Elyas Sabeti
Data Discovery Using Lossless Compression-Based Sparse Representation
Mar 17, 2021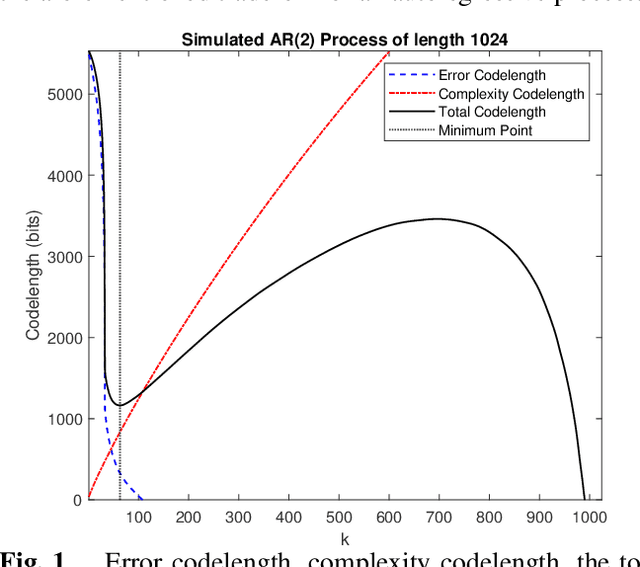
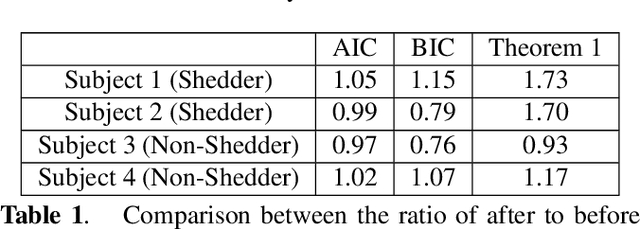
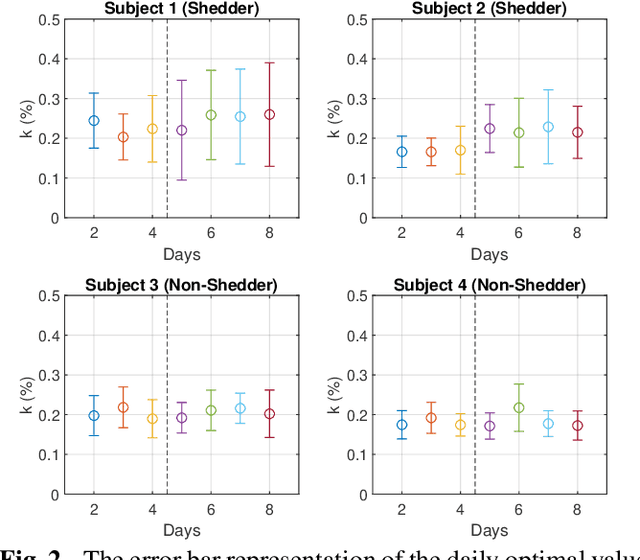
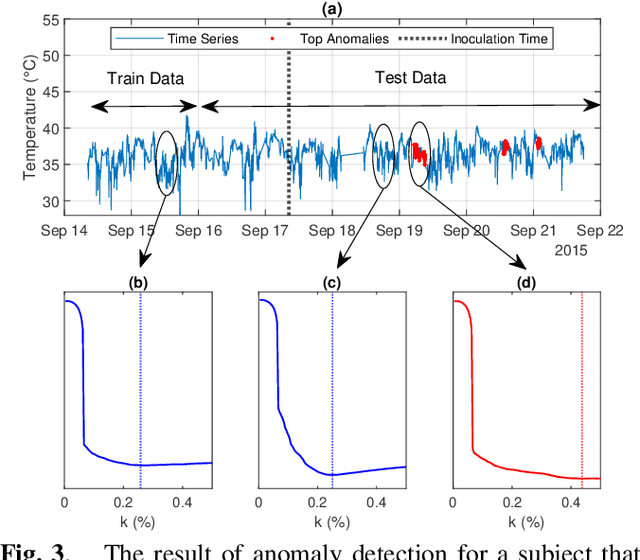
Abstract:Sparse representation has been widely used in data compression, signal and image denoising, dimensionality reduction and computer vision. While overcomplete dictionaries are required for sparse representation of multidimensional data, orthogonal bases represent one-dimensional data well. In this paper, we propose a data-driven sparse representation using orthonormal bases under the lossless compression constraint. We show that imposing such constraint under the Minimum Description Length (MDL) principle leads to a unique and optimal sparse representation for one-dimensional data, which results in discriminative features useful for data discovery.
Multiple Abnormality Detection for Automatic Medical Image Diagnosis Using Bifurcated Convolutional Neural Network
Oct 15, 2018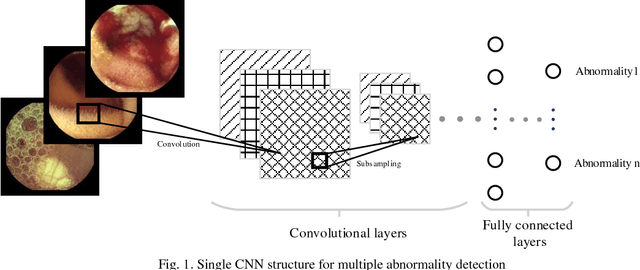
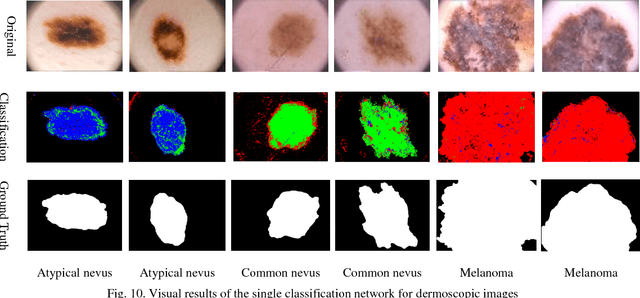
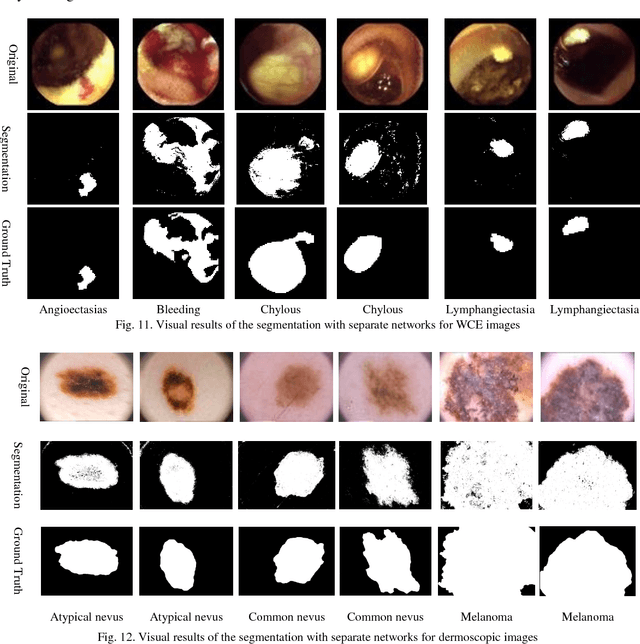
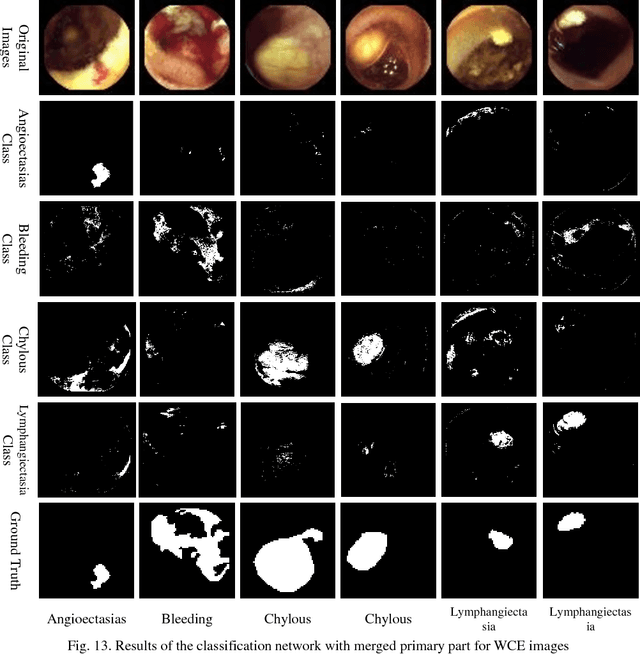
Abstract:Automating classification and segmentation process of abnormal regions in different body organs has a crucial role in most of medical imaging applications such as funduscopy, endoscopy, and dermoscopy. Detecting multiple abnormalities in each type of images is necessary for better and more accurate diagnosis procedure and medical decisions. In recent years portable medical imaging devices such as capsule endoscopy and digital dermatoscope have been introduced and made the diagnosis procedure easier and more efficient. However, these portable devices have constrained power resources and limited computational capability. To address this problem, we propose a bifurcated structure for convolutional neural networks performing both classification and segmentation of multiple abnormalities simultaneously. The proposed network is first trained by each abnormality separately. Then the network is trained using all abnormalities. In order to reduce the computational complexity, the network is redesigned to share some features which are common among all abnormalities. Later, these shared features are used in different settings (directions) to segment and classify the abnormal region of the image. Finally, results of the classification and segmentation directions are fused to obtain the classified segmentation map. Proposed framework is simulated using four frequent gastrointestinal abnormalities as well as three dermoscopic lesions and for evaluation of the proposed framework the results are compared with the corresponding ground truth map. Properties of the bifurcated network like low complexity and resource sharing make it suitable to be implemented as a part of portable medical imaging devices.
Atypicality for Heart Rate Variability Using a Pattern-Tree Weighting Method
Oct 12, 2017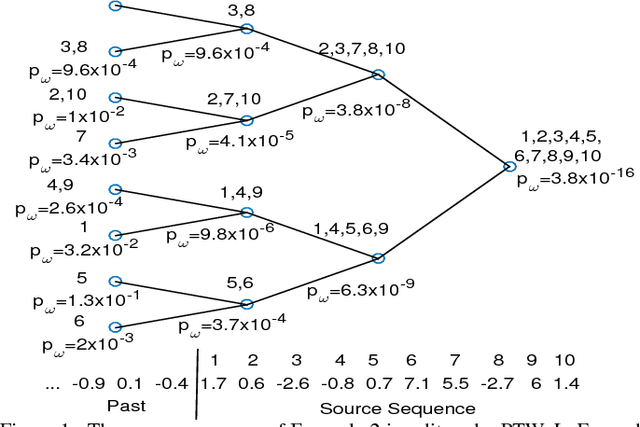
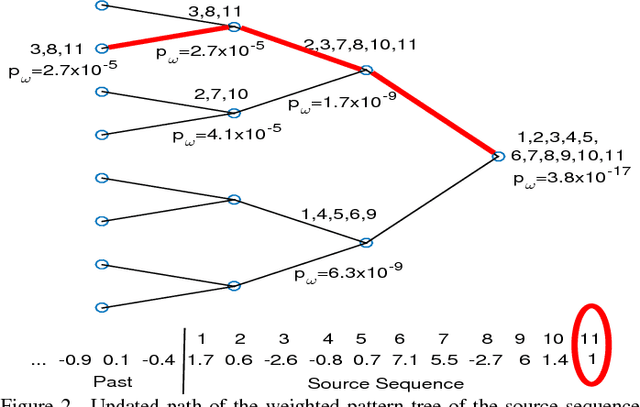
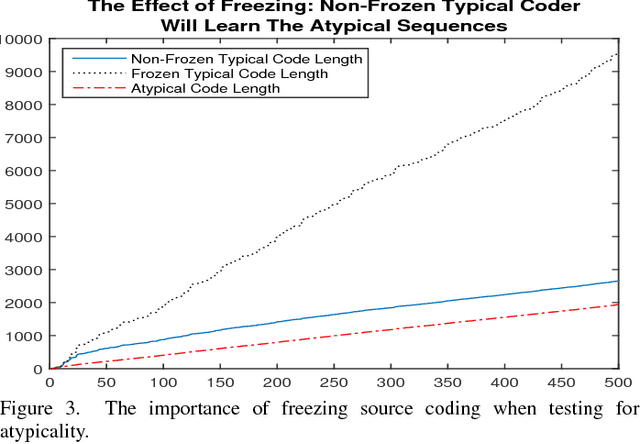
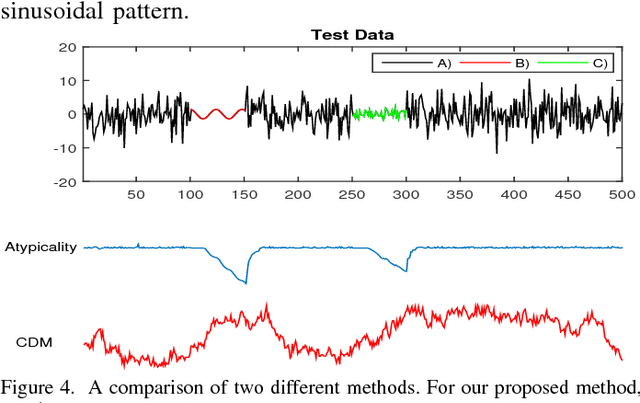
Abstract:Heart rate variability (HRV) is a vital measure of the autonomic nervous system functionality and a key indicator of cardiovascular condition. This paper proposes a novel method, called pattern tree which is an extension of Willem's context tree to real-valued data, to investigate HRV via an atypicality framework. In a previous paper atypicality was developed as method for mining and discovery in "Big Data," which requires a universal approach. Using the proposed pattern tree as a universal source coder in this framework led to discovery of arrhythmias and unknown patterns in HRV Holter Monitoring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge