François Caron
INRIA Bordeaux - Sud-Ouest, IMB
Anytime-valid, Bayes-assisted,Prediction-Powered Inference
May 23, 2025Abstract:Given a large pool of unlabelled data and a smaller amount of labels, prediction-powered inference (PPI) leverages machine learning predictions to increase the statistical efficiency of standard confidence interval procedures based solely on labelled data, while preserving their fixed-time validity. In this paper, we extend the PPI framework to the sequential setting, where labelled and unlabelled datasets grow over time. Exploiting Ville's inequality and the method of mixtures, we propose prediction-powered confidence sequence procedures that are valid uniformly over time and naturally accommodate prior knowledge on the quality of the predictions to further boost efficiency. We carefully illustrate the design choices behind our method and demonstrate its effectiveness in real and synthetic examples.
Rapidly Varying Completely Random Measures for Modeling Extremely Sparse Networks
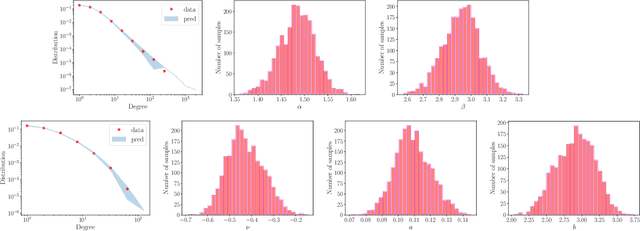
May 19, 2025Abstract:Completely random measures (CRMs) are fundamental to Bayesian nonparametric models, with applications in clustering, feature allocation, and network analysis. A key quantity of interest is the Laplace exponent, whose asymptotic behavior determines how the random structures scale. When the Laplace exponent grows nearly linearly - known as rapid variation - the induced models exhibit approximately linear growth in the number of clusters, features, or edges with sample size or network nodes. This regime is especially relevant for modeling sparse networks, yet existing CRM constructions lack tractability under rapid variation. We address this by introducing a new class of CRMs with index of variation $\alpha\in(0,1]$, defined as mixtures of stable or generalized gamma processes. These models offer interpretable parameters, include well-known CRMs as limiting cases, and retain analytical tractability through a tractable Laplace exponent and simple size-biased representation. We analyze the asymptotic properties of this CRM class and apply it to the Caron-Fox framework for sparse graphs. The resulting models produce networks with near-linear edge growth, aligning with empirical evidence from large-scale networks. Additionally, we present efficient algorithms for simulation and posterior inference, demonstrating practical advantages through experiments on real-world sparse network datasets.
FAB-PPI: Frequentist, Assisted by Bayes, Prediction-Powered Inference
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Prediction-powered inference (PPI) enables valid statistical inference by combining experimental data with machine learning predictions. When a sufficient number of high-quality predictions is available, PPI results in more accurate estimates and tighter confidence intervals than traditional methods. In this paper, we propose to inform the PPI framework with prior knowledge on the quality of the predictions. The resulting method, which we call frequentist, assisted by Bayes, PPI (FAB-PPI), improves over PPI when the observed prediction quality is likely under the prior, while maintaining its frequentist guarantees. Furthermore, when using heavy-tailed priors, FAB-PPI adaptively reverts to standard PPI in low prior probability regions. We demonstrate the benefits of FAB-PPI in real and synthetic examples.
Deep neural networks with dependent weights: Gaussian Process mixture limit, heavy tails, sparsity and compressibility
May 17, 2022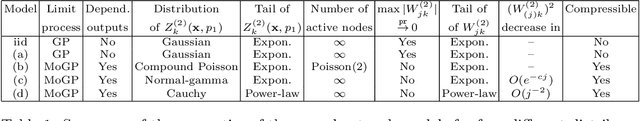
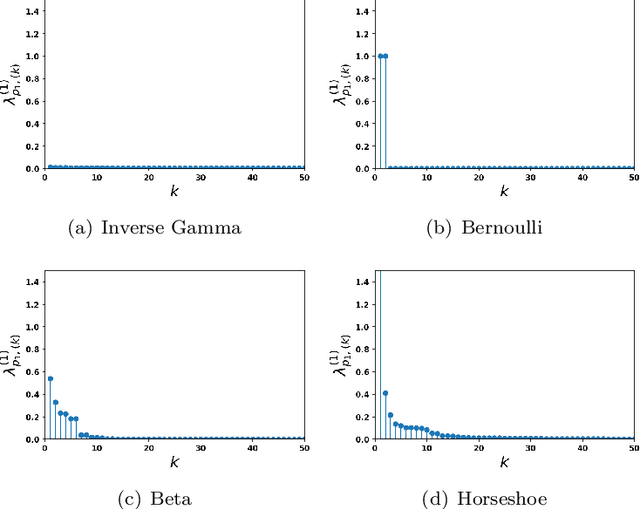
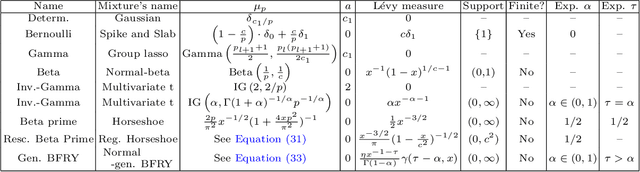
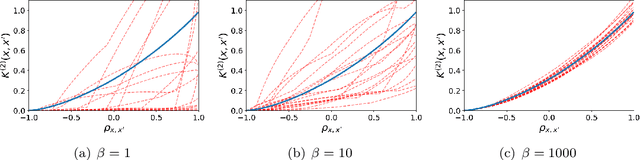
Abstract:This article studies the infinite-width limit of deep feedforward neural networks whose weights are dependent, and modelled via a mixture of Gaussian distributions. Each hidden node of the network is assigned a nonnegative random variable that controls the variance of the outgoing weights of that node. We make minimal assumptions on these per-node random variables: they are iid and their sum, in each layer, converges to some finite random variable in the infinite-width limit. Under this model, we show that each layer of the infinite-width neural network can be characterised by two simple quantities: a non-negative scalar parameter and a L\'evy measure on the positive reals. If the scalar parameters are strictly positive and the L\'evy measures are trivial at all hidden layers, then one recovers the classical Gaussian process (GP) limit, obtained with iid Gaussian weights. More interestingly, if the L\'evy measure of at least one layer is non-trivial, we obtain a mixture of Gaussian processes (MoGP) in the large-width limit. The behaviour of the neural network in this regime is very different from the GP regime. One obtains correlated outputs, with non-Gaussian distributions, possibly with heavy tails. Additionally, we show that, in this regime, the weights are compressible, and feature learning is possible. Many sparsity-promoting neural network models can be recast as special cases of our approach, and we discuss their infinite-width limits; we also present an asymptotic analysis of the pruning error. We illustrate some of the benefits of the MoGP regime over the GP regime in terms of representation learning and compressibility on simulated, MNIST and Fashion MNIST datasets.
Non-exchangeable feature allocation models with sublinear growth of the feature sizes
Mar 30, 2020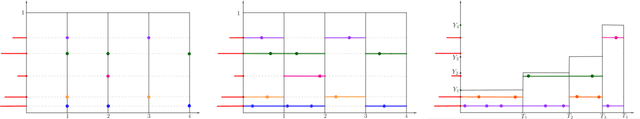

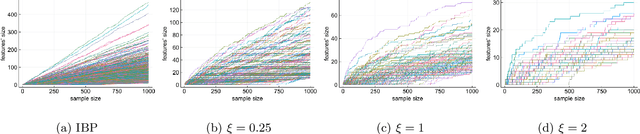
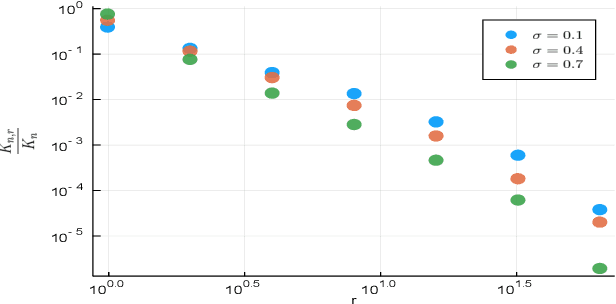
Abstract:Feature allocation models are popular models used in different applications such as unsupervised learning or network modeling. In particular, the Indian buffet process is a flexible and simple one-parameter feature allocation model where the number of features grows unboundedly with the number of objects. The Indian buffet process, like most feature allocation models, satisfies a symmetry property of exchangeability: the distribution is invariant under permutation of the objects. While this property is desirable in some cases, it has some strong implications. Importantly, the number of objects sharing a particular feature grows linearly with the number of objects. In this article, we describe a class of non-exchangeable feature allocation models where the number of objects sharing a given feature grows sublinearly, where the rate can be controlled by a tuning parameter. We derive the asymptotic properties of the model, and show that such model provides a better fit and better predictive performances on various datasets.
A unified construction for series representations and finite approximations of completely random measures
May 26, 2019



Abstract:Infinite-activity completely random measures (CRMs) have become important building blocks of complex Bayesian nonparametric models. They have been successfully used in various applications such as clustering, density estimation, latent feature models, survival analysis or network science. Popular infinite-activity CRMs include the (generalized) gamma process and the (stable) beta process. However, except in some specific cases, exact simulation or scalable inference with these models is challenging and finite-dimensional approximations are often considered. In this work, we propose a general and unified framework to derive both series representations and finite-dimensional approximations of CRMs. Our framework can be seen as an extension of constructions based on size-biased sampling of Poisson point process [Perman1992]. It includes as special cases several known series representations as well as novel ones. In particular, we show that one can get novel series representations for the generalized gamma process and the stable beta process. We also provide some analysis of the truncation error.
Beyond the Chinese Restaurant and Pitman-Yor processes: Statistical Models with Double Power-law Behavior
Feb 13, 2019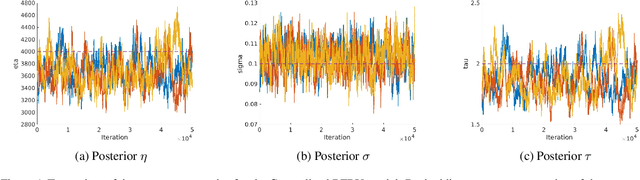
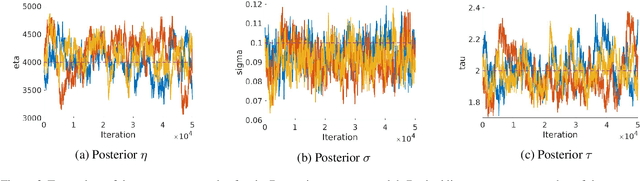
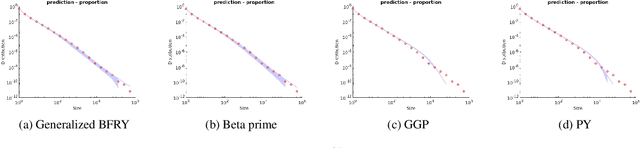
Abstract:Bayesian nonparametric approaches, in particular the Pitman-Yor process and the associated two-parameter Chinese Restaurant process, have been successfully used in applications where the data exhibit a power-law behavior. Examples include natural language processing, natural images or networks. There is also growing empirical evidence that some datasets exhibit a two-regime power-law behavior: one regime for small frequencies, and a second regime, with a different exponent, for high frequencies. In this paper, we introduce a class of completely random measures which are doubly regularly-varying. Contrary to the Pitman-Yor process, we show that when completely random measures in this class are normalized to obtain random probability measures and associated random partitions, such partitions exhibit a double power-law behavior. We discuss in particular three models within this class: the beta prime process (Broderick et al. (2015, 2018), a novel process called generalized BFRY process, and a mixture construction. We derive efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms to estimate the parameters of these models. Finally, we show that the proposed models provide a better fit than the Pitman-Yor process on various datasets.
Modelling sparsity, heterogeneity, reciprocity and community structure in temporal interaction data
Oct 26, 2018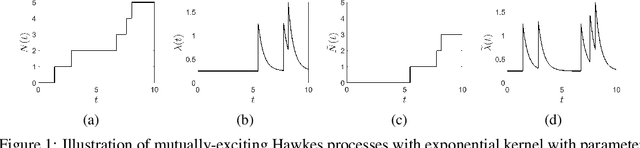

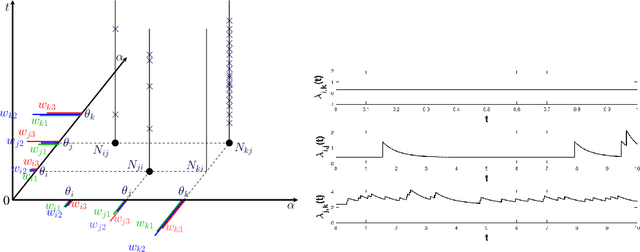
Abstract:We propose a novel class of network models for temporal dyadic interaction data. Our goal is to capture a number of important features often observed in social interactions: sparsity, degree heterogeneity, community structure and reciprocity. We propose a family of models based on self-exciting Hawkes point processes in which events depend on the history of the process. The key component is the conditional intensity function of the Hawkes Process, which captures the fact that interactions may arise as a response to past interactions (reciprocity), or due to shared interests between individuals (community structure). In order to capture the sparsity and degree heterogeneity, the base (non time dependent) part of the intensity function builds on compound random measures following Todeschini et al. (2016). We conduct experiments on a variety of real-world temporal interaction data and show that the proposed model outperforms many competing approaches for link prediction, and leads to interpretable parameters.
A Bayesian model for sparse graphs with flexible degree distribution and overlapping community structure
Oct 03, 2018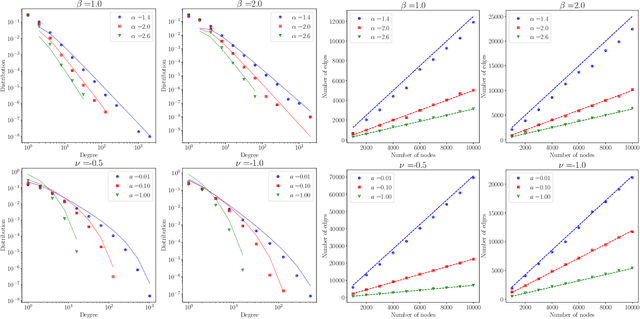


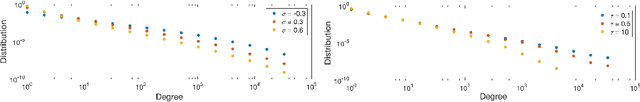
Abstract:We consider a non-projective class of inhomogeneous random graph models with interpretable parameters and a number of interesting asymptotic properties. Using the results of Bollob\'as et al. [2007], we show that i) the class of models is sparse and ii) depending on the choice of the parameters, the model is either scale-free, with power-law exponent greater than 2, or with an asymptotic degree distribution which is power-law with exponential cut-off. We propose an extension of the model that can accommodate an overlapping community structure. Scalable posterior inference can be performed due to the specific choice of the link probability. We present experiments on five different real-world networks with up to 100,000 nodes and edges, showing that the model can provide a good fit to the degree distribution and recovers well the latent community structure.
Non-exchangeable random partition models for microclustering
Nov 20, 2017

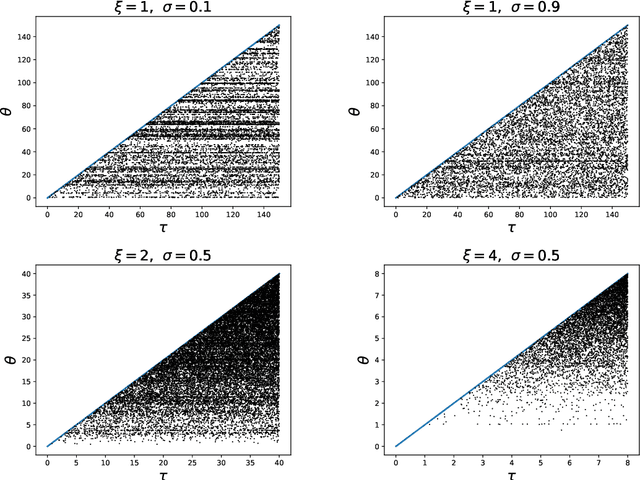
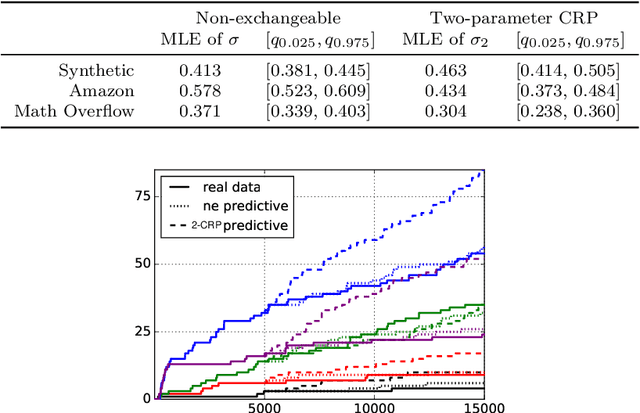
Abstract:Many popular random partition models, such as the Chinese restaurant process and its two-parameter extension, fall in the class of exchangeable random partitions, and have found wide applicability in model-based clustering, population genetics, ecology or network analysis. While the exchangeability assumption is sensible in many cases, it has some strong implications. In particular, Kingman's representation theorem implies that the size of the clusters necessarily grows linearly with the sample size; this feature may be undesirable for some applications, as recently pointed out by Miller et al. (2015). We present here a flexible class of non-exchangeable random partition models which are able to generate partitions whose cluster sizes grow sublinearly with the sample size, and where the growth rate is controlled by one parameter. Along with this result, we provide the asymptotic behaviour of the number of clusters of a given size, and show that the model can exhibit a power-law behavior, controlled by another parameter. The construction is based on completely random measures and a Poisson embedding of the random partition, and inference is performed using a Sequential Monte Carlo algorithm. Additionally, we show how the model can also be directly used to generate sparse multigraphs with power-law degree distributions and degree sequences with sublinear growth. Finally, experiments on real datasets emphasize the usefulness of the approach compared to a two-parameter Chinese restaurant process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge