Feifan Yang
MUSE: A Simple Yet Effective Multimodal Search-Based Framework for Lifelong User Interest Modeling
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Lifelong user interest modeling is crucial for industrial recommender systems, yet existing approaches rely predominantly on ID-based features, suffering from poor generalization on long-tail items and limited semantic expressiveness. While recent work explores multimodal representations for behavior retrieval in the General Search Unit (GSU), they often neglect multimodal integration in the fine-grained modeling stage -- the Exact Search Unit (ESU). In this work, we present a systematic analysis of how to effectively leverage multimodal signals across both stages of the two-stage lifelong modeling framework. Our key insight is that simplicity suffices in the GSU: lightweight cosine similarity with high-quality multimodal embeddings outperforms complex retrieval mechanisms. In contrast, the ESU demands richer multimodal sequence modeling and effective ID-multimodal fusion to unlock its full potential. Guided by these principles, we propose MUSE, a simple yet effective multimodal search-based framework. MUSE has been deployed in Taobao display advertising system, enabling 100K-length user behavior sequence modeling and delivering significant gains in top-line metrics with negligible online latency overhead. To foster community research, we share industrial deployment practices and open-source the first large-scale dataset featuring ultra-long behavior sequences paired with high-quality multimodal embeddings. Our code and data is available at https://taobao-mm.github.io.
Enhancing Taobao Display Advertising with Multimodal Representations: Challenges, Approaches and Insights
Jul 28, 2024



Abstract:Despite the recognized potential of multimodal data to improve model accuracy, many large-scale industrial recommendation systems, including Taobao display advertising system, predominantly depend on sparse ID features in their models. In this work, we explore approaches to leverage multimodal data to enhance the recommendation accuracy. We start from identifying the key challenges in adopting multimodal data in a manner that is both effective and cost-efficient for industrial systems. To address these challenges, we introduce a two-phase framework, including: 1) the pre-training of multimodal representations to capture semantic similarity, and 2) the integration of these representations with existing ID-based models. Furthermore, we detail the architecture of our production system, which is designed to facilitate the deployment of multimodal representations. Since the integration of multimodal representations in mid-2023, we have observed significant performance improvements in Taobao display advertising system. We believe that the insights we have gathered will serve as a valuable resource for practitioners seeking to leverage multimodal data in their systems.
Psycholinguistic Tripartite Graph Network for Personality Detection
Jun 09, 2021



Abstract:Most of the recent work on personality detection from online posts adopts multifarious deep neural networks to represent the posts and builds predictive models in a data-driven manner, without the exploitation of psycholinguistic knowledge that may unveil the connections between one's language usage and his psychological traits. In this paper, we propose a psycholinguistic knowledge-based tripartite graph network, TrigNet, which consists of a tripartite graph network and a BERT-based graph initializer. The graph network injects structural psycholinguistic knowledge from LIWC, a computerized instrument for psycholinguistic analysis, by constructing a heterogeneous tripartite graph. The graph initializer is employed to provide initial embeddings for the graph nodes. To reduce the computational cost in graph learning, we further propose a novel flow graph attention network (GAT) that only transmits messages between neighboring parties in the tripartite graph. Benefiting from the tripartite graph, TrigNet can aggregate post information from a psychological perspective, which is a novel way of exploiting domain knowledge. Extensive experiments on two datasets show that TrigNet outperforms the existing state-of-art model by 3.47 and 2.10 points in average F1. Moreover, the flow GAT reduces the FLOPS and Memory measures by 38% and 32%, respectively, in comparison to the original GAT in our setting.
Blur-Attention: A boosting mechanism for non-uniform blurred image restoration
Aug 19, 2020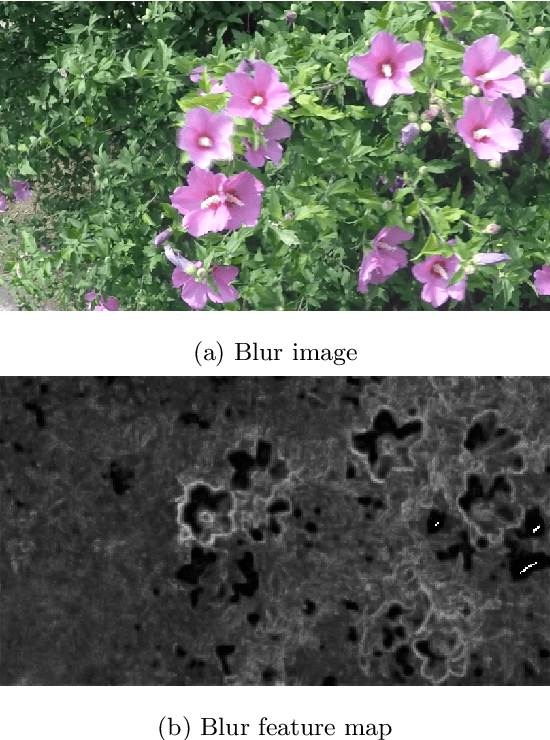
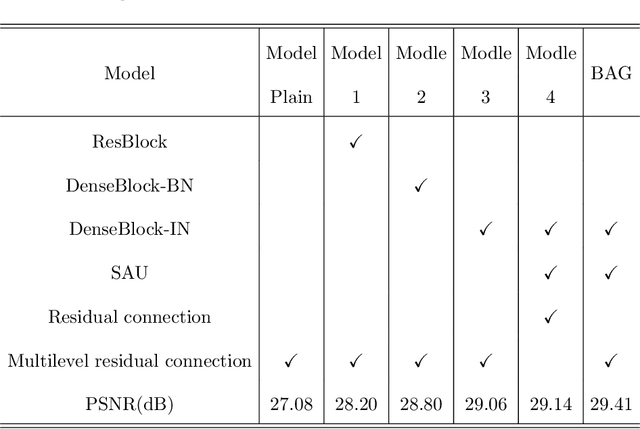
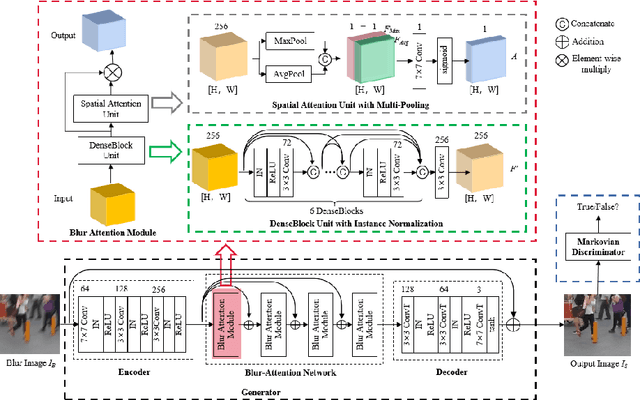
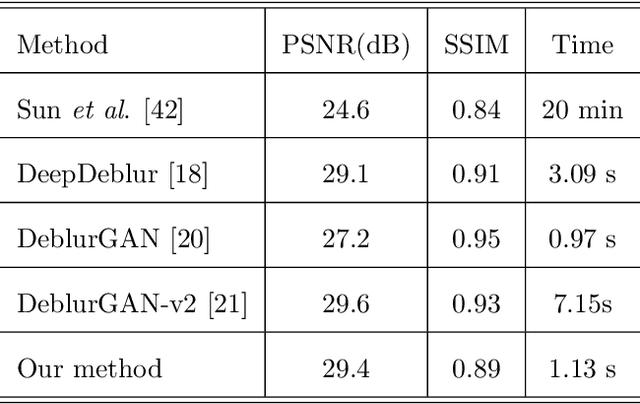
Abstract:Dynamic scene deblurring is a challenging problem in computer vision. It is difficult to accurately estimate the spatially varying blur kernel by traditional methods. Data-driven-based methods usually employ kernel-free end-to-end mapping schemes, which are apt to overlook the kernel estimation. To address this issue, we propose a blur-attention module to dynamically capture the spatially varying features of non-uniform blurred images. The module consists of a DenseBlock unit and a spatial attention unit with multi-pooling feature fusion, which can effectively extract complex spatially varying blur features. We design a multi-level residual connection structure to connect multiple blur-attention modules to form a blur-attention network. By introducing the blur-attention network into a conditional generation adversarial framework, we propose an end-to-end blind motion deblurring method, namely Blur-Attention-GAN (BAG), for a single image. Our method can adaptively select the weights of the extracted features according to the spatially varying blur features, and dynamically restore the images. Experimental results show that the deblurring capability of our method achieved outstanding objective performance in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and subjective visual quality. Furthermore, by visualizing the features extracted by the blur-attention module, comprehensive discussions are provided on its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge