quantification of status update freshness, enabling reliable real-time blockage detection (LoS identification) in dynamic wireless environments. By integrating raytracing techniques, we automate large-scale collection and labeling of channel data, specifically tailored to the evolving conditions of the environment. The introduced AoI is integrated with the loss function to prioritize more recent information to fine-tune deep learning models in case of performance degradation (model drift). The effectiveness of the proposed solution is demonstrated in realistic urban simulations, highlighting the trade-off between input resolution, computational cost, and model performance. A resolution reduction of 4x8 from an original channel sample size of (32, 1024) along the angle and subcarrier dimension results in a computational speedup of 32 times. The proposed fine-tuning successfully mitigates performance degradation while requiring only 1% of the available data samples, enabling automated and fast mitigation of model drifts.
VaN3Twin: the Multi-Technology V2X Digital Twin with Ray-Tracing in the Loop
May 20, 2025Abstract:This paper presents VaN3Twin-the first open-source, full-stack Network Digital Twin (NDT) framework for simulating the coexistence of multiple Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication technologies with accurate physical-layer modeling via ray tracing. VaN3Twin extends the ms-van3t simulator by integrating Sionna Ray Tracer (RT) in the loop, enabling high-fidelity representation of wireless propagation, including diverse Line-of-Sight (LoS) conditions with focus on LoS blockage due to other vehicles' meshes, Doppler effect, and site-dependent effects-e.g., scattering and diffraction. Unlike conventional simulation tools, the proposed framework supports realistic coexistence analysis across DSRC and C-V2X technologies operating over shared spectrum. A dedicated interference tracking module captures cross-technology interference at the time-frequency resource block level and enhances signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) estimation by eliminating artifacts such as the bimodal behavior induced by separate LoS/NLoS propagation models. Compared to field measurements, VaN3Twin reduces application-layer disagreement by 50% in rural and over 70% in urban environments with respect to current state-of-the-art simulation tools, demonstrating its value for scalable and accurate digital twin-based V2X coexistence simulation.
Digital Twins of the EM Environment: Benchmark for Ray Launching Models
Jun 07, 2024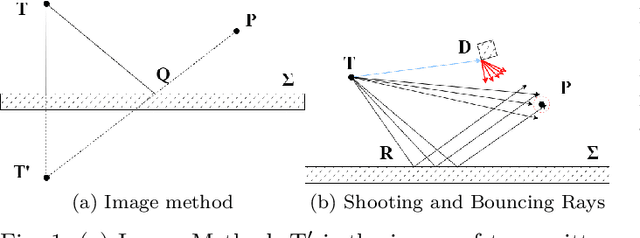
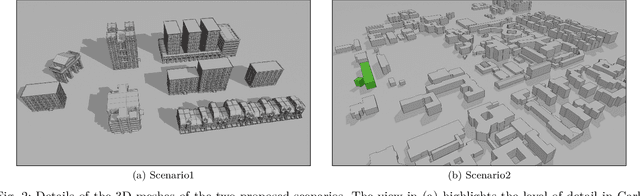
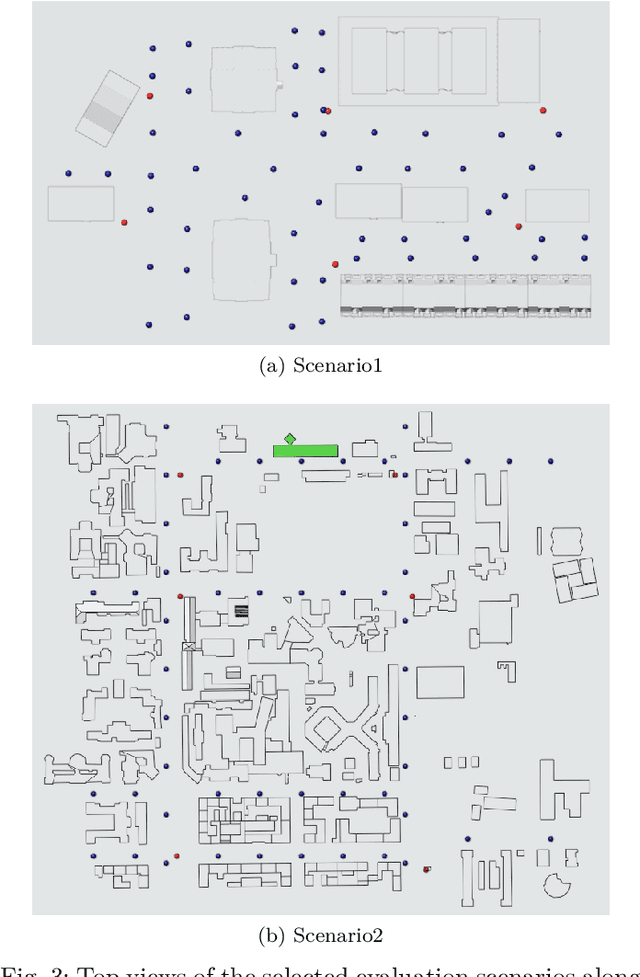
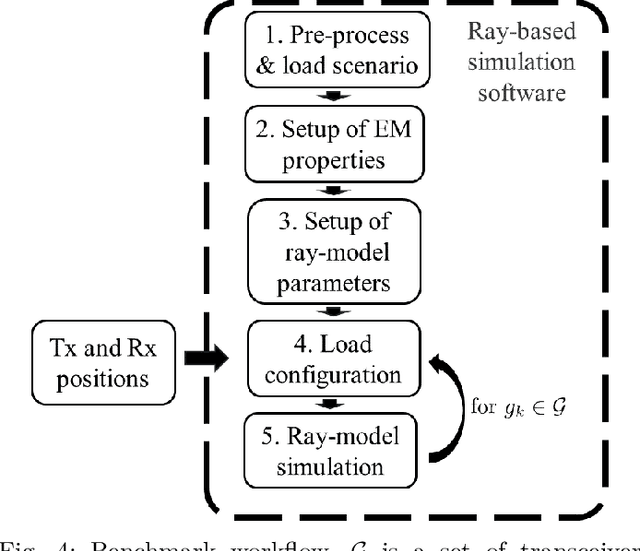
Abstract:Digital Twin has emerged as a promising paradigm for accurately representing the electromagnetic (EM) wireless environments. The resulting virtual representation of the reality facilitates comprehensive insights into the propagation environment, empowering multi-layer decision-making processes at the physical communication level. This paper investigates the digitization of wireless communication propagation, with particular emphasis on the indispensable aspect of ray-based propagation simulation for real-time Digital Twins. A benchmark for ray-based propagation simulations is presented to evaluate computational time, with two urban scenarios characterized by different mesh complexity, single and multiple wireless link configurations, and simulations with/without diffuse scattering. Exhaustive empirical analyses are performed showing and comparing the behavior of different ray-based solutions. By offering standardized simulations and scenarios, this work provides a technical benchmark for practitioners involved in the implementation of real-time Digital Twins and optimization of ray-based propagation models.
Integrated Communication and Imaging: Design, Analysis, and Performances of COSMIC Waveforms
May 29, 2024

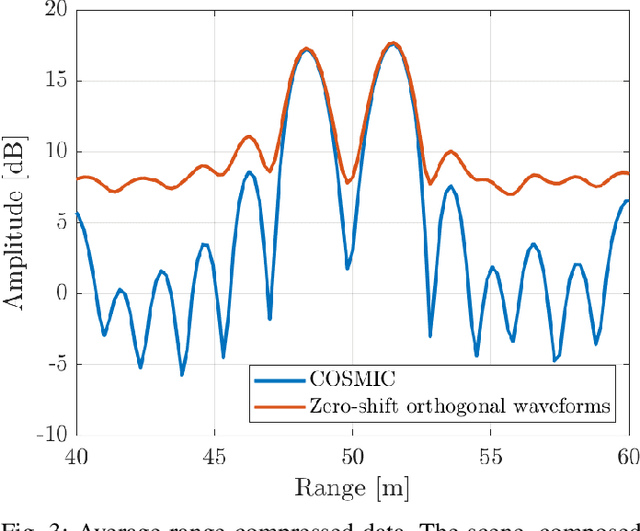

Abstract:This paper proposes a novel waveform design method named COSMIC (Connectivity-Oriented Sensing Method for Imaging and Communication). These waveforms are engineered to convey communication symbols while adhering to an extended orthogonality condition, enabling their use in generating radio images of the environment. A Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) Radar-Communication (RadCom) device transmits COSMIC waveforms from each antenna simultaneously within the same time window and frequency band, indicating that orthogonality is not achieved by space, time, or frequency multiplexing. Indeed, orthogonality among the waveforms is achieved by leveraging the degrees of freedom provided by the assumption that the field of view is limited or significantly smaller than the transmitted signals' length. The RadCom device receives and processes the echoes from an infinite number of infinitesimal scatterers within its field of view, constructing an electromagnetic image of the environment. Concurrently, these waveforms can also carry information to other connected network entities. This work provides the algebraic concepts used to generate COSMIC waveforms. Moreover, an opportunistic optimization of the imaging and communication efficiency is discussed. Simulation results demonstrate that COSMIC waveforms enable accurate environmental imaging while maintaining acceptable communication performances.
Artificial Neural Networks-based Real-time Classification of ENG Signals for Implanted Nerve Interfaces
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:Neuropathies are gaining higher relevance in clinical settings, as they risk permanently jeopardizing a person's life. To support the recovery of patients, the use of fully implanted devices is emerging as one of the most promising solutions. However, these devices, even if becoming an integral part of a fully complex neural nanonetwork system, pose numerous challenges. In this article, we address one of them, which consists of the classification of motor/sensory stimuli. The task is performed by exploring four different types of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to extract various sensory stimuli from the electroneurographic (ENG) signal measured in the sciatic nerve of rats. Different sizes of the data sets are considered to analyze the feasibility of the investigated ANNs for real-time classification through a comparison of their performance in terms of accuracy, F1-score, and prediction time. The design of the ANNs takes advantage of the modelling of the ENG signal as a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system to describe the measures taken by state-of-the-art implanted nerve interfaces. These are based on the use of multi-contact cuff electrodes to achieve nanoscale spatial discrimination of the nerve activity. The MIMO ENG signal model is another contribution of this paper. Our results show that some ANNs are more suitable for real-time applications, being capable of achieving accuracies over $90\%$ for signal windows of $100$ and $200\,$ms with a low enough processing time to be effective for pathology recovery.
Exploring ISAC Technology for UAV SAR Imaging
Jan 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper illustrates the potential of an Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) system, operating in the sub-6 GHz frequency range, for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging via an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) employed as an aerial base station. The primary aim is to validate the system's ability to generate SAR imagery within the confines of modern communication standards, including considerations like power limits, carrier frequency, bandwidth, and other relevant parameters. The paper presents two methods for processing the signal reflected by the scene. Additionally, we analyze two key performance indicators for their respective fields, the Noise Equivalent Sigma Zero (NESZ) and the Bit Error Rate (BER), using the QUAsi Deterministic RadIo channel GenerAtor (QuaDRiGa), demonstrating the system's capability to image buried targets in challenging scenarios. The paper shows simulated Impulse Response Functions (IRF) as possible pulse compression techniques under different assumptions. An experimental campaign is conducted to validate the proposed setup by producing a SAR image of the environment captured using a UAV flying with a Software-Defined Radio (SDR) as a payload.
A Multi-Modal Simulation Framework to Enable Digital Twin-based V2X Communications in Dynamic Environments
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:Digital Twins (DTs) for physical wireless environments have been recently proposed as accurate virtual representations of the propagation environment that can enable multi-layer decisions at the physical communication equipment. At high frequency bands, DTs can help to overcome the challenges emerging in the high mobility conditions featuring vehicular environments. In this paper, we propose a novel data-driven workflow for the creation of the DT of a Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication scenario and a multi-modal simulation framework for the generation of realistic sensor data and accurate mmWave/sub-THz wireless channels. The proposed method leverages an automotive simulation and testing framework based on the Unreal Engine game engine and an accurate ray-tracing channel simulator. Simulations over an urban scenario show the achievable realistic sensor and channel modelling both at the infrastructure and at an ego-vehicle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge