Eivind Meyer
Deep Occupancy-Predictive Representations for Autonomous Driving
Mar 07, 2023Abstract:Manually specifying features that capture the diversity in traffic environments is impractical. Consequently, learning-based agents cannot realize their full potential as neural motion planners for autonomous vehicles. Instead, this work proposes to learn which features are task-relevant. Given its immediate relevance to motion planning, our proposed architecture encodes the probabilistic occupancy map as a proxy for obtaining pre-trained state representations. By leveraging a map-aware graph formulation of the environment, our agent-centric encoder generalizes to arbitrary road networks and traffic situations. We show that our approach significantly improves the downstream performance of a reinforcement learning agent operating in urban traffic environments.
Geometric Deep Learning for Autonomous Driving: Unlocking the Power of Graph Neural Networks With CommonRoad-Geometric
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:Heterogeneous graphs offer powerful data representations for traffic, given their ability to model the complex interaction effects among a varying number of traffic participants and the underlying road infrastructure. With the recent advent of graph neural networks (GNNs) as the accompanying deep learning framework, the graph structure can be efficiently leveraged for various machine learning applications such as trajectory prediction. As a first of its kind, our proposed Python framework offers an easy-to-use and fully customizable data processing pipeline to extract standardized graph datasets from traffic scenarios. Providing a platform for GNN-based autonomous driving research, it improves comparability between approaches and allows researchers to focus on model implementation instead of dataset curation.
Risk-based implementation of COLREGs for autonomous surface vehicles using deep reinforcement learning
Nov 30, 2021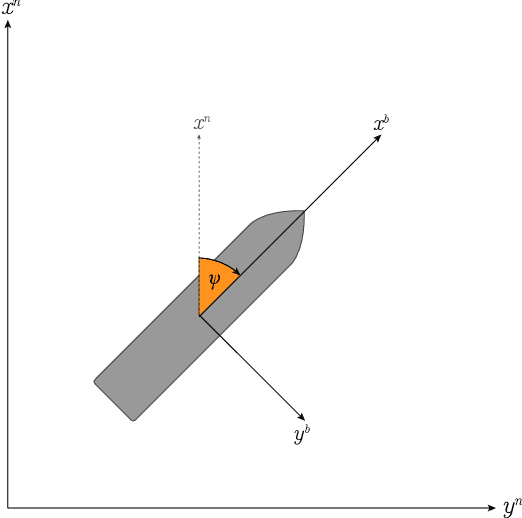


Abstract:Autonomous systems are becoming ubiquitous and gaining momentum within the marine sector. Since the electrification of transport is happening simultaneously, autonomous marine vessels can reduce environmental impact, lower costs, and increase efficiency. Although close monitoring is still required to ensure safety, the ultimate goal is full autonomy. One major milestone is to develop a control system that is versatile enough to handle any weather and encounter that is also robust and reliable. Additionally, the control system must adhere to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs) for successful interaction with human sailors. Since the COLREGs were written for the human mind to interpret, they are written in ambiguous prose and therefore not machine-readable or verifiable. Due to these challenges and the wide variety of situations to be tackled, classical model-based approaches prove complicated to implement and computationally heavy. Within machine learning (ML), deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown great potential for a wide range of applications. The model-free and self-learning properties of DRL make it a promising candidate for autonomous vessels. In this work, a subset of the COLREGs is incorporated into a DRL-based path following and obstacle avoidance system using collision risk theory. The resulting autonomous agent dynamically interpolates between path following and COLREG-compliant collision avoidance in the training scenario, isolated encounter situations, and AIS-based simulations of real-world scenarios.
COLREG-Compliant Collision Avoidance for Unmanned Surface Vehicle using Deep Reinforcement Learning
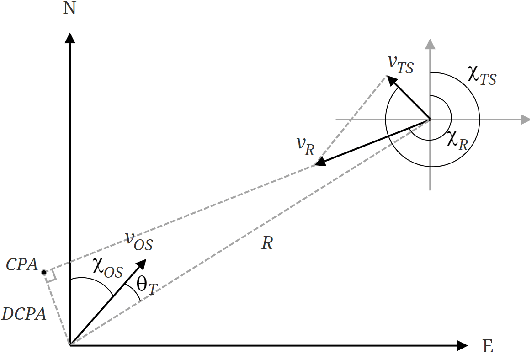
Jun 16, 2020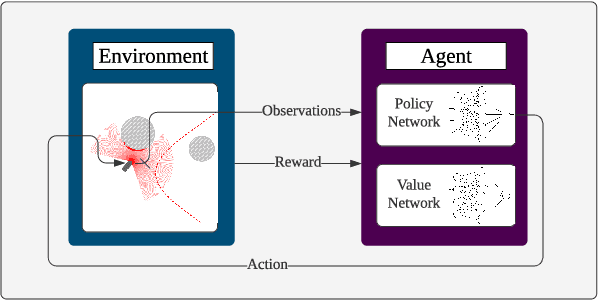
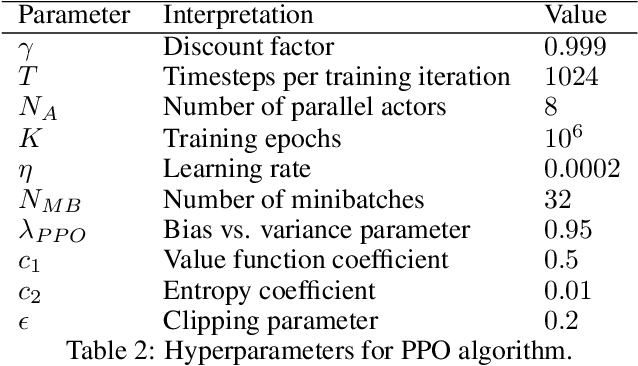

Abstract:Path Following and Collision Avoidance, be it for unmanned surface vessels or other autonomous vehicles, are two fundamental guidance problems in robotics. For many decades, they have been subject to academic study, leading to a vast number of proposed approaches. However, they have mostly been treated as separate problems, and have typically relied on non-linear first-principles models with parameters that can only be determined experimentally. The rise of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) in recent years suggests an alternative approach: end-to-end learning of the optimal guidance policy from scratch by means of a trial-and-error based approach. In this article, we explore the potential of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), a DRL algorithm with demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on Continuous Control tasks, when applied to the dual-objective problem of controlling an underactuated Autonomous Surface Vehicle in a COLREGs compliant manner such that it follows an a priori known desired path while avoiding collisions with other vessels along the way. Based on high-fidelity elevation and AIS tracking data from the Trondheim Fjord, an inlet of the Norwegian sea, we evaluate the trained agent's performance in challenging, dynamic real-world scenarios where the ultimate success of the agent rests upon its ability to navigate non-uniform marine terrain while handling challenging, but realistic vessel encounters.
Taming an autonomous surface vehicle for path following and collision avoidance using deep reinforcement learning
Dec 18, 2019



Abstract:In this article, we explore the feasibility of applying proximal policy optimization, a state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning algorithm for continuous control tasks, on the dual-objective problem of controlling an underactuated autonomous surface vehicle to follow an a priori known path while avoiding collisions with non-moving obstacles along the way. The artificial intelligent agent, which is equipped with multiple rangefinder sensors for obstacle detection, is trained and evaluated in a challenging, stochastically generated simulation environment based on the OpenAI gym python toolkit. Notably, the agent is provided with real-time insight into its own reward function, allowing it to dynamically adapt its guidance strategy. Depending on its strategy, which ranges from radical path-adherence to radical obstacle avoidance, the trained agent achieves an episodic success rate between 84 and 100%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge