Florian Lautenschlager
Anomaly Detection in Beehives: An Algorithm Comparison
Oct 08, 2021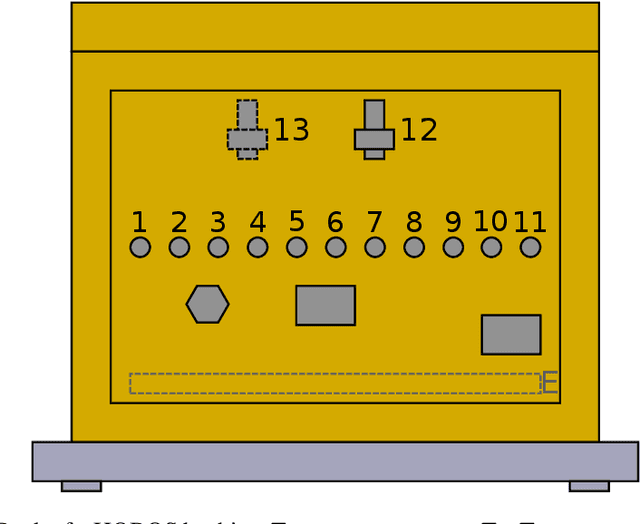
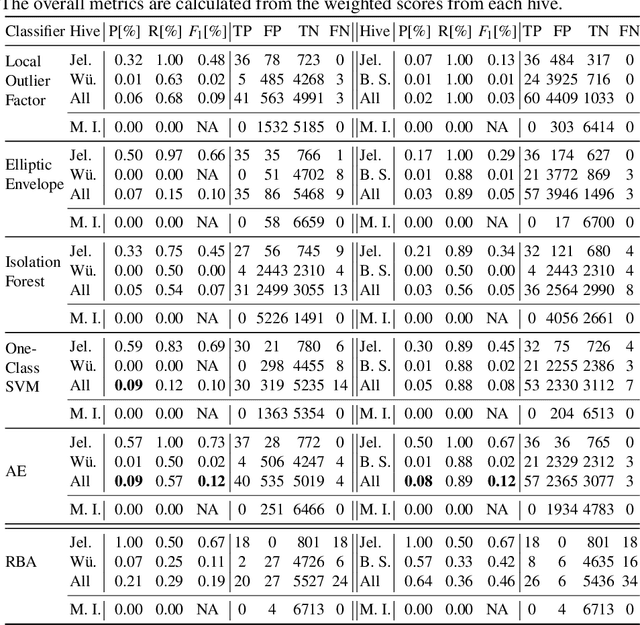
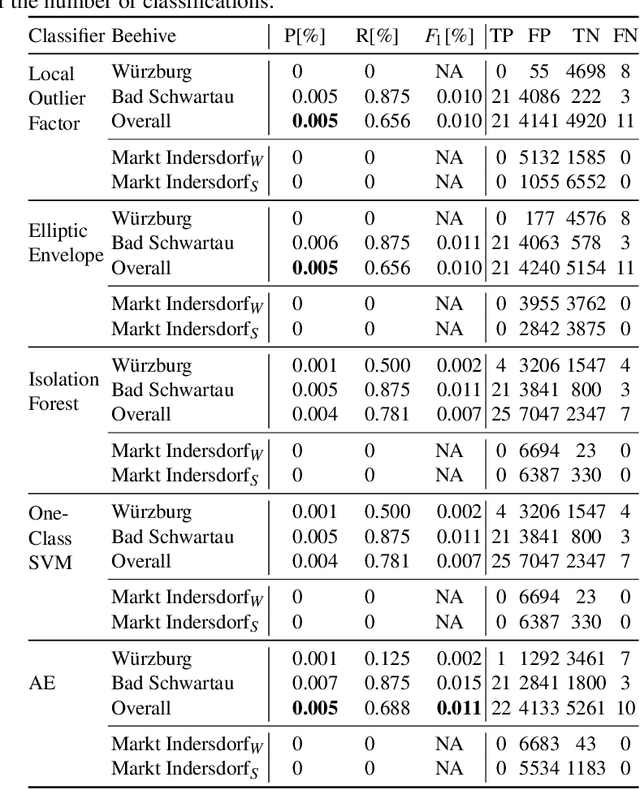
Abstract:Sensor-equipped beehives allow monitoring the living conditions of bees. Machine learning models can use the data of such hives to learn behavioral patterns and find anomalous events. One type of event that is of particular interest to apiarists for economical reasons is bee swarming. Other events of interest are behavioral anomalies from illness and technical anomalies, e.g. sensor failure. Beekeepers can be supported by suitable machine learning models which can detect these events. In this paper we compare multiple machine learning models for anomaly detection and evaluate them for their applicability in the context of beehives. Namely we employed Deep Recurrent Autoencoder, Elliptic Envelope, Isolation Forest, Local Outlier Factor and One-Class SVM. Through evaluation with real world datasets of different hives and with different sensor setups we find that the autoencoder is the best multi-purpose anomaly detector in comparison.
Anomaly Detection in Beehives using Deep Recurrent Autoencoders
Mar 10, 2020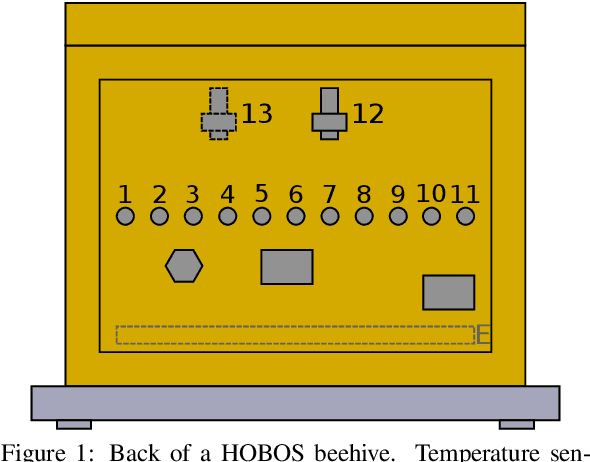
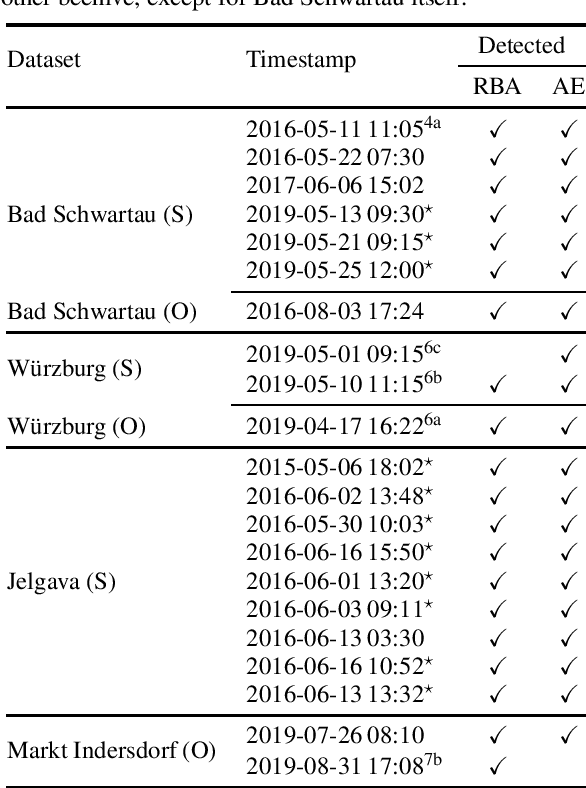
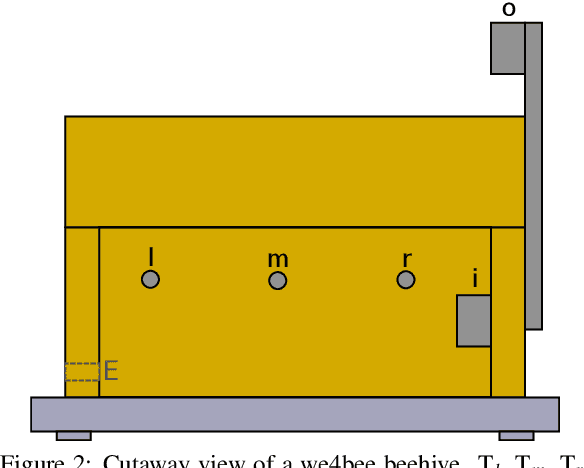
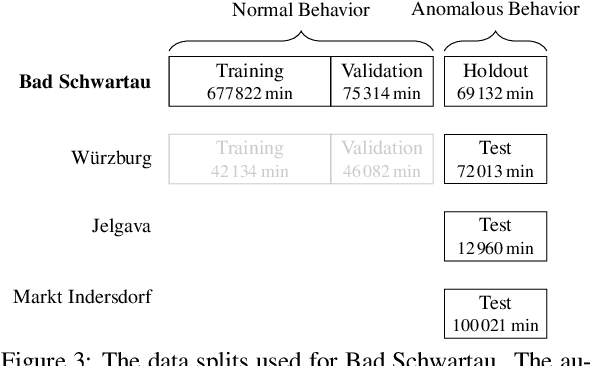
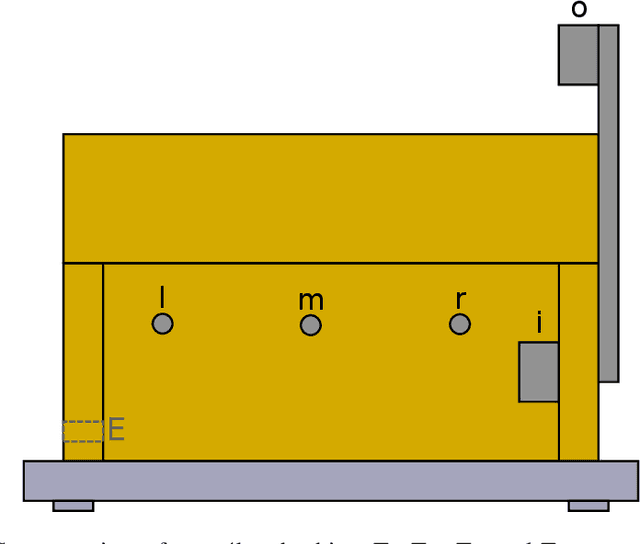
Abstract:Precision beekeeping allows to monitor bees' living conditions by equipping beehives with sensors. The data recorded by these hives can be analyzed by machine learning models to learn behavioral patterns of or search for unusual events in bee colonies. One typical target is the early detection of bee swarming as apiarists want to avoid this due to economical reasons. Advanced methods should be able to detect any other unusual or abnormal behavior arising from illness of bees or from technical reasons, e.g. sensor failure. In this position paper we present an autoencoder, a deep learning model, which detects any type of anomaly in data independent of its origin. Our model is able to reveal the same swarms as a simple rule-based swarm detection algorithm but is also triggered by any other anomaly. We evaluated our model on real world data sets that were collected on different hives and with different sensor setups.
SimLoss: Class Similarities in Cross Entropy
Mar 06, 2020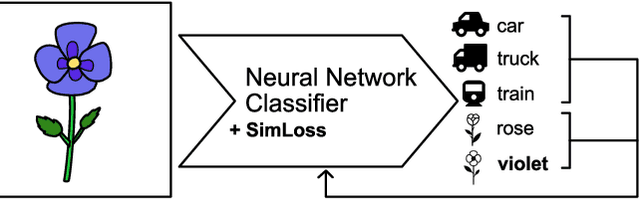
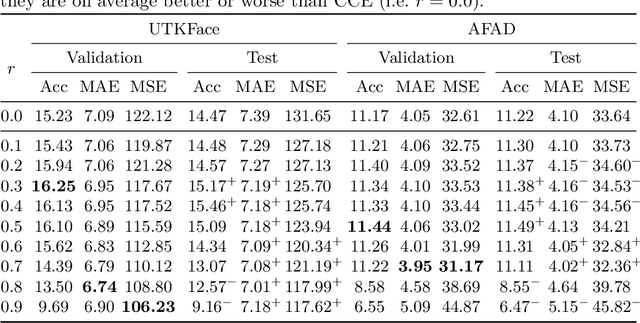
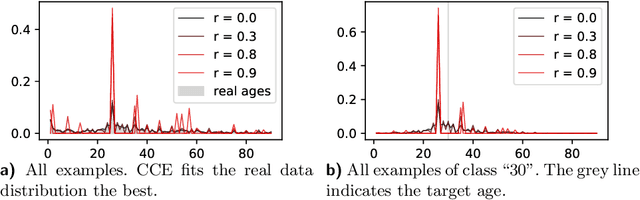

Abstract:One common loss function in neural network classification tasks is Categorical Cross Entropy (CCE), which punishes all misclassifications equally. However, classes often have an inherent structure. For instance, classifying an image of a rose as "violet" is better than as "truck". We introduce SimLoss, a drop-in replacement for CCE that incorporates class similarities along with two techniques to construct such matrices from task-specific knowledge. We test SimLoss on Age Estimation and Image Classification and find that it brings significant improvements over CCE on several metrics. SimLoss therefore allows for explicit modeling of background knowledge by simply exchanging the loss function, while keeping the neural network architecture the same. Code and additional resources can be found at https://github.com/konstantinkobs/SimLoss.
MapLUR: Exploring a new Paradigm for Estimating Air Pollution using Deep Learning on Map Images
Feb 18, 2020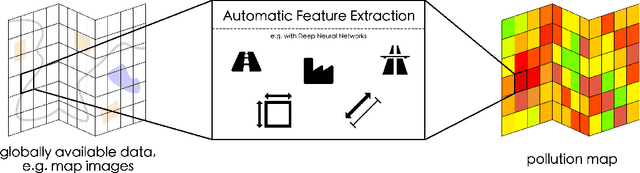
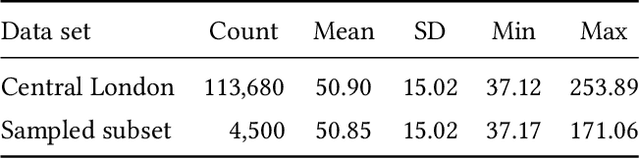
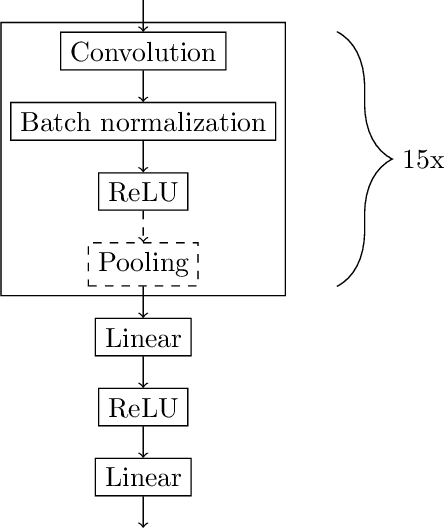

Abstract:Land-use regression (LUR) models are important for the assessment of air pollution concentrations in areas without measurement stations. While many such models exist, they often use manually constructed features based on restricted, locally available data. Thus, they are typically hard to reproduce and challenging to adapt to areas beyond those they have been developed for. In this paper, we advocate a paradigm shift for LUR models: We propose the Data-driven, Open, Global (DOG) paradigm that entails models based on purely data-driven approaches using only openly and globally available data. Progress within this paradigm will alleviate the need for experts to adapt models to the local characteristics of the available data sources and thus facilitate the generalizability of air pollution models to new areas on a global scale. In order to illustrate the feasibility of the DOG paradigm for LUR, we introduce a deep learning model called MapLUR. It is based on a convolutional neural network architecture and is trained exclusively on globally and openly available map data without requiring manual feature engineering. We compare our model to state-of-the-art baselines like linear regression, random forests and multi-layer perceptrons using a large data set of modeled $\text{NO}_2$ concentrations in Central London. Our results show that MapLUR significantly outperforms these approaches even though they are provided with manually tailored features. Furthermore, we illustrate that the automatic feature extraction inherent to models based on the DOG paradigm can learn features that are readily interpretable and closely resemble those commonly used in traditional LUR approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge