Fengming Lin
Reg-TTR, Test-Time Refinement for Fast, Robust and Accurate Image Registration
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Traditional image registration methods are robust but slow due to their iterative nature. While deep learning has accelerated inference, it often struggles with domain shifts. Emerging registration foundation models offer a balance of speed and robustness, yet typically cannot match the peak accuracy of specialized models trained on specific datasets. To mitigate this limitation, we propose Reg-TTR, a test-time refinement framework that synergizes the complementary strengths of both deep learning and conventional registration techniques. By refining the predictions of pre-trained models at inference, our method delivers significantly improved registration accuracy at a modest computational cost, requiring only 21% additional inference time (0.56s). We evaluate Reg-TTR on two distinct tasks and show that it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance while maintaining inference speeds close to previous deep learning methods. As foundation models continue to emerge, our framework offers an efficient strategy to narrow the performance gap between registration foundation models and SOTA methods trained on specialized datasets. The source code will be publicly available following the acceptance of this work.
Vision Language Models: A Survey of 26K Papers
Oct 10, 2025



Abstract:We present a transparent, reproducible measurement of research trends across 26,104 accepted papers from CVPR, ICLR, and NeurIPS spanning 2023-2025. Titles and abstracts are normalized, phrase-protected, and matched against a hand-crafted lexicon to assign up to 35 topical labels and mine fine-grained cues about tasks, architectures, training regimes, objectives, datasets, and co-mentioned modalities. The analysis quantifies three macro shifts: (1) a sharp rise of multimodal vision-language-LLM work, which increasingly reframes classic perception as instruction following and multi-step reasoning; (2) steady expansion of generative methods, with diffusion research consolidating around controllability, distillation, and speed; and (3) resilient 3D and video activity, with composition moving from NeRFs to Gaussian splatting and a growing emphasis on human- and agent-centric understanding. Within VLMs, parameter-efficient adaptation like prompting/adapters/LoRA and lightweight vision-language bridges dominate; training practice shifts from building encoders from scratch to instruction tuning and finetuning strong backbones; contrastive objectives recede relative to cross-entropy/ranking and distillation. Cross-venue comparisons show CVPR has a stronger 3D footprint and ICLR the highest VLM share, while reliability themes such as efficiency or robustness diffuse across areas. We release the lexicon and methodology to enable auditing and extension. Limitations include lexicon recall and abstract-only scope, but the longitudinal signals are consistent across venues and years.
From Pixels to Polygons: A Survey of Deep Learning Approaches for Medical Image-to-Mesh Reconstruction
May 06, 2025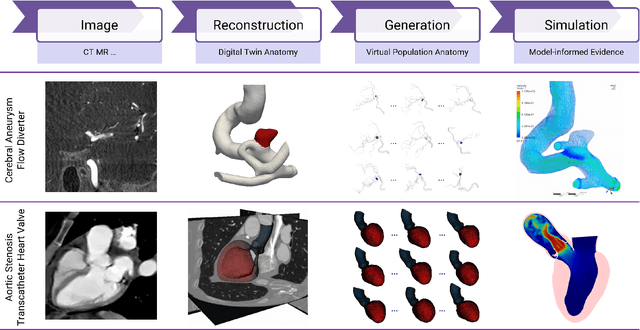
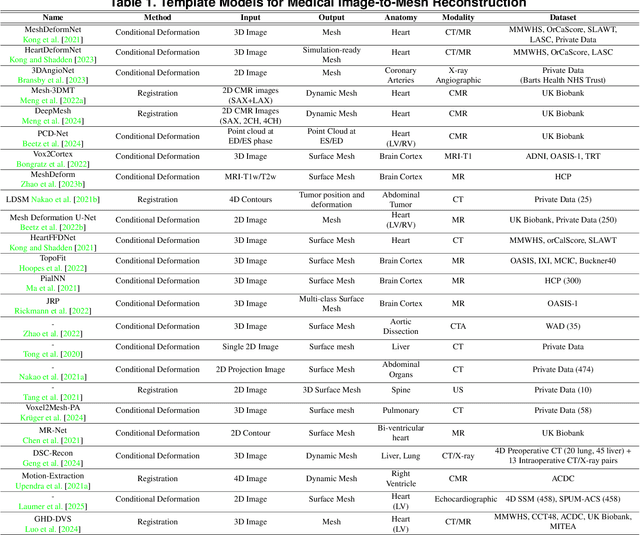
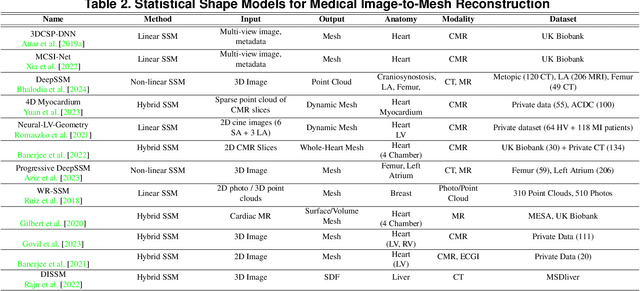
Abstract:Deep learning-based medical image-to-mesh reconstruction has rapidly evolved, enabling the transformation of medical imaging data into three-dimensional mesh models that are critical in computational medicine and in silico trials for advancing our understanding of disease mechanisms, and diagnostic and therapeutic techniques in modern medicine. This survey systematically categorizes existing approaches into four main categories: template models, statistical models, generative models, and implicit models. Each category is analysed in detail, examining their methodological foundations, strengths, limitations, and applicability to different anatomical structures and imaging modalities. We provide an extensive evaluation of these methods across various anatomical applications, from cardiac imaging to neurological studies, supported by quantitative comparisons using standard metrics. Additionally, we compile and analyze major public datasets available for medical mesh reconstruction tasks and discuss commonly used evaluation metrics and loss functions. The survey identifies current challenges in the field, including requirements for topological correctness, geometric accuracy, and multi-modality integration. Finally, we present promising future research directions in this domain. This systematic review aims to serve as a comprehensive reference for researchers and practitioners in medical image analysis and computational medicine.
SMILE-UHURA Challenge -- Small Vessel Segmentation at Mesoscopic Scale from Ultra-High Resolution 7T Magnetic Resonance Angiograms
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:The human brain receives nutrients and oxygen through an intricate network of blood vessels. Pathology affecting small vessels, at the mesoscopic scale, represents a critical vulnerability within the cerebral blood supply and can lead to severe conditions, such as Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases. The advent of 7 Tesla MRI systems has enabled the acquisition of higher spatial resolution images, making it possible to visualise such vessels in the brain. However, the lack of publicly available annotated datasets has impeded the development of robust, machine learning-driven segmentation algorithms. To address this, the SMILE-UHURA challenge was organised. This challenge, held in conjunction with the ISBI 2023, in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, aimed to provide a platform for researchers working on related topics. The SMILE-UHURA challenge addresses the gap in publicly available annotated datasets by providing an annotated dataset of Time-of-Flight angiography acquired with 7T MRI. This dataset was created through a combination of automated pre-segmentation and extensive manual refinement. In this manuscript, sixteen submitted methods and two baseline methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively on two different datasets: held-out test MRAs from the same dataset as the training data (with labels kept secret) and a separate 7T ToF MRA dataset where both input volumes and labels are kept secret. The results demonstrate that most of the submitted deep learning methods, trained on the provided training dataset, achieved reliable segmentation performance. Dice scores reached up to 0.838 $\pm$ 0.066 and 0.716 $\pm$ 0.125 on the respective datasets, with an average performance of up to 0.804 $\pm$ 0.15.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Brain Vessel Segmentation through Transwarp Contrastive Learning
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to align the labelled source distribution with the unlabelled target distribution to obtain domain-invariant predictive models. Since cross-modality medical data exhibit significant intra and inter-domain shifts and most are unlabelled, UDA is more important while challenging in medical image analysis. This paper proposes a simple yet potent contrastive learning framework for UDA to narrow the inter-domain gap between labelled source and unlabelled target distribution. Our method is validated on cerebral vessel datasets. Experimental results show that our approach can learn latent features from labelled 3DRA modality data and improve vessel segmentation performance in unlabelled MRA modality data.
GS-EMA: Integrating Gradient Surgery Exponential Moving Average with Boundary-Aware Contrastive Learning for Enhanced Domain Generalization in Aneurysm Segmentation
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:The automated segmentation of cerebral aneurysms is pivotal for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Confronted with significant domain shifts and class imbalance in 3D Rotational Angiography (3DRA) data from various medical institutions, the task becomes challenging. These shifts include differences in image appearance, intensity distribution, resolution, and aneurysm size, all of which complicate the segmentation process. To tackle these issues, we propose a novel domain generalization strategy that employs gradient surgery exponential moving average (GS-EMA) optimization technique coupled with boundary-aware contrastive learning (BACL). Our approach is distinct in its ability to adapt to new, unseen domains by learning domain-invariant features, thereby improving the robustness and accuracy of aneurysm segmentation across diverse clinical datasets. The results demonstrate that our proposed approach can extract more domain-invariant features, minimizing over-segmentation and capturing more complete aneurysm structures.
Adaptive Semi-Supervised Segmentation of Brain Vessels with Ambiguous Labels
Aug 07, 2023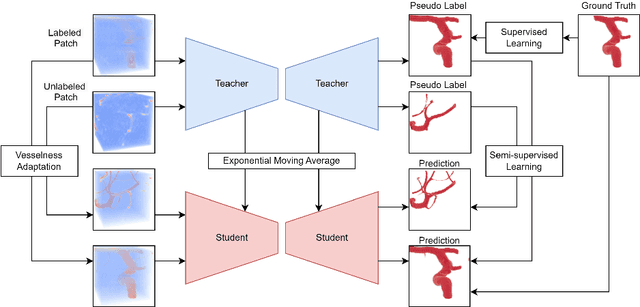
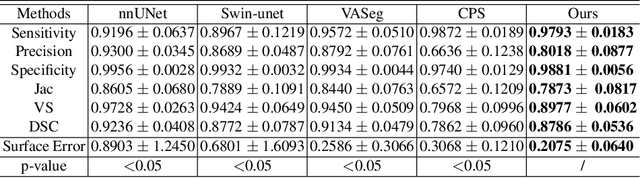
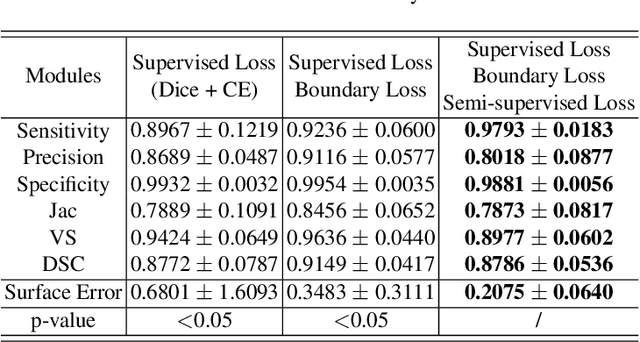
Abstract:Accurate segmentation of brain vessels is crucial for cerebrovascular disease diagnosis and treatment. However, existing methods face challenges in capturing small vessels and handling datasets that are partially or ambiguously annotated. In this paper, we propose an adaptive semi-supervised approach to address these challenges. Our approach incorporates innovative techniques including progressive semi-supervised learning, adaptative training strategy, and boundary enhancement. Experimental results on 3DRA datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method in terms of mesh-based segmentation metrics. By leveraging the partially and ambiguously labeled data, which only annotates the main vessels, our method achieves impressive segmentation performance on mislabeled fine vessels, showcasing its potential for clinical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge