Graph Neural Network Policies and Imitation Learning for Multi-Domain Task-Oriented Dialogues
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2022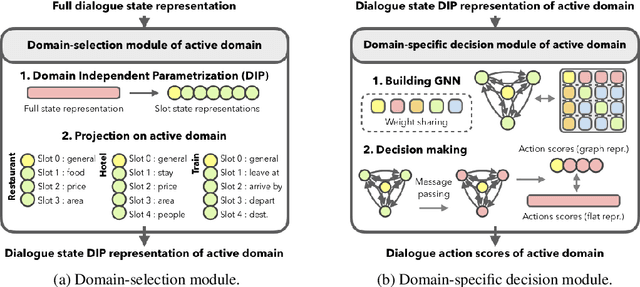

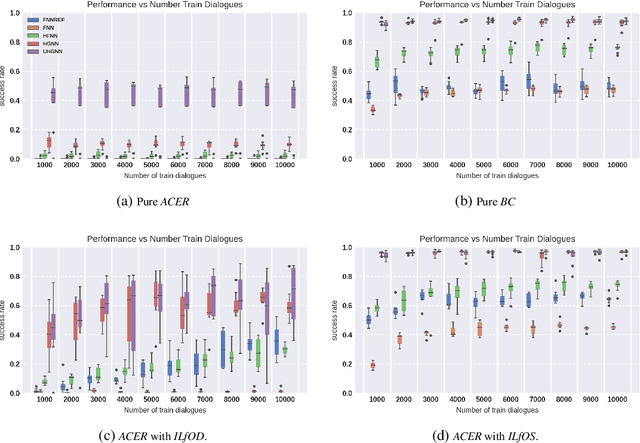
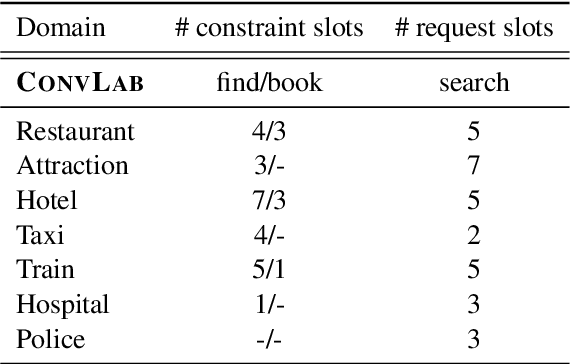
Task-oriented dialogue systems are designed to achieve specific goals while conversing with humans. In practice, they may have to handle simultaneously several domains and tasks. The dialogue manager must therefore be able to take into account domain changes and plan over different domains/tasks in order to deal with multidomain dialogues. However, learning with reinforcement in such context becomes difficult because the state-action dimension is larger while the reward signal remains scarce. Our experimental results suggest that structured policies based on graph neural networks combined with different degrees of imitation learning can effectively handle multi-domain dialogues. The reported experiments underline the benefit of structured policies over standard policies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge