Esteban Flores
Probabilistic approach to feedback control enhances multi-legged locomotion on rugged landscapes
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Achieving robust legged locomotion on complex terrains poses challenges due to the high uncertainty in robot-environment interactions. Recent advances in bipedal and quadrupedal robots demonstrate good mobility on rugged terrains but rely heavily on sensors for stability due to low static stability from a high center of mass and a narrow base of support. We hypothesize that a multi-legged robotic system can leverage morphological redundancy from additional legs to minimize sensing requirements when traversing challenging terrains. Studies suggest that a multi-legged system with sufficient legs can reliably navigate noisy landscapes without sensing and control, albeit at a low speed of up to 0.1 body lengths per cycle (BLC). However, the control framework to enhance speed on challenging terrains remains underexplored due to the complex environmental interactions, making it difficult to identify the key parameters to control in these high-degree-of-freedom systems. Here, we present a bio-inspired vertical body undulation wave as a novel approach to mitigate environmental disturbances affecting robot speed, supported by experiments and probabilistic models. Finally, we introduce a control framework which monitors foot-ground contact patterns on rugose landscapes using binary foot-ground contact sensors to estimate terrain rugosity. The controller adjusts the vertical body wave based on the deviation of the limb's averaged actual-to-ideal foot-ground contact ratio, achieving a significant enhancement of up to 0.235 BLC on rugose laboratory terrain. We observed a $\sim$ 50\% increase in speed and a $\sim$ 40\% reduction in speed variance compared to the open-loop controller. Additionally, the controller operates in complex terrains outside the lab, including pine straw, robot-sized rocks, mud, and leaves.
Steering Elongate Multi-legged Robots By Modulating Body Undulation Waves
Oct 01, 2024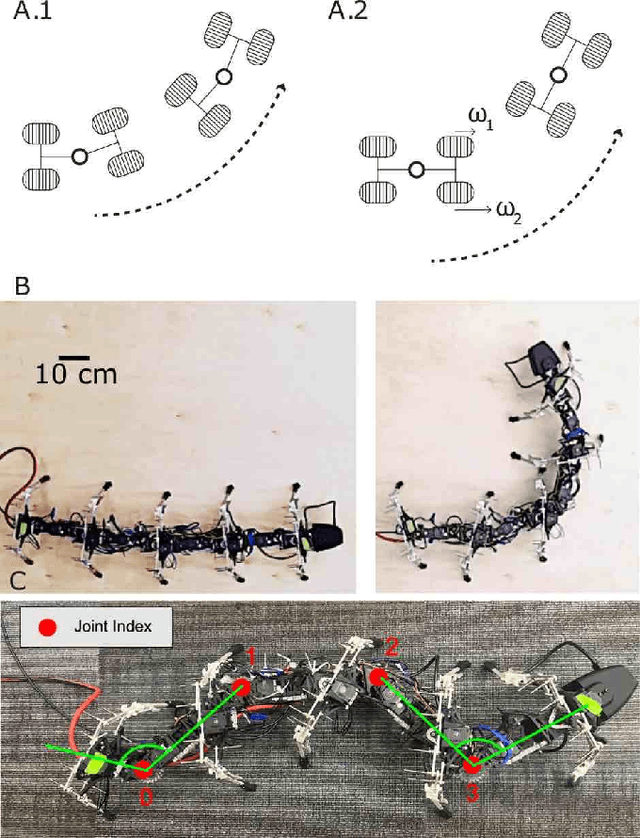
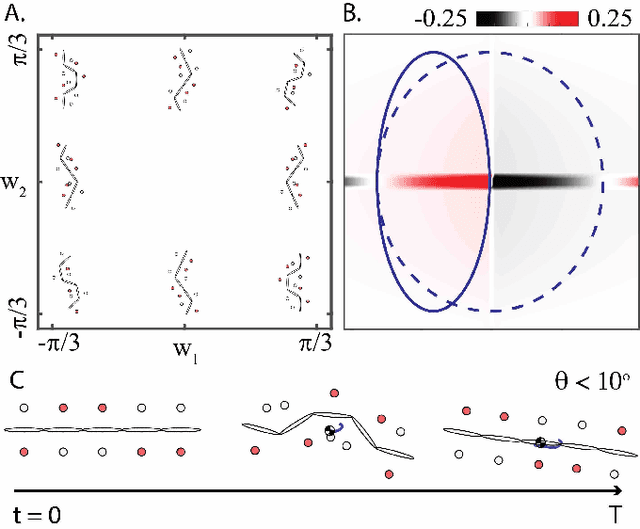
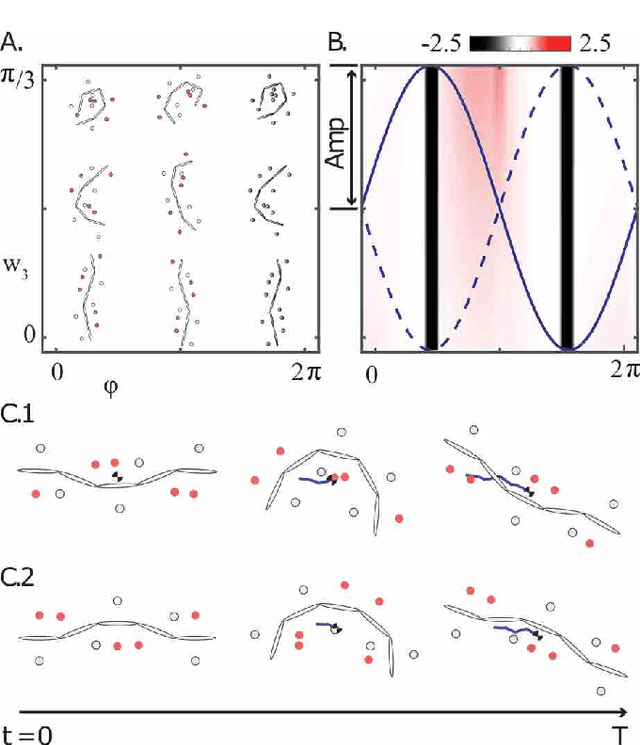
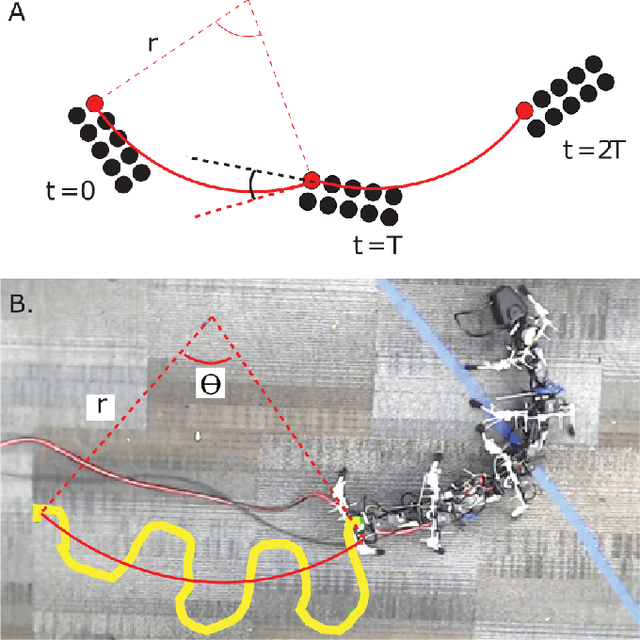
Abstract:Centipedes exhibit great maneuverability in diverse environments due to their many legs and body-driven control. By leveraging similar morphologies, their robotic counterparts also demonstrate effective terrestrial locomotion. However, the success of these multi-legged robots is largely limited to forward locomotion; steering is substantially less studied, in part due to the challenges in coordinating their many body joints. Furthermore, steering behavior is complex and can include different combinations of desired rotational/translational displacement. In this paper, we explore steering strategies in multi-legged robots based on tools derived from geometric mechanics (GM). We characterize the steering motion in the plane by the rotation angle, the steering radius, and the heading direction angle. We identify an effective turning strategy by superimposing two traveling waves in the lateral body undulation and further explore variations of the "turning wave" to enable a broad spectrum of steering behaviors. By combining an amplitude modulation and a phase modulation, we develop a control strategy for steering behaviors that enables steering with a range of rotation angles (from 0{\deg} to 20{\deg}) and steering radius (from 0.28 to 0.38 body length) while keeping the heading direction angle close to 0. Lastly, we test our control framework on an elongate multi-legged robot model to verify the effectiveness of our proposed strategy. Our work demonstrates the generality of the two-wave template for effective steering of multi-legged elongate robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge