Virgile Sucal
Open-Source Large Language Models as Multilingual Crowdworkers: Synthesizing Open-Domain Dialogues in Several Languages With No Examples in Targets and No Machine Translation
Mar 05, 2025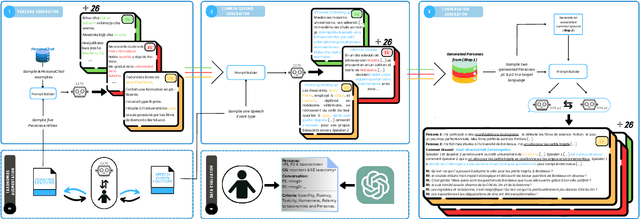
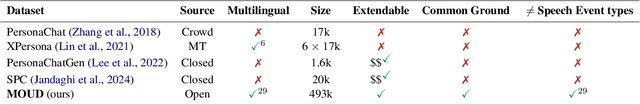
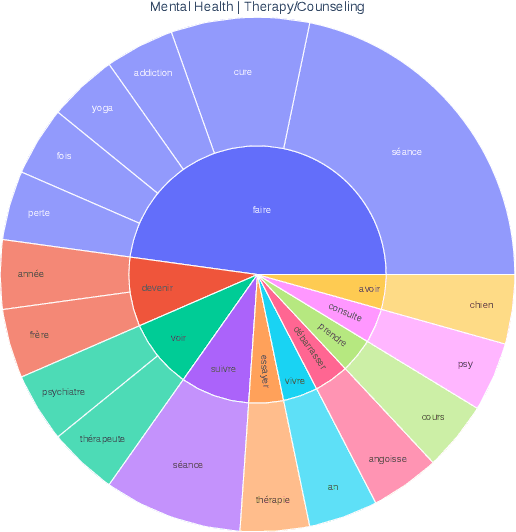
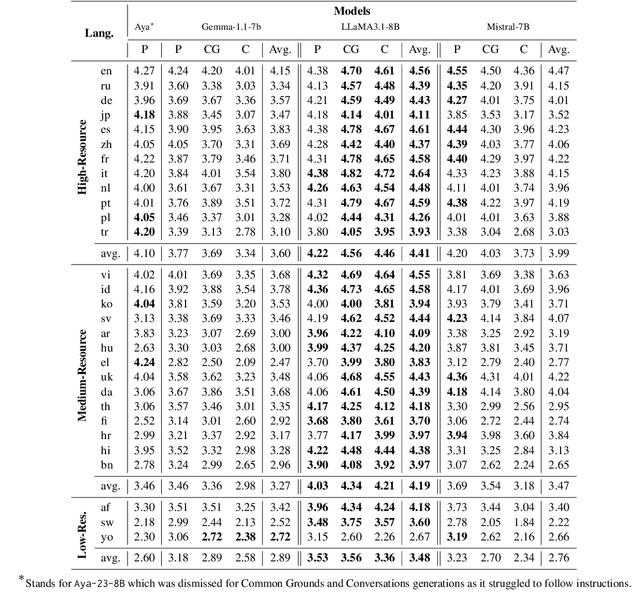
Abstract:The prevailing paradigm in the domain of Open-Domain Dialogue agents predominantly focuses on the English language, encompassing both models and datasets. Furthermore, the financial and temporal investments required for crowdsourcing such datasets for finetuning are substantial, particularly when multiple languages are involved. Fortunately, advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have unveiled a plethora of possibilities across diverse tasks. Specifically, instruction-tuning has enabled LLMs to execute tasks based on natural language instructions, occasionally surpassing the performance of human crowdworkers. Additionally, these models possess the capability to function in various languages within a single thread. Consequently, to generate new samples in different languages, we propose leveraging these capabilities to replicate the data collection process. We introduce a pipeline for generating Open-Domain Dialogue data in multiple Target Languages using LLMs, with demonstrations provided in a unique Source Language. By eschewing explicit Machine Translation in this approach, we enhance the adherence to language-specific nuances. We apply this methodology to the PersonaChat dataset. To enhance the openness of generated dialogues and mimic real life scenarii, we added the notion of speech events corresponding to the type of conversation the speakers are involved in and also that of common ground which represents the premises of a conversation.
Language Portability Strategies for Open-domain Dialogue with Pre-trained Language Models from High to Low Resource Languages
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:In this paper we propose a study of linguistic portability strategies of large pre-trained language models (PLMs) used for open-domain dialogue systems in a high-resource language for this task. In particular the target low-resource language (L_T) will be simulated with French, as it lacks of task-specific resources and allows our human evaluation, when the source language (L_S) is English. For obvious reasons, recent works using such models for open-domain dialogue are mostly developed in English. Yet building specific PLMs for each possible target language supposes collecting new datasets and is costly. For this reason, trying to leverage all existing resources (PLMs and data) in both L_S and L_T , we wish to assess the performance achievable in L_T with different approaches. The first two approaches evaluate the usage of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) at different levels: TrainOnTarget where a L_S dataset is translated before fine-tuning in L_T and TestOnSource where a L_S model is coupled with NMT modules during inference. Then, the advent of BLOOM [2], the world first open-access multilingual large PLM, allow researchers to develop new approaches aiming to leverage not only the model's full accessibility but also its multilingualism and translation abilities. In this context the task is learned in L_S first and adapted to L_T using the MAD-X Adapter architecture [16]. In the two sets of experiments models are evaluated in spoken dialogue conditions with human and the strategies can be compared in terms of perceived interaction quality.
Role-Play Zero-Shot Prompting with Large Language Models for Open-Domain Human-Machine Conversation
Jun 26, 2024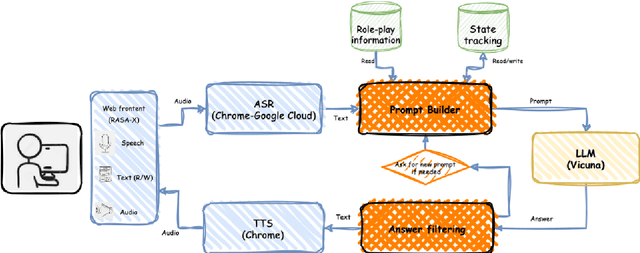
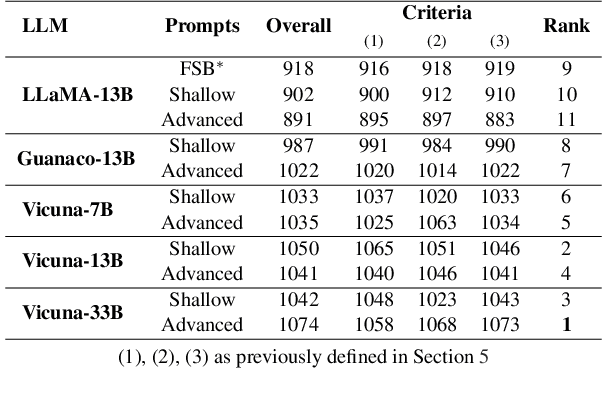
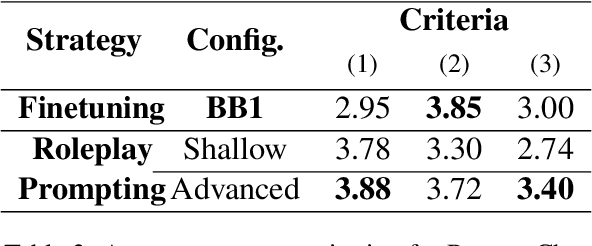
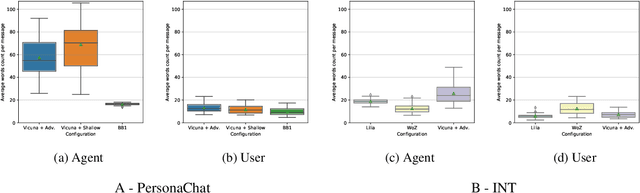
Abstract:Recently, various methods have been proposed to create open-domain conversational agents with Large Language Models (LLMs). These models are able to answer user queries, but in a one-way Q&A format rather than a true conversation. Fine-tuning on particular datasets is the usual way to modify their style to increase conversational ability, but this is expensive and usually only available in a few languages. In this study, we explore role-play zero-shot prompting as an efficient and cost-effective solution for open-domain conversation, using capable multilingual LLMs (Beeching et al., 2023) trained to obey instructions. We design a prompting system that, when combined with an instruction-following model - here Vicuna (Chiang et al., 2023) - produces conversational agents that match and even surpass fine-tuned models in human evaluation in French in two different tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge