Elena Volodina
University of Gothenburg
Grandma Karl is 27 years old -- research agenda for pseudonymization of research data
Aug 30, 2023

Abstract:Accessibility of research data is critical for advances in many research fields, but textual data often cannot be shared due to the personal and sensitive information which it contains, e.g names or political opinions. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) suggests pseudonymization as a solution to secure open access to research data, but we need to learn more about pseudonymization as an approach before adopting it for manipulation of research data. This paper outlines a research agenda within pseudonymization, namely need of studies into the effects of pseudonymization on unstructured data in relation to e.g. readability and language assessment, as well as the effectiveness of pseudonymization as a way of protecting writer identity, while also exploring different ways of developing context-sensitive algorithms for detection, labelling and replacement of personal information in unstructured data. The recently granted project on pseudonymization Grandma Karl is 27 years old addresses exactly those challenges.
Crowdsourcing Relative Rankings of Multi-Word Expressions: Experts versus Non-Experts
Jun 17, 2022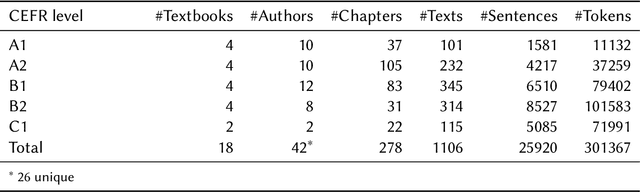
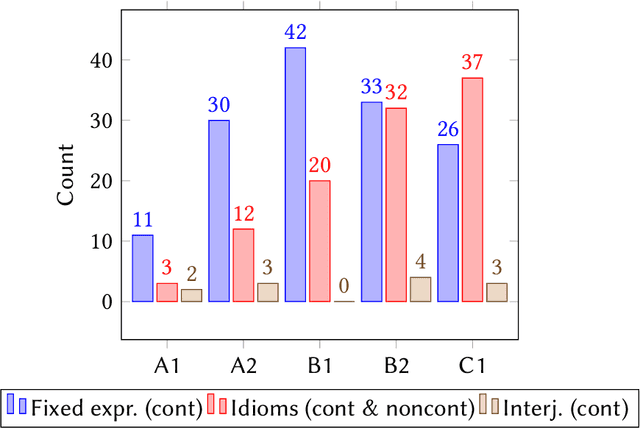
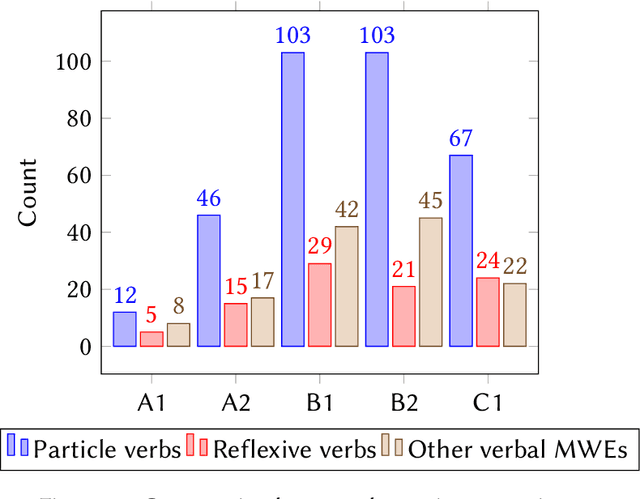
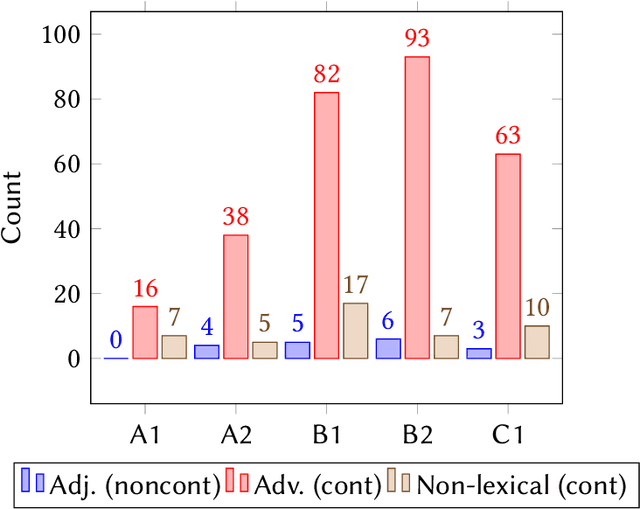
Abstract:In this study we investigate to which degree experts and non-experts agree on questions of difficulty in a crowdsourcing experiment. We ask non-experts (second language learners of Swedish) and two groups of experts (teachers of Swedish as a second/foreign language and CEFR experts) to rank multi-word expressions in a crowdsourcing experiment. We find that the resulting rankings by all the three tested groups correlate to a very high degree, which suggests that judgments produced in a comparative setting are not influenced by professional insights into Swedish as a second language.
DaLAJ - a dataset for linguistic acceptability judgments for Swedish: Format, baseline, sharing
May 14, 2021


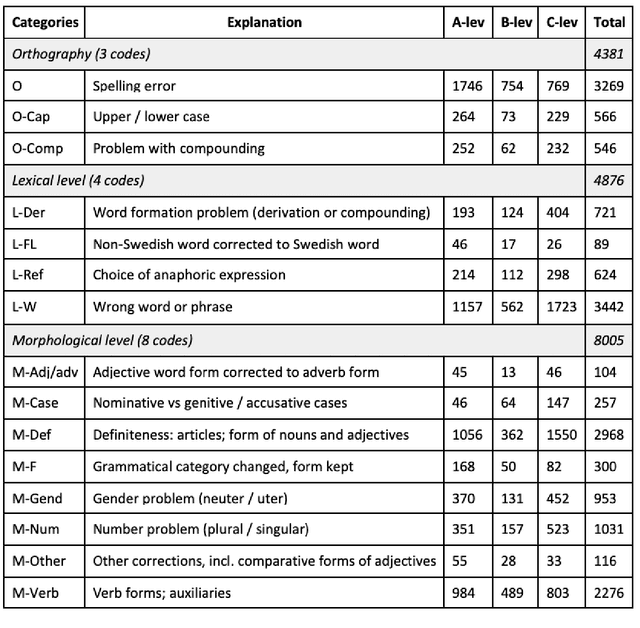
Abstract:We present DaLAJ 1.0, a Dataset for Linguistic Acceptability Judgments for Swedish, comprising 9 596 sentences in its first version; and the initial experiment using it for the binary classification task. DaLAJ is based on the SweLL second language learner data, consisting of essays at different levels of proficiency. To make sure the dataset can be freely available despite the GDPR regulations, we have sentence-scrambled learner essays and removed part of the metadata about learners, keeping for each sentence only information about the mother tongue and the level of the course where the essay has been written. We use the normalized version of learner language as the basis for the DaLAJ sentences, and keep only one error per sentence. We repeat the same sentence for each individual correction tag used in the sentence. For DaLAJ 1.0 we have used four error categories (out of 35 available in SweLL), all connected to lexical or word-building choices. Our baseline results for the binary classification show an accuracy of 58% for DaLAJ 1.0 using BERT embeddings. The dataset is included in the SwedishGlue (Swe. SuperLim) benchmark. Below, we describe the format of the dataset, first experiments, our insights and the motivation for the chosen approach to data sharing.
Candidate sentence selection for language learning exercises: from a comprehensive framework to an empirical evaluation
Jun 12, 2017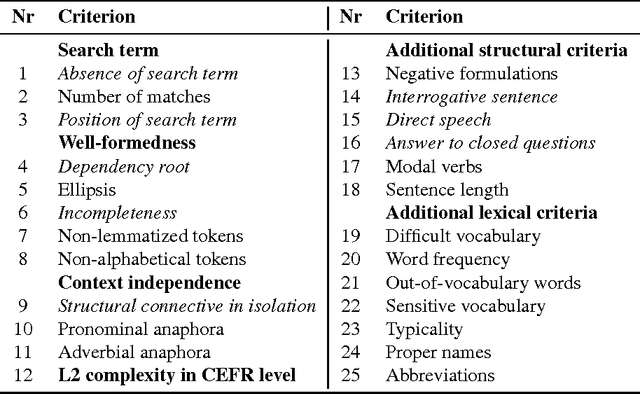
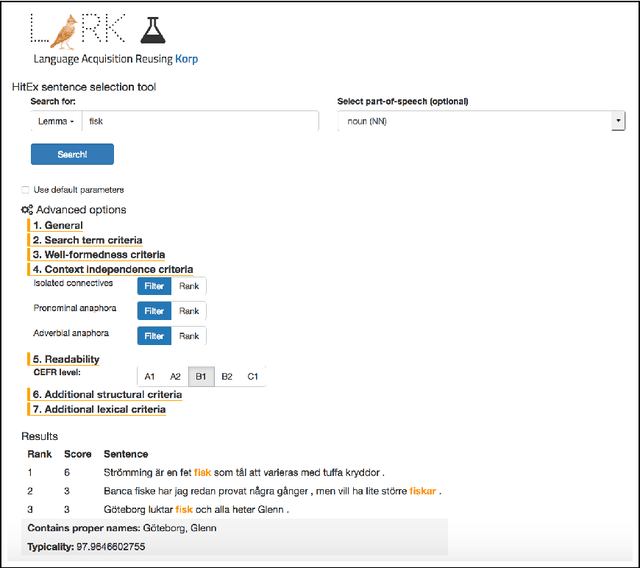
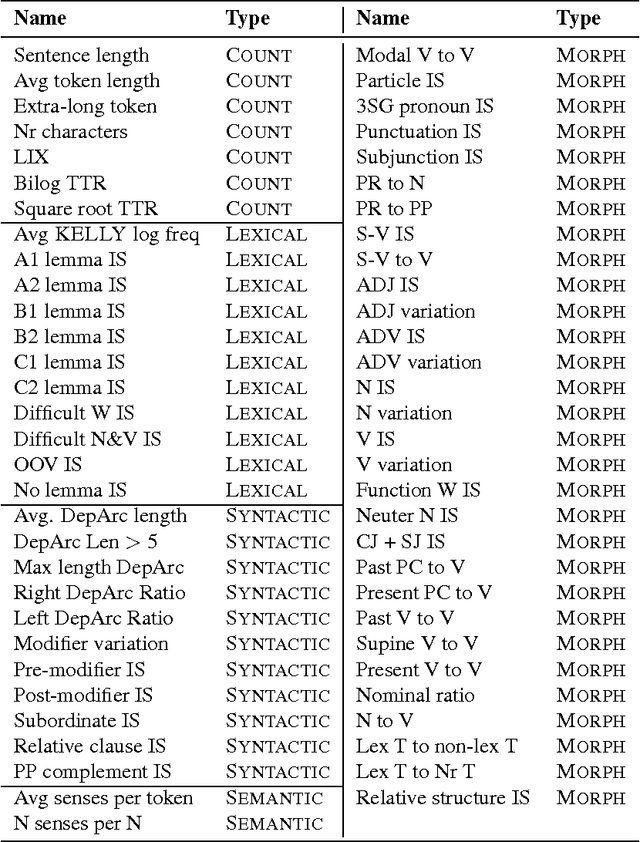
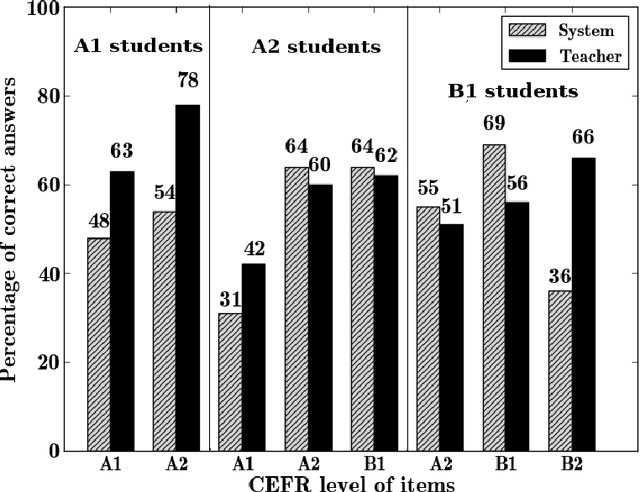
Abstract:We present a framework and its implementation relying on Natural Language Processing methods, which aims at the identification of exercise item candidates from corpora. The hybrid system combining heuristics and machine learning methods includes a number of relevant selection criteria. We focus on two fundamental aspects: linguistic complexity and the dependence of the extracted sentences on their original context. Previous work on exercise generation addressed these two criteria only to a limited extent, and a refined overall candidate sentence selection framework appears also to be lacking. In addition to a detailed description of the system, we present the results of an empirical evaluation conducted with language teachers and learners which indicate the usefulness of the system for educational purposes. We have integrated our system into a freely available online learning platform.
SweLL on the rise: Swedish Learner Language corpus for European Reference Level studies
Apr 22, 2016


Abstract:We present a new resource for Swedish, SweLL, a corpus of Swedish Learner essays linked to learners' performance according to the Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR). SweLL consists of three subcorpora - SpIn, SW1203 and Tisus, collected from three different educational establishments. The common metadata for all subcorpora includes age, gender, native languages, time of residence in Sweden, type of written task. Depending on the subcorpus, learner texts may contain additional information, such as text genres, topics, grades. Five of the six CEFR levels are represented in the corpus: A1, A2, B1, B2 and C1 comprising in total 339 essays. C2 level is not included since courses at C2 level are not offered. The work flow consists of collection of essays and permits, essay digitization and registration, meta-data annotation, automatic linguistic annotation. Inter-rater agreement is presented on the basis of SW1203 subcorpus. The work on SweLL is still ongoing with more than 100 essays waiting in the pipeline. This article both describes the resource and the "how-to" behind the compilation of SweLL.
A Readable Read: Automatic Assessment of Language Learning Materials based on Linguistic Complexity
Mar 29, 2016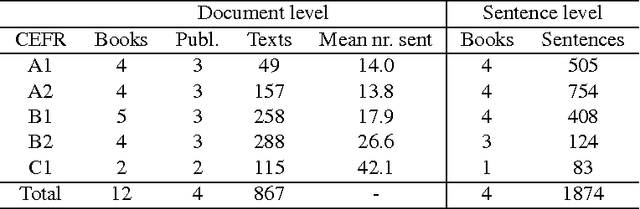
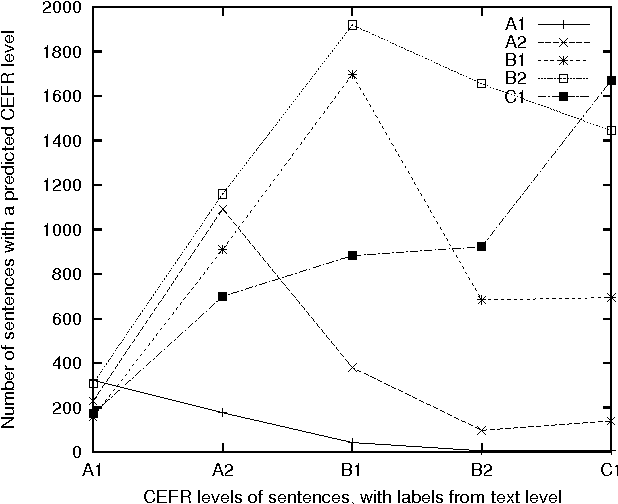
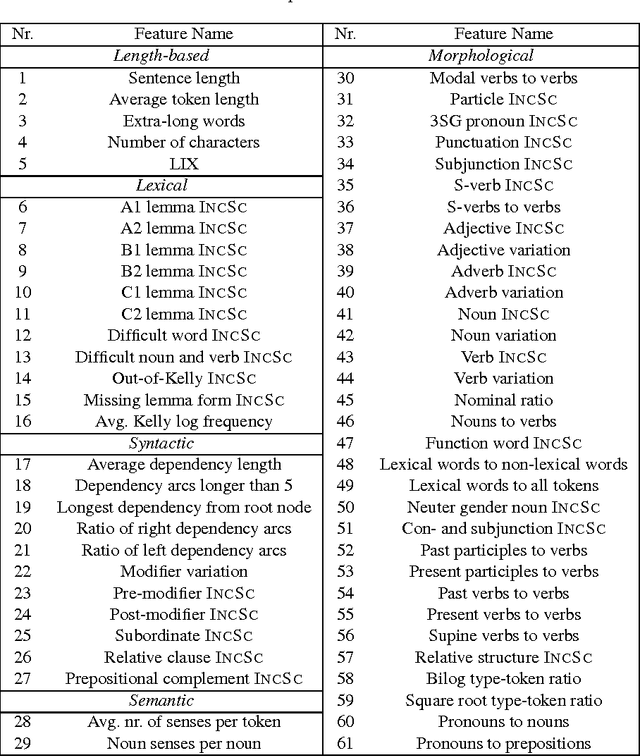
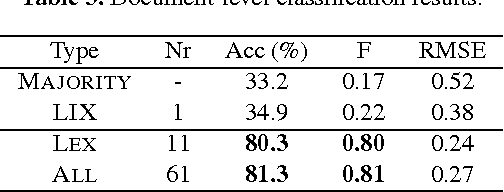
Abstract:Corpora and web texts can become a rich language learning resource if we have a means of assessing whether they are linguistically appropriate for learners at a given proficiency level. In this paper, we aim at addressing this issue by presenting the first approach for predicting linguistic complexity for Swedish second language learning material on a 5-point scale. After showing that the traditional Swedish readability measure, L\"asbarhetsindex (LIX), is not suitable for this task, we propose a supervised machine learning model, based on a range of linguistic features, that can reliably classify texts according to their difficulty level. Our model obtained an accuracy of 81.3% and an F-score of 0.8, which is comparable to the state of the art in English and is considerably higher than previously reported results for other languages. We further studied the utility of our features with single sentences instead of full texts since sentences are a common linguistic unit in language learning exercises. We trained a separate model on sentence-level data with five classes, which yielded 63.4% accuracy. Although this is lower than the document level performance, we achieved an adjacent accuracy of 92%. Furthermore, we found that using a combination of different features, compared to using lexical features alone, resulted in 7% improvement in classification accuracy at the sentence level, whereas at the document level, lexical features were more dominant. Our models are intended for use in a freely accessible web-based language learning platform for the automatic generation of exercises.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge