Eugene Pomerantsev
Data Augmentation for Electrocardiograms
Apr 09, 2022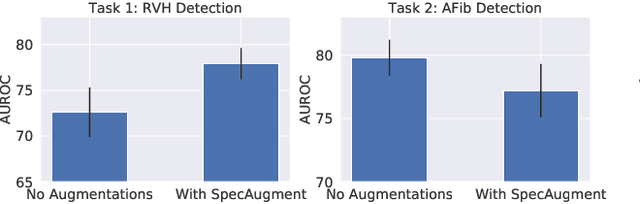
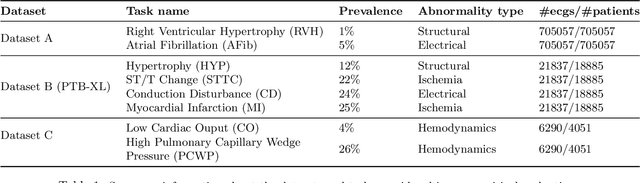
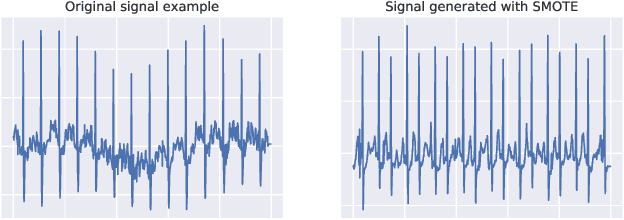
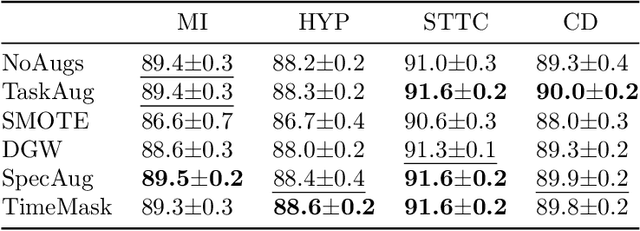
Abstract:Neural network models have demonstrated impressive performance in predicting pathologies and outcomes from the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). However, these models often need to be trained with large, labelled datasets, which are not available for many predictive tasks of interest. In this work, we perform an empirical study examining whether training time data augmentation methods can be used to improve performance on such data-scarce ECG prediction problems. We investigate how data augmentation strategies impact model performance when detecting cardiac abnormalities from the ECG. Motivated by our finding that the effectiveness of existing augmentation strategies is highly task-dependent, we introduce a new method, TaskAug, which defines a flexible augmentation policy that is optimized on a per-task basis. We outline an efficient learning algorithm to do so that leverages recent work in nested optimization and implicit differentiation. In experiments, considering three datasets and eight predictive tasks, we find that TaskAug is competitive with or improves on prior work, and the learned policies shed light on what transformations are most effective for different tasks. We distill key insights from our experimental evaluation, generating a set of best practices for applying data augmentation to ECG prediction problems.
Learning to Predict with Supporting Evidence: Applications to Clinical Risk Prediction
Mar 04, 2021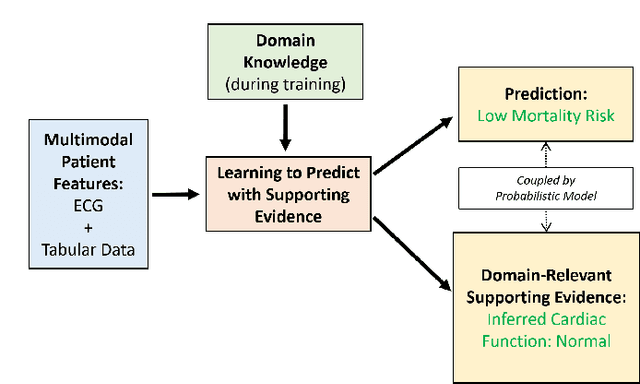
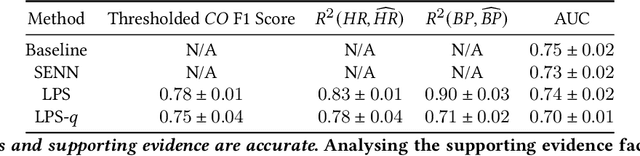
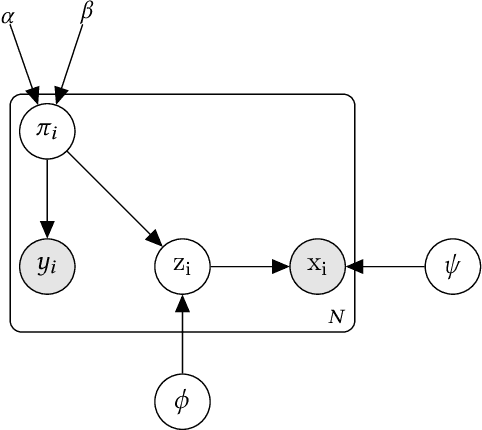
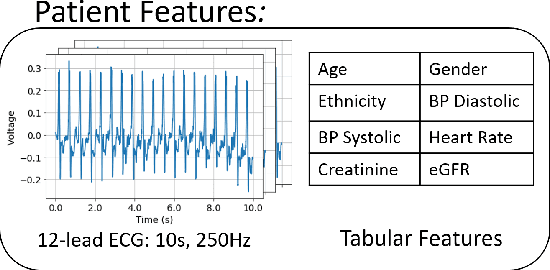
Abstract:The impact of machine learning models on healthcare will depend on the degree of trust that healthcare professionals place in the predictions made by these models. In this paper, we present a method to provide people with clinical expertise with domain-relevant evidence about why a prediction should be trusted. We first design a probabilistic model that relates meaningful latent concepts to prediction targets and observed data. Inference of latent variables in this model corresponds to both making a prediction and providing supporting evidence for that prediction. We present a two-step process to efficiently approximate inference: (i) estimating model parameters using variational learning, and (ii) approximating maximum a posteriori estimation of latent variables in the model using a neural network, trained with an objective derived from the probabilistic model. We demonstrate the method on the task of predicting mortality risk for patients with cardiovascular disease. Specifically, using electrocardiogram and tabular data as input, we show that our approach provides appropriate domain-relevant supporting evidence for accurate predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge