Damiano Varagnolo
CasTGAN: Cascaded Generative Adversarial Network for Realistic Tabular Data Synthesis
Jul 01, 2023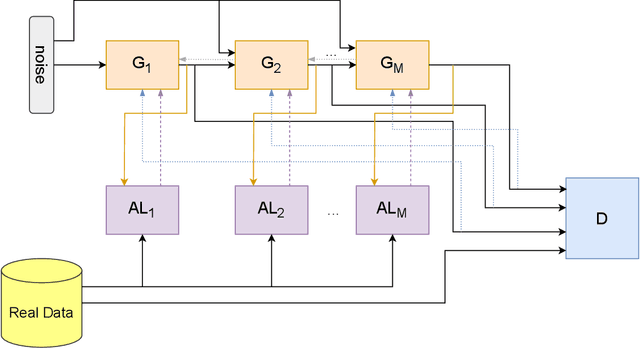
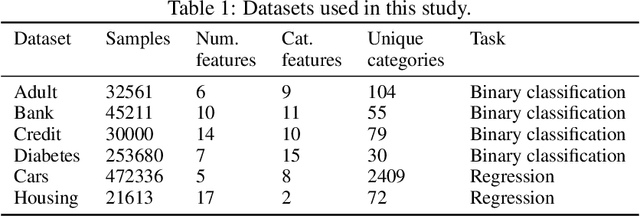
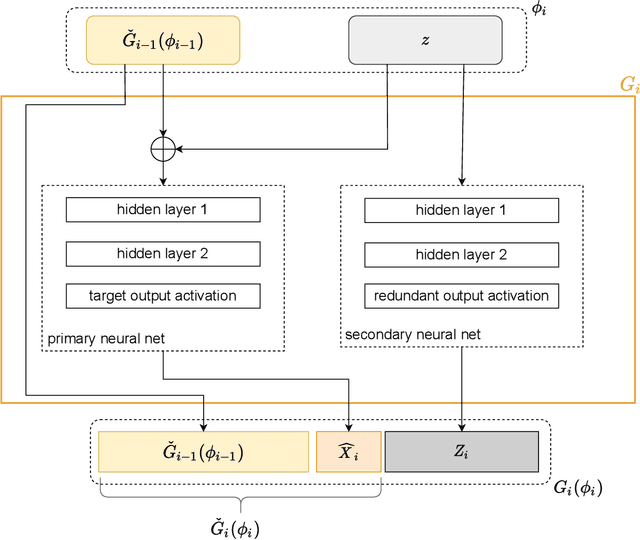
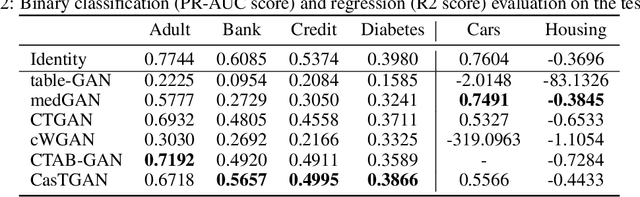
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have drawn considerable attention in recent years for their proven capability in generating synthetic data which can be utilized for multiple purposes. While GANs have demonstrated tremendous successes in producing synthetic data samples that replicate the dynamics of the original datasets, the validity of the synthetic data and the underlying privacy concerns represent major challenges which are not sufficiently addressed. In this work, we design a cascaded tabular GAN framework (CasTGAN) for generating realistic tabular data with a specific focus on the validity of the output. In this context, validity refers to the the dependency between features that can be found in the real data, but is typically misrepresented by traditional generative models. Our key idea entails that employing a cascaded architecture in which a dedicated generator samples each feature, the synthetic output becomes more representative of the real data. Our experimental results demonstrate that our model well captures the constraints and the correlations between the features of the real data, especially the high dimensional datasets. Furthermore, we evaluate the risk of white-box privacy attacks on our model and subsequently show that applying some perturbations to the auxiliary learners in CasTGAN increases the overall robustness of our model against targeted attacks.
Risk-based implementation of COLREGs for autonomous surface vehicles using deep reinforcement learning
Nov 30, 2021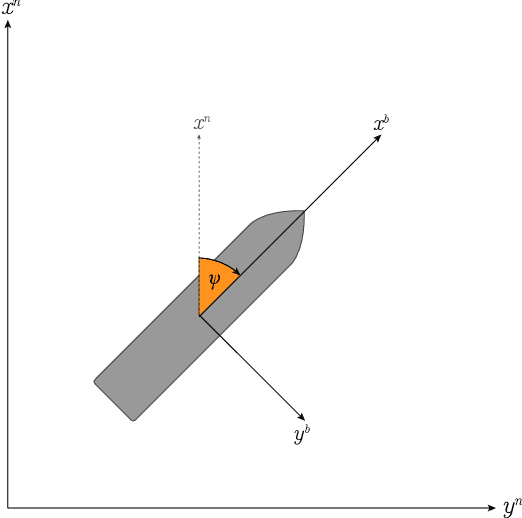

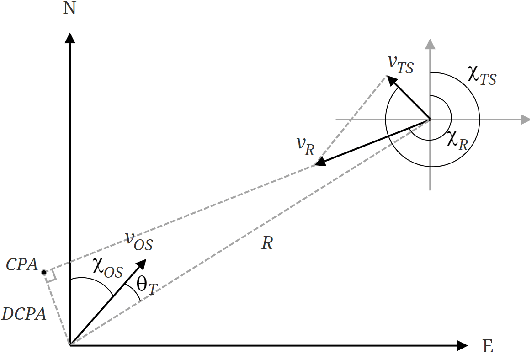

Abstract:Autonomous systems are becoming ubiquitous and gaining momentum within the marine sector. Since the electrification of transport is happening simultaneously, autonomous marine vessels can reduce environmental impact, lower costs, and increase efficiency. Although close monitoring is still required to ensure safety, the ultimate goal is full autonomy. One major milestone is to develop a control system that is versatile enough to handle any weather and encounter that is also robust and reliable. Additionally, the control system must adhere to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs) for successful interaction with human sailors. Since the COLREGs were written for the human mind to interpret, they are written in ambiguous prose and therefore not machine-readable or verifiable. Due to these challenges and the wide variety of situations to be tackled, classical model-based approaches prove complicated to implement and computationally heavy. Within machine learning (ML), deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown great potential for a wide range of applications. The model-free and self-learning properties of DRL make it a promising candidate for autonomous vessels. In this work, a subset of the COLREGs is incorporated into a DRL-based path following and obstacle avoidance system using collision risk theory. The resulting autonomous agent dynamically interpolates between path following and COLREG-compliant collision avoidance in the training scenario, isolated encounter situations, and AIS-based simulations of real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge