Matthieu Riou
Findings from Experiments of On-line Joint Reinforcement Learning of Semantic Parser and Dialogue Manager with real Users
Oct 25, 2021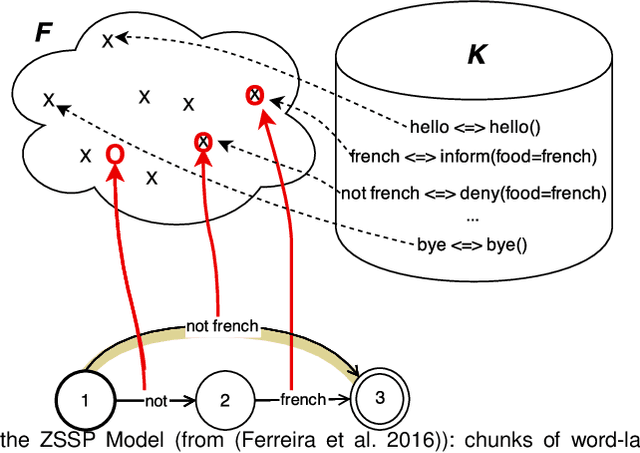

Abstract:Design of dialogue systems has witnessed many advances lately, yet acquiring huge set of data remains an hindrance to their fast development for a new task or language. Besides, training interactive systems with batch data is not satisfactory. On-line learning is pursued in this paper as a convenient way to alleviate these difficulties. After the system modules are initiated, a single process handles data collection, annotation and use in training algorithms. A new challenge is to control the cost of the on-line learning borne by the user. Our work focuses on learning the semantic parsing and dialogue management modules (speech recognition and synthesis offer ready-for-use solutions). In this context we investigate several variants of simultaneous learning which are tested in user trials. In our experiments, with varying merits, they can all achieve good performance with only a few hundreds of training dialogues and overstep a handcrafted system. The analysis of these experiments gives us some insights, discussed in the paper, into the difficulty for the system's trainers to establish a coherent and constant behavioural strategy to enable a fast and good-quality training phase.
Joint On-line Learning of a Zero-shot Spoken Semantic Parser and a Reinforcement Learning Dialogue Manager
Oct 01, 2018
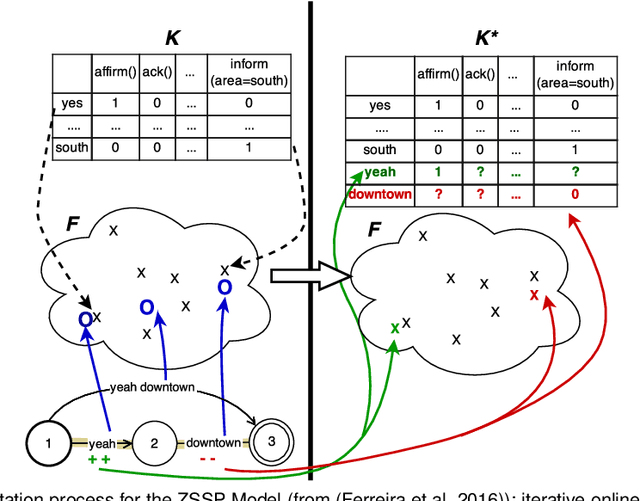
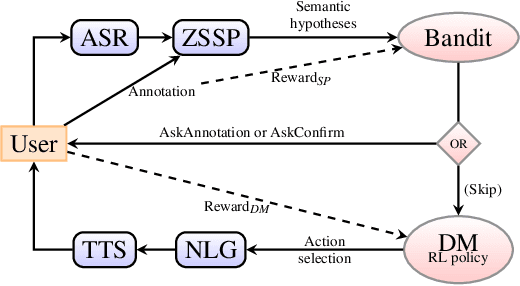
Abstract:Despite many recent advances for the design of dialogue systems, a true bottleneck remains the acquisition of data required to train its components. Unlike many other language processing applications, dialogue systems require interactions with users, therefore it is complex to develop them with pre-recorded data. Building on previous works, on-line learning is pursued here as a most convenient way to address the issue. Data collection, annotation and use in learning algorithms are performed in a single process. The main difficulties are then: to bootstrap an initial basic system, and to control the level of additional cost on the user side. Considering that well-performing solutions can be used directly off the shelf for speech recognition and synthesis, the study is focused on learning the spoken language understanding and dialogue management modules only. Several variants of joint learning are investigated and tested with user trials to confirm that the overall on-line learning can be obtained after only a few hundred training dialogues and can overstep an expert-based system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge