Kin Man Lam
Point Clouds Are Specialized Images: A Knowledge Transfer Approach for 3D Understanding
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning (SSRL) has gained increasing attention in point cloud understanding, in addressing the challenges posed by 3D data scarcity and high annotation costs. This paper presents PCExpert, a novel SSRL approach that reinterprets point clouds as "specialized images". This conceptual shift allows PCExpert to leverage knowledge derived from large-scale image modality in a more direct and deeper manner, via extensively sharing the parameters with a pre-trained image encoder in a multi-way Transformer architecture. The parameter sharing strategy, combined with a novel pretext task for pre-training, i.e., transformation estimation, empowers PCExpert to outperform the state of the arts in a variety of tasks, with a remarkable reduction in the number of trainable parameters. Notably, PCExpert's performance under LINEAR fine-tuning (e.g., yielding a 90.02% overall accuracy on ScanObjectNN) has already approached the results obtained with FULL model fine-tuning (92.66%), demonstrating its effective and robust representation capability.
Blur-Attention: A boosting mechanism for non-uniform blurred image restoration
Aug 19, 2020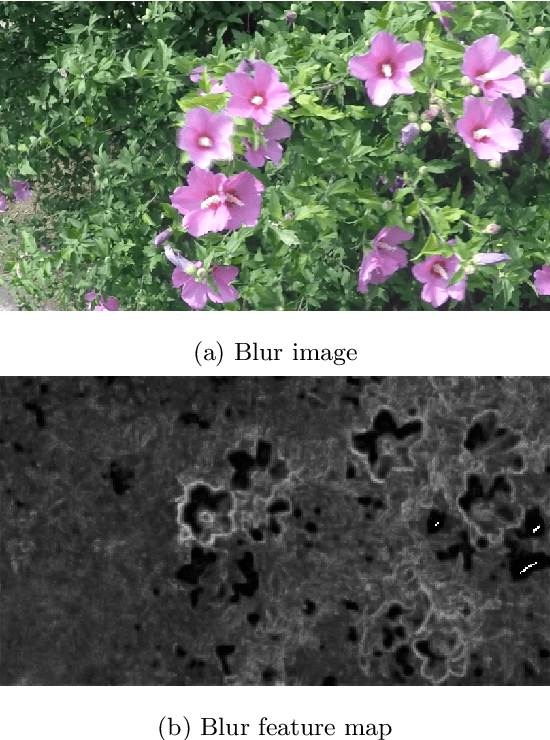
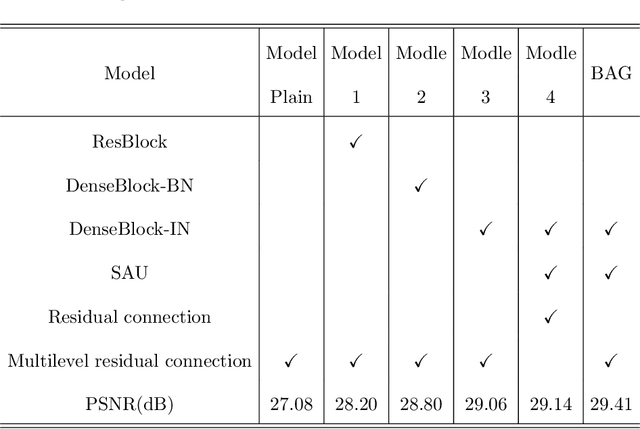
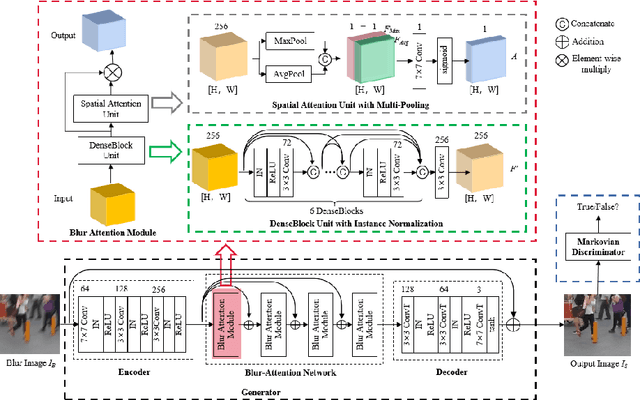
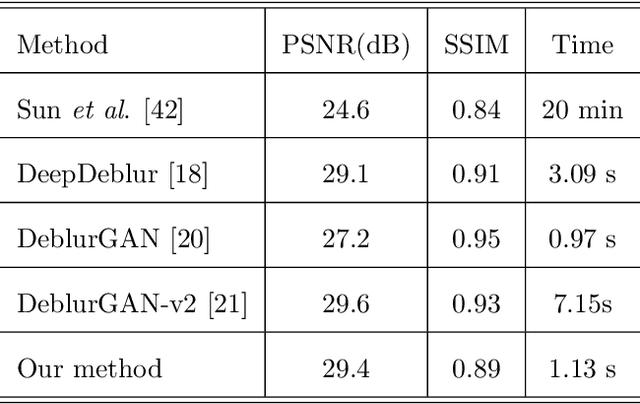
Abstract:Dynamic scene deblurring is a challenging problem in computer vision. It is difficult to accurately estimate the spatially varying blur kernel by traditional methods. Data-driven-based methods usually employ kernel-free end-to-end mapping schemes, which are apt to overlook the kernel estimation. To address this issue, we propose a blur-attention module to dynamically capture the spatially varying features of non-uniform blurred images. The module consists of a DenseBlock unit and a spatial attention unit with multi-pooling feature fusion, which can effectively extract complex spatially varying blur features. We design a multi-level residual connection structure to connect multiple blur-attention modules to form a blur-attention network. By introducing the blur-attention network into a conditional generation adversarial framework, we propose an end-to-end blind motion deblurring method, namely Blur-Attention-GAN (BAG), for a single image. Our method can adaptively select the weights of the extracted features according to the spatially varying blur features, and dynamically restore the images. Experimental results show that the deblurring capability of our method achieved outstanding objective performance in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and subjective visual quality. Furthermore, by visualizing the features extracted by the blur-attention module, comprehensive discussions are provided on its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge