Eunjin Kim
Survey of Genetic and Differential Evolutionary Algorithm Approaches to Search Documents Based On Semantic Similarity
Jul 15, 2025
Abstract:Identifying similar documents within extensive volumes of data poses a significant challenge. To tackle this issue, researchers have developed a variety of effective distributed computing techniques. With the advancement of computing power and the rise of big data, deep neural networks and evolutionary computing algorithms such as genetic algorithms and differential evolution algorithms have achieved greater success. This survey will explore the most recent advancements in the search for documents based on their semantic text similarity, focusing on genetic and differential evolutionary computing algorithms.
Survey of Swarm Intelligence Approaches to Search Documents Based On Semantic Similarity
Jul 15, 2025
Abstract:Swarm Intelligence (SI) is gaining a lot of popularity in artificial intelligence, where the natural behavior of animals and insects is observed and translated into computer algorithms called swarm computing to solve real-world problems. Due to their effectiveness, they are applied in solving various computer optimization problems. This survey will review all the latest developments in Searching for documents based on semantic similarity using Swarm Intelligence algorithms and recommend future research directions.
BF-STVSR: B-Splines and Fourier-Best Friends for High Fidelity Spatial-Temporal Video Super-Resolution
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:Enhancing low-resolution, low-frame-rate videos to high-resolution, high-frame-rate quality is essential for a seamless user experience, motivating advancements in Continuous Spatial-Temporal Video Super Resolution (C-STVSR). While prior methods employ Implicit Neural Representation (INR) for continuous encoding, they often struggle to capture the complexity of video data, relying on simple coordinate concatenation and pre-trained optical flow network for motion representation. Interestingly, we find that adding position encoding, contrary to common observations, does not improve-and even degrade performance. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when combined with pre-trained optical flow networks, which can limit the model's flexibility. To address these issues, we propose BF-STVSR, a C-STVSR framework with two key modules tailored to better represent spatial and temporal characteristics of video: 1) B-spline Mapper for smooth temporal interpolation, and 2) Fourier Mapper for capturing dominant spatial frequencies. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art PSNR and SSIM performance, showing enhanced spatial details and natural temporal consistency.
Bag of Tricks for Developing Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis Framework to Overcome Data Scarcity
Oct 18, 2022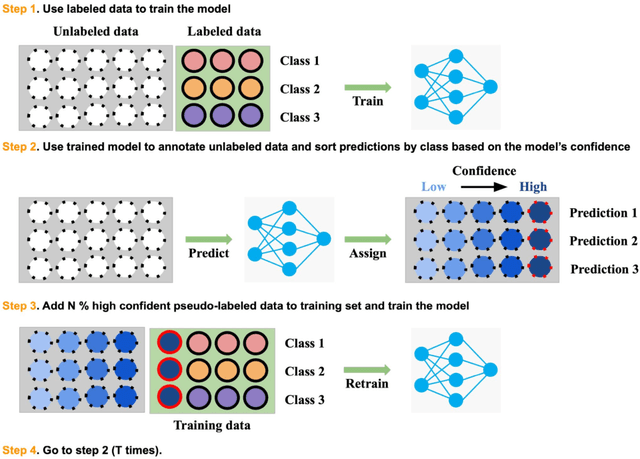
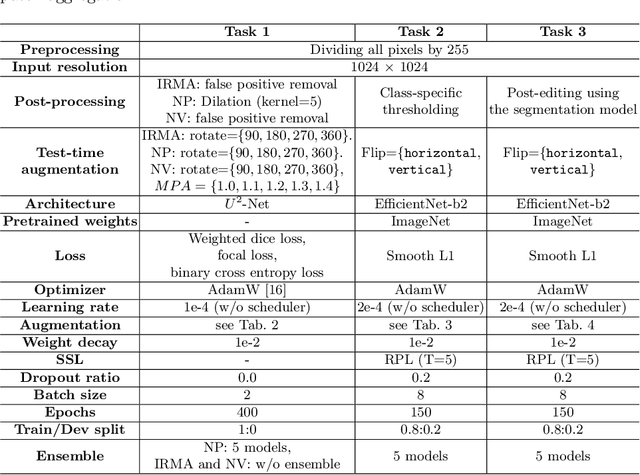
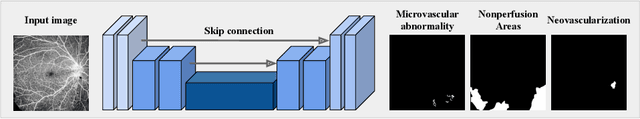
Abstract:Recently, diabetic retinopathy (DR) screening utilizing ultra-wide optical coherence tomography angiography (UW-OCTA) has been used in clinical practices to detect signs of early DR. However, developing a deep learning-based DR analysis system using UW-OCTA images is not trivial due to the difficulty of data collection and the absence of public datasets. By realistic constraints, a model trained on small datasets may obtain sub-par performance. Therefore, to help ophthalmologists be less confused about models' incorrect decisions, the models should be robust even in data scarcity settings. To address the above practical challenging, we present a comprehensive empirical study for DR analysis tasks, including lesion segmentation, image quality assessment, and DR grading. For each task, we introduce a robust training scheme by leveraging ensemble learning, data augmentation, and semi-supervised learning. Furthermore, we propose reliable pseudo labeling that excludes uncertain pseudo-labels based on the model's confidence scores to reduce the negative effect of noisy pseudo-labels. By exploiting the proposed approaches, we achieved 1st place in the Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis Challenge.
A Survey on Computational Intelligence-based Transfer Learning
Jun 17, 2022
Abstract:The goal of transfer learning (TL) is providing a framework for exploiting acquired knowledge from source to target data. Transfer learning approaches compared to traditional machine learning approaches are capable of modeling better data patterns from the current domain. However, vanilla TL needs performance improvements by using computational intelligence-based TL. This paper studies computational intelligence-based transfer learning techniques and categorizes them into neural network-based, evolutionary algorithm-based, swarm intelligence-based and fuzzy logic-based transfer learning.
Fuzzy Relational Modeling of Cost and Affordability for Advanced Technology Manufacturing Environment
Oct 11, 2003



Abstract:Relational representation of knowledge makes it possible to perform all the computations and decision making in a uniform relational way by means of special relational compositions called triangle and square products. In this paper some applications in manufacturing related to cost analysis are described. Testing fuzzy relational structures for various relational properties allows us to discover dependencies, hierarchies, similarities, and equivalences of the attributes characterizing technological processes and manufactured artifacts in their relationship to costs and performance. A brief overview of mathematical aspects of BK-relational products is given in Appendix 1 together with further references in the literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge