Fatih Erden
A Survey on Detection, Classification, and Tracking of Aerial Threats using Radar and Communications Systems
Feb 08, 2024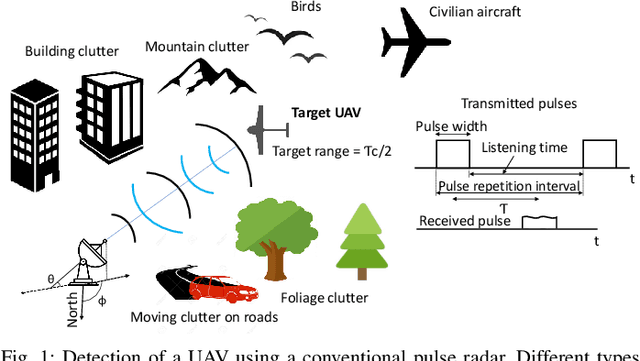
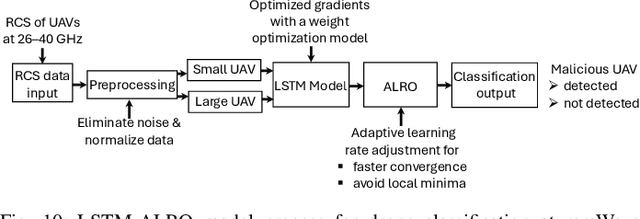
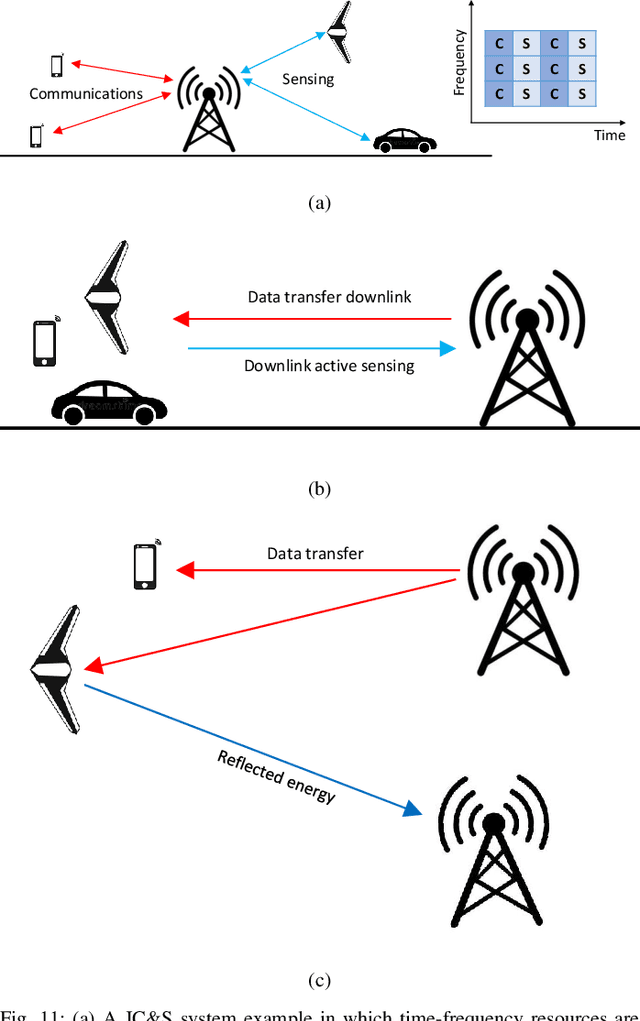
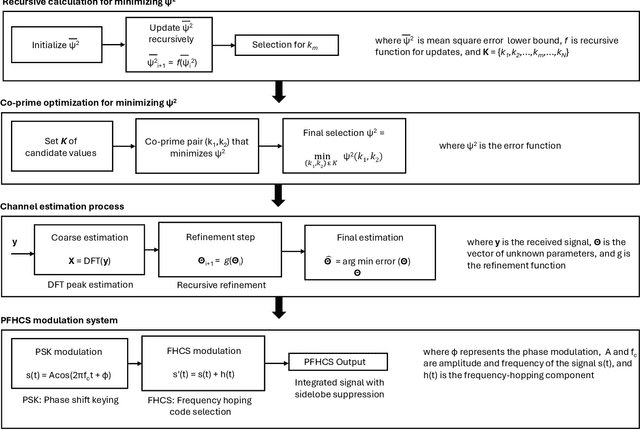
Abstract:The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for a variety of commercial, civilian, and defense applications has increased many folds in recent years. While UAVs are expected to transform future air operations, there are instances where they can be used for malicious purposes. In this context, the detection, classification, and tracking (DCT) of UAVs (DCT-U) for safety and surveillance of national air space is a challenging task when compared to DCT of manned aerial vehicles. In this survey, we discuss the threats and challenges from malicious UAVs and we subsequently study three radio frequency (RF)-based systems for DCT-U. These RF-based systems include radars, communication systems, and RF analyzers. Radar systems are further divided into conventional and modern radar systems, while communication systems can be used for joint communications and sensing (JC&S) in active mode and act as a source of illumination to passive radars for DCT-U. The limitations of the three RF-based systems are also provided. The survey briefly discusses non-RF systems for DCT-U and their limitations. Future directions based on the lessons learned are provided at the end of the survey.
A Survey on Detection, Tracking, and Classification of Aerial Threats using Radars and Communications Systems
Nov 18, 2022



Abstract:The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for different applications has increased many folds in recent years. The UAVs are expected to change the future air operations. However, there are instances where the UAVs can be used for malicious purposes. The detection, tracking, and classification of UAVs is challenging compared to manned aerial vehicles (MAVs) mainly due to small size, complex shapes, and ability to fly close to the terrain and in autonomous flight patterns in swarms. In this survey, we will discuss current and future aerial threats, and provide an overview of radar systems to counter such threats. We also study the performance parameters of radar systems for the detection, tracking, and classification of UAVs compared to MAVs. In addition to dedicated radar systems, we review the use of joint communication-radar (JCR) systems, as well as passive monitoring of changes in the common communication signals, e.g., FM, LTE, and any transmissions that may radiate from a UAV, for the detection, tracking, and classification of UAVs are provided. Finally, limitations of radar systems and comparison with other techniques that do not rely on radars for detection, tracking, and classification of aerial threats are provided.
A Framework for Developing Algorithms for Estimating Propagation Parameters from Measurements
Sep 13, 2021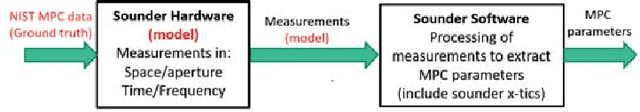
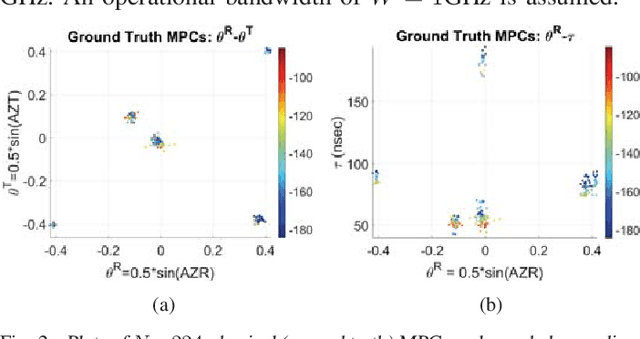
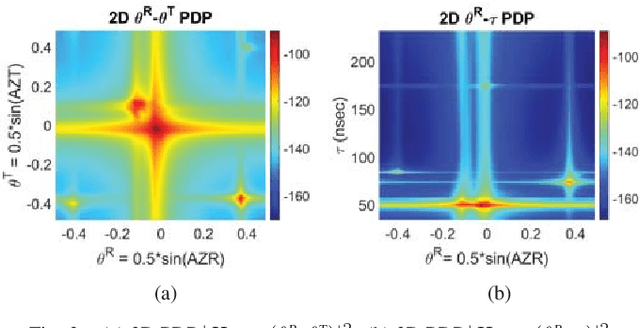
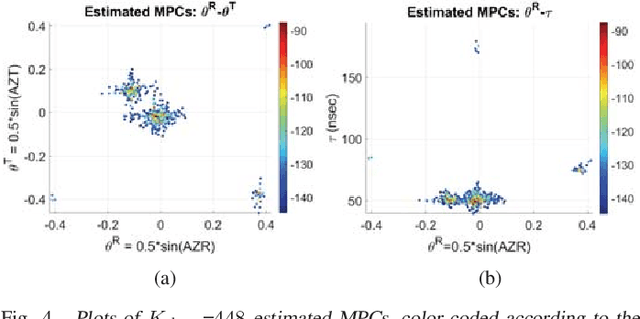
Abstract:A framework is proposed for developing and evaluating algorithms for extracting multipath propagation components (MPCs) from measurements collected by sounders at millimeter-wave (mmW) frequencies. To focus on algorithmic performance, an idealized model is proposed for the spatial frequency response of the propagation environment measured by a sounder. The input to the sounder model is a pre-determined set of MPC parameters that serve as the "ground truth." A three-dimensional angle-delay (beamspace) representation of the measured spatial frequency response serves as a natural domain for implementing and analyzing MPC extraction algorithms. Metrics for quantifying the error in estimated MPC parameters are introduced. Initial results are presented for a greedy matching pursuit algorithm that performs a least-squares (LS) reconstruction of the MPC path gains within the iterations. The results indicate that the simple greedy-LS algorithm has the ability to extract MPCs over a large dynamic range, and suggest several avenues for further performance improvement through extensions of the greedy-LS algorithm as well as by incorporating features of other algorithms, such as SAGE and RIMAX.
Channel Rank Improvement in Urban Drone Corridors Using Passive Intelligent Reflectors
Aug 04, 2021



Abstract:Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) techniques can help in scaling the achievable air-to-ground (A2G) channel capacity while communicating with drones. However, spatial multiplexing with drones suffers from rank deficient channels due to the unobstructed line-of-sight (LoS), especially in millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies that use narrow beams. One possible solution is utilizing low-cost and low-complexity metamaterial-based intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS) to enrich the multipath environment, taking into account that the drones are restricted to fly only within well-defined drone corridors. A hurdle with this solution is placing the IRSs optimally. In this study, we propose an approach for IRS placement with a goal to improve the spatial multiplexing gains, and hence to maximize the average channel capacity in a predefined drone corridor. Our results at 6 GHz, 28 GHz and 60 GHz show that the proposed approach increases the average rates for all frequency bands for a given drone corridor, when compared with the environment where there are no IRSs present, and IRS-aided channels perform close to each other at sub-6 and mmWave bands.
Sub-Terahertz and mmWave Penetration Loss Measurements for Indoor Environments
Mar 03, 2021



Abstract:Millimeter-wave (mmWave) and terahertz (THz) spectrum can support significantly higher data rates compared to lower frequency bands and hence are being actively considered for 5G wireless networks and beyond. These bands have high free-space path loss (FSPL) in line-of-sight (LOS) propagation due to their shorter wavelength. Moreover, in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenario, these two bands suffer higher penetration loss than lower frequency bands which could seriously affect the network coverage. It is therefore critical to study the NLOS penetration loss introduced by different building materials at mmWave and THz bands, to help establish link budgets for an accurate performance analysis in indoor environments. In this work, we measured the penetration loss and the attenuation of several common constructional materials at mmWave (28 and 39 GHz) and sub-THz (120 and 144 GHz) bands. Measurements were conducted using a channel sounder based on NI PXI platforms. Results show that the penetration loss changes extensively based on the frequency and the material properties, ranging from 0.401 dB for ceiling tile at 28 GHz, to 16.608 dB for plywood at 144 GHz. Ceiling tile has the lowest measured attenuation at 28 GHz, while clear glass has the highest attenuation of 27.633 dB/cm at 144 GHz. As expected, the penetration loss and attenuation increased with frequency for all the tested materials.
28 GHz Indoor and Outdoor Propagation Analysis at a Regional Airport
Jan 07, 2021



Abstract:In the upcoming 5G communication, the millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology will play an important role due to its large bandwidth and high data rate. However, mmWave frequencies have higher free-space path loss (FSPL) in line-of-sight (LOS) propagation compared to the currently used sub-6 GHz frequencies. What is more, in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) propagation, the attenuation of mmWave is larger compared to the lower frequencies, which can seriously degrade the performance. It is therefore necessary to investigate mmWave propagation characteristics for a given deployment scenario to understand coverage and rate performance for that environment. In this paper, we focus on 28 GHz wideband mmWave signal propagation characteristics at Johnston Regional Airport (JNX), a local airport near Raleigh, NC. To collect data, we use an NI PXI based channel sounder at 28 GHz for indoor, outdoor, and indoor-to-outdoor scenarios. Results on LOS propagation, reflection, penetration, signal coverage, and multi-path components (MPCs) show a lower indoor FSPL, a richer scattering, and a better coverage compared to outdoor. We also observe high indoor-to-outdoor propagation losses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge