Fabrice Lefèvre
Open-Source Large Language Models as Multilingual Crowdworkers: Synthesizing Open-Domain Dialogues in Several Languages With No Examples in Targets and No Machine Translation
Mar 05, 2025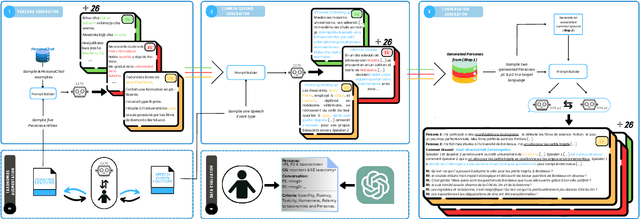
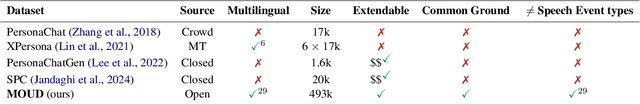
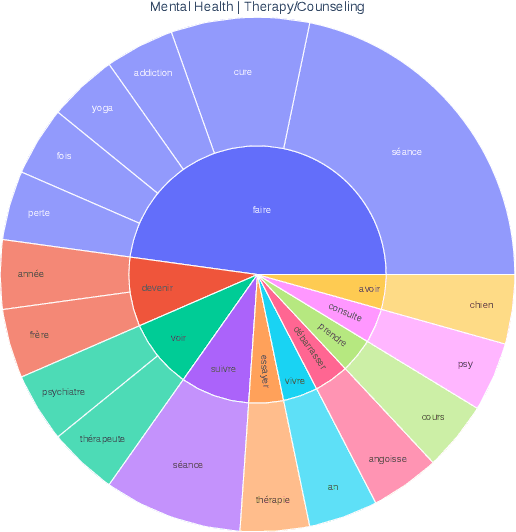
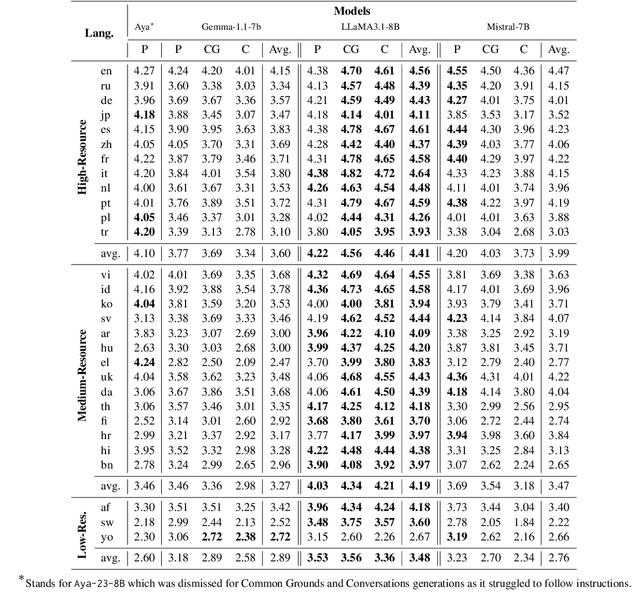
Abstract:The prevailing paradigm in the domain of Open-Domain Dialogue agents predominantly focuses on the English language, encompassing both models and datasets. Furthermore, the financial and temporal investments required for crowdsourcing such datasets for finetuning are substantial, particularly when multiple languages are involved. Fortunately, advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have unveiled a plethora of possibilities across diverse tasks. Specifically, instruction-tuning has enabled LLMs to execute tasks based on natural language instructions, occasionally surpassing the performance of human crowdworkers. Additionally, these models possess the capability to function in various languages within a single thread. Consequently, to generate new samples in different languages, we propose leveraging these capabilities to replicate the data collection process. We introduce a pipeline for generating Open-Domain Dialogue data in multiple Target Languages using LLMs, with demonstrations provided in a unique Source Language. By eschewing explicit Machine Translation in this approach, we enhance the adherence to language-specific nuances. We apply this methodology to the PersonaChat dataset. To enhance the openness of generated dialogues and mimic real life scenarii, we added the notion of speech events corresponding to the type of conversation the speakers are involved in and also that of common ground which represents the premises of a conversation.
FlowAct: A Proactive Multimodal Human-robot Interaction System with Continuous Flow of Perception and Modular Action Sub-systems
Aug 28, 2024Abstract:The evolution of autonomous systems in the context of human-robot interaction systems necessitates a synergy between the continuous perception of the environment and the potential actions to navigate or interact within it. We present Flowact, a proactive multimodal human-robot interaction architecture, working as an asynchronous endless loop of robot sensors into actuators and organized by two controllers, the Environment State Tracking (EST) and the Action Planner. The EST continuously collects and publishes a representation of the operative environment, ensuring a steady flow of perceptual data. This persistent perceptual flow is pivotal for our advanced Action Planner which orchestrates a collection of modular action subsystems, such as movement and speaking modules, governing their initiation or cessation based on the evolving environmental narrative. The EST employs a fusion of diverse sensory modalities to build a rich, real-time representation of the environment that is distributed to the Action Planner. This planner uses a decision-making framework to dynamically coordinate action modules, allowing them to respond proactively and coherently to changes in the environment. Through a series of real-world experiments, we exhibit the efficacy of the system in maintaining a continuous perception-action loop, substantially enhancing the responsiveness and adaptability of autonomous pro-active agents. The modular architecture of the action subsystems facilitates easy extensibility and adaptability to a broad spectrum of tasks and scenarios.
Language Portability Strategies for Open-domain Dialogue with Pre-trained Language Models from High to Low Resource Languages
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:In this paper we propose a study of linguistic portability strategies of large pre-trained language models (PLMs) used for open-domain dialogue systems in a high-resource language for this task. In particular the target low-resource language (L_T) will be simulated with French, as it lacks of task-specific resources and allows our human evaluation, when the source language (L_S) is English. For obvious reasons, recent works using such models for open-domain dialogue are mostly developed in English. Yet building specific PLMs for each possible target language supposes collecting new datasets and is costly. For this reason, trying to leverage all existing resources (PLMs and data) in both L_S and L_T , we wish to assess the performance achievable in L_T with different approaches. The first two approaches evaluate the usage of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) at different levels: TrainOnTarget where a L_S dataset is translated before fine-tuning in L_T and TestOnSource where a L_S model is coupled with NMT modules during inference. Then, the advent of BLOOM [2], the world first open-access multilingual large PLM, allow researchers to develop new approaches aiming to leverage not only the model's full accessibility but also its multilingualism and translation abilities. In this context the task is learned in L_S first and adapted to L_T using the MAD-X Adapter architecture [16]. In the two sets of experiments models are evaluated in spoken dialogue conditions with human and the strategies can be compared in terms of perceived interaction quality.
Role-Play Zero-Shot Prompting with Large Language Models for Open-Domain Human-Machine Conversation
Jun 26, 2024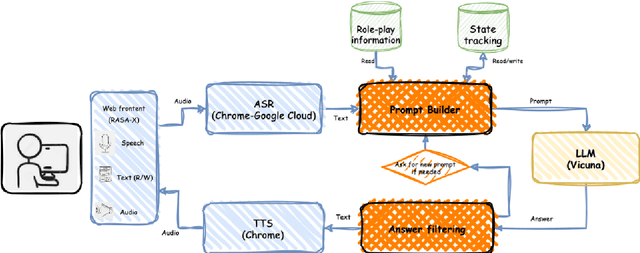
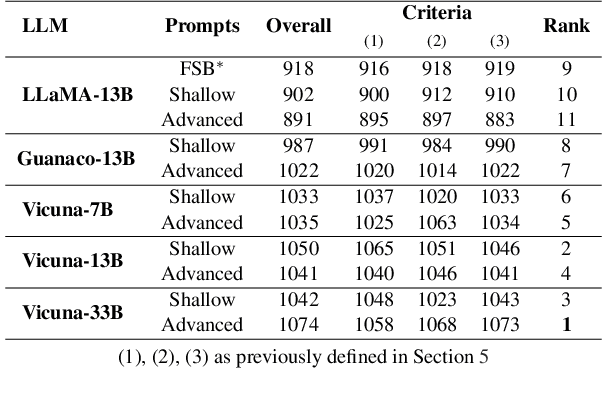
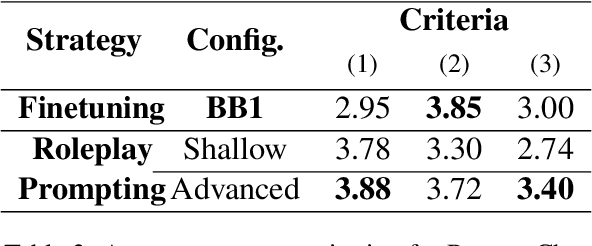
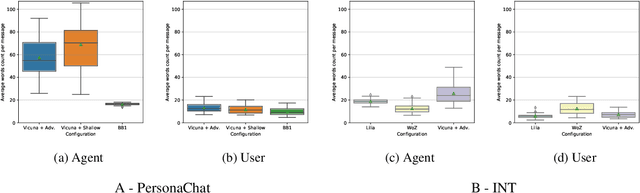
Abstract:Recently, various methods have been proposed to create open-domain conversational agents with Large Language Models (LLMs). These models are able to answer user queries, but in a one-way Q&A format rather than a true conversation. Fine-tuning on particular datasets is the usual way to modify their style to increase conversational ability, but this is expensive and usually only available in a few languages. In this study, we explore role-play zero-shot prompting as an efficient and cost-effective solution for open-domain conversation, using capable multilingual LLMs (Beeching et al., 2023) trained to obey instructions. We design a prompting system that, when combined with an instruction-following model - here Vicuna (Chiang et al., 2023) - produces conversational agents that match and even surpass fine-tuned models in human evaluation in French in two different tasks.
Graph Neural Network Policies and Imitation Learning for Multi-Domain Task-Oriented Dialogues
Oct 11, 2022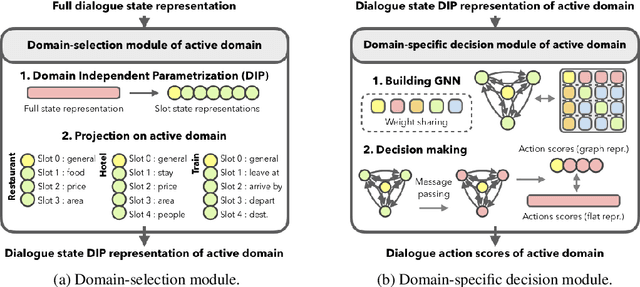

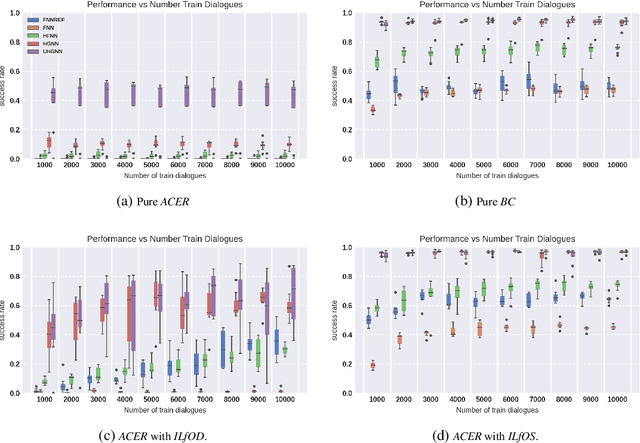
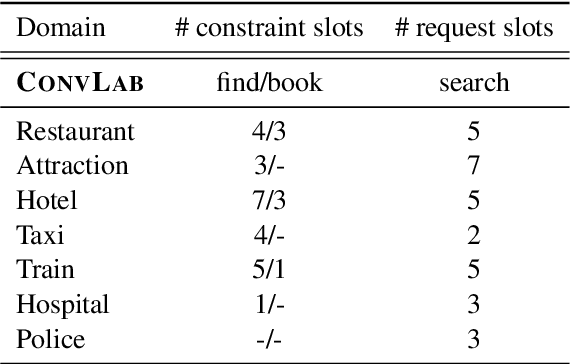
Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue systems are designed to achieve specific goals while conversing with humans. In practice, they may have to handle simultaneously several domains and tasks. The dialogue manager must therefore be able to take into account domain changes and plan over different domains/tasks in order to deal with multidomain dialogues. However, learning with reinforcement in such context becomes difficult because the state-action dimension is larger while the reward signal remains scarce. Our experimental results suggest that structured policies based on graph neural networks combined with different degrees of imitation learning can effectively handle multi-domain dialogues. The reported experiments underline the benefit of structured policies over standard policies.
Findings from Experiments of On-line Joint Reinforcement Learning of Semantic Parser and Dialogue Manager with real Users
Oct 25, 2021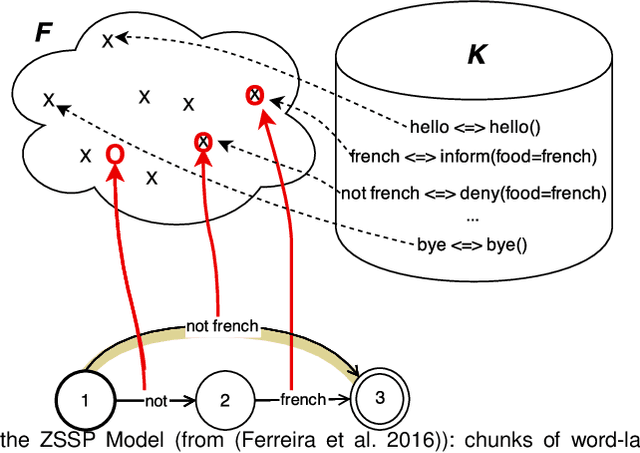
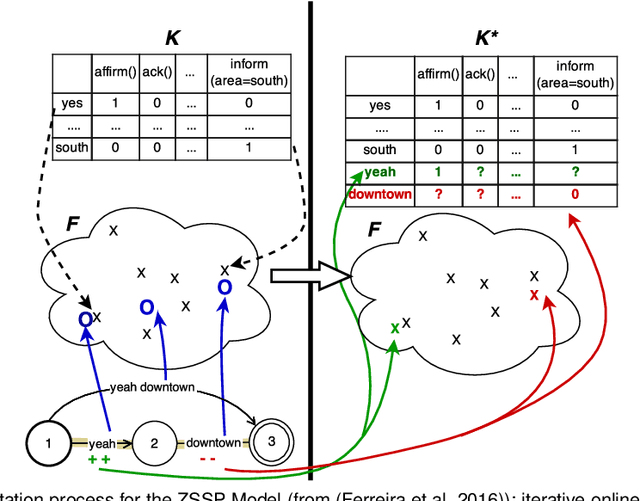

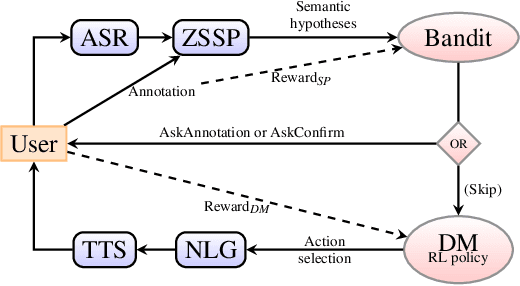
Abstract:Design of dialogue systems has witnessed many advances lately, yet acquiring huge set of data remains an hindrance to their fast development for a new task or language. Besides, training interactive systems with batch data is not satisfactory. On-line learning is pursued in this paper as a convenient way to alleviate these difficulties. After the system modules are initiated, a single process handles data collection, annotation and use in training algorithms. A new challenge is to control the cost of the on-line learning borne by the user. Our work focuses on learning the semantic parsing and dialogue management modules (speech recognition and synthesis offer ready-for-use solutions). In this context we investigate several variants of simultaneous learning which are tested in user trials. In our experiments, with varying merits, they can all achieve good performance with only a few hundreds of training dialogues and overstep a handcrafted system. The analysis of these experiments gives us some insights, discussed in the paper, into the difficulty for the system's trainers to establish a coherent and constant behavioural strategy to enable a fast and good-quality training phase.
Diluted Near-Optimal Expert Demonstrations for Guiding Dialogue Stochastic Policy Optimisation
Nov 25, 2020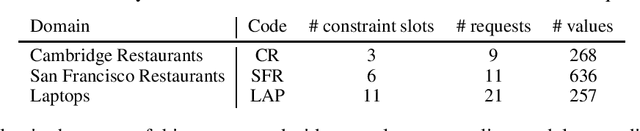
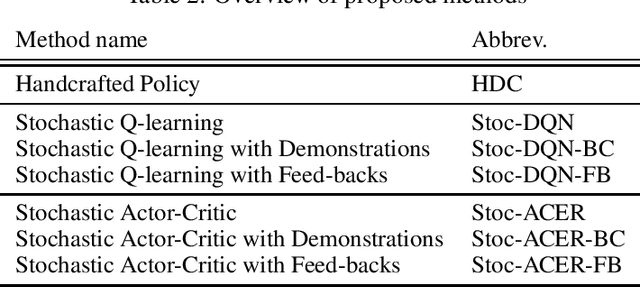
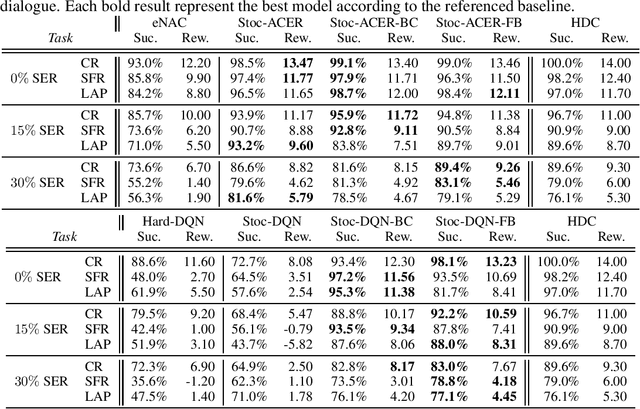
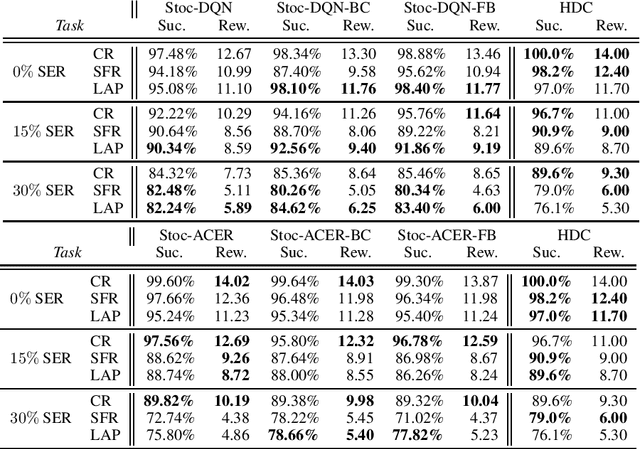
Abstract:A learning dialogue agent can infer its behaviour from interactions with the users. These interactions can be taken from either human-to-human or human-machine conversations. However, human interactions are scarce and costly, making learning from few interactions essential. One solution to speedup the learning process is to guide the agent's exploration with the help of an expert. We present in this paper several imitation learning strategies for dialogue policy where the guiding expert is a near-optimal handcrafted policy. We incorporate these strategies with state-of-the-art reinforcement learning methods based on Q-learning and actor-critic. We notably propose a randomised exploration policy which allows for a seamless hybridisation of the learned policy and the expert. Our experiments show that our hybridisation strategy outperforms several baselines, and that it can accelerate the learning when facing real humans.
Joint On-line Learning of a Zero-shot Spoken Semantic Parser and a Reinforcement Learning Dialogue Manager
Oct 01, 2018
Abstract:Despite many recent advances for the design of dialogue systems, a true bottleneck remains the acquisition of data required to train its components. Unlike many other language processing applications, dialogue systems require interactions with users, therefore it is complex to develop them with pre-recorded data. Building on previous works, on-line learning is pursued here as a most convenient way to address the issue. Data collection, annotation and use in learning algorithms are performed in a single process. The main difficulties are then: to bootstrap an initial basic system, and to control the level of additional cost on the user side. Considering that well-performing solutions can be used directly off the shelf for speech recognition and synthesis, the study is focused on learning the spoken language understanding and dialogue management modules only. Several variants of joint learning are investigated and tested with user trials to confirm that the overall on-line learning can be obtained after only a few hundred training dialogues and can overstep an expert-based system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge