Farhad Keramat
Towards Embodied Agentic AI: Review and Classification of LLM- and VLM-Driven Robot Autonomy and Interaction
Aug 07, 2025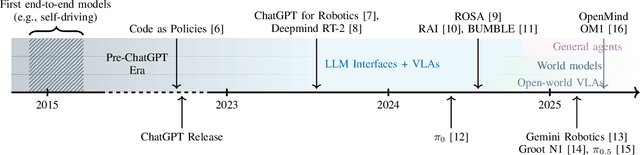
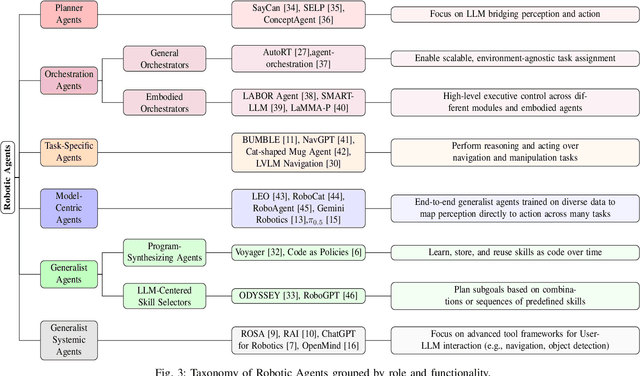
Abstract:Foundation models, including large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), have recently enabled novel approaches to robot autonomy and human-robot interfaces. In parallel, vision-language-action models (VLAs) or large behavior models (BLMs) are increasing the dexterity and capabilities of robotic systems. This survey paper focuses on those words advancing towards agentic applications and architectures. This includes initial efforts exploring GPT-style interfaces to tooling, as well as more complex system where AI agents are coordinators, planners, perception actors, or generalist interfaces. Such agentic architectures allow robots to reason over natural language instructions, invoke APIs, plan task sequences, or assist in operations and diagnostics. In addition to peer-reviewed research, due to the fast-evolving nature of the field, we highlight and include community-driven projects, ROS packages, and industrial frameworks that show emerging trends. We propose a taxonomy for classifying model integration approaches and present a comparative analysis of the role that agents play in different solutions in today's literature.
A Customizable Conflict Resolution and Attribute-Based Access Control Framework for Multi-Robot Systems
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:As multi-robot systems continue to advance and become integral to various applications, managing conflicts and ensuring secure access control are critical challenges that need to be addressed. Access control is essential in multi-robot systems to ensure secure and authorized interactions among robots, protect sensitive data, and prevent unauthorized access to resources. This paper presents a novel framework for customizable conflict resolution and attribute-based access control in multi-robot systems for ROS 2 leveraging the Hyperledger Fabric blockchain. We introduce an attribute-based access control (ABAC) Fabric-ROS 2 bridge to enable secure communication and control between users and robots. By defining conflict resolution policies based on task priorities, robot capabilities, and user-defined constraints, our framework offers a flexible way to resolve conflicts. Additionally, it incorporates attribute-based access control, granting access rights based on user and robot attributes. ABAC offers a modular approach to control access compared to existing access control approaches in ROS 2, such as SROS2. Through this framework, multi-robot systems can be managed efficiently, securely, and adaptably, ensuring controlled access to resources and managing conflicts. Our experimental evaluation shows that our framework marginally improves latency and throughput over exiting Fabric and ROS 2 integration solutions. At higher network load, it is the only solution to operate reliably without a diverging transaction commitment latency. We also demonstrate how conflicts arising from simultaneous control or a robot by two users are resolved in real-time and motion distortion is effectively eliminated.
Distributed Robotic Systems in the Edge-Cloud Continuum with ROS 2: a Review on Novel Architectures and Technology Readiness
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:Robotic systems are more connected, networked, and distributed than ever. New architectures that comply with the \textit{de facto} robotics middleware standard, ROS\,2, have recently emerged to fill the gap in terms of hybrid systems deployed from edge to cloud. This paper reviews new architectures and technologies that enable containerized robotic applications to seamlessly run at the edge or in the cloud. We also overview systems that include solutions from extension to ROS\,2 tooling to the integration of Kubernetes and ROS\,2. Another important trend is robot learning, and how new simulators and cloud simulations are enabling, e.g., large-scale reinforcement learning or distributed federated learning solutions. This has also enabled deeper integration of continuous interaction and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines for robotic systems development, going beyond standard software unit tests with simulated tests to build and validate code automatically. We discuss the current technology readiness and list the potential new application scenarios that are becoming available. Finally, we discuss the current challenges in distributed robotic systems and list open research questions in the field.
Decentralized Vision-Based Byzantine Agent Detection in Multi-Robot Systems with IOTA Smart Contracts
Oct 07, 2022


Abstract:Multiple opportunities lie at the intersection of multi-robot systems and distributed ledger technologies (DLTs). In this work, we investigate the potential of new DLT solutions such as IOTA, for detecting anomalies and byzantine agents in multi-robot systems in a decentralized manner. Traditional blockchain approaches are not applicable to real-world networked and decentralized robotic systems where connectivity conditions are not ideal. To address this, we leverage recent advances in partition-tolerant and byzantine-tolerant collaborative decision-making processes with IOTA smart contracts. We show how our work in vision-based anomaly and change detection can be applied to detecting byzantine agents within multiple robots operating in the same environment. We show that IOTA smart contracts add a low computational overhead while allowing to build trust within the multi-robot system. The proposed approach effectively enables byzantine robot detection based on the comparison of images submitted by the different robots and detection of anomalies and changes between them.
Partition-Tolerant and Byzantine-Tolerant Decision-Making for Distributed Robotic Systems with IOTA and ROS 2
Aug 29, 2022



Abstract:With the increasing ubiquity of autonomous robotic solutions, the interest in their connectivity and in the cooperation within multi-robot systems is rising. Two aspects that are a matter of current research are robot security and secure multi-robot collaboration robust to byzantine agents. Blockchain and other distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) have been proposed to address the challenges in both domains. Nonetheless, some key challenges include scalability and deployment within real-world networks. This paper presents an approach to integrating IOTA and ROS 2 for more scalable DLT-based robotic systems while allowing for network partition tolerance after deployment. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first implementation of IOTA smart contracts for robotic systems, and the first integrated design with ROS 2. This is in comparison to the vast majority of the literature which relies on Ethereum. We present a general IOTA+ROS 2 architecture leading to partition-tolerant decision-making processes that also inherit byzantine tolerance properties from the embedded blockchain structures. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework for a cooperative mapping application in a system with intermittent network connectivity. We show both superior performance with respect to Ethereum in the presence of network partitions, and a low impact in terms of computational resource utilization. These results open the path for wider integration of blockchain solutions in distributed robotic systems with less stringent connectivity and computational requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge