Eike Rehder
3DMOTFormer: Graph Transformer for Online 3D Multi-Object Tracking
Aug 12, 2023Abstract:Tracking 3D objects accurately and consistently is crucial for autonomous vehicles, enabling more reliable downstream tasks such as trajectory prediction and motion planning. Based on the substantial progress in object detection in recent years, the tracking-by-detection paradigm has become a popular choice due to its simplicity and efficiency. State-of-the-art 3D multi-object tracking (MOT) approaches typically rely on non-learned model-based algorithms such as Kalman Filter but require many manually tuned parameters. On the other hand, learning-based approaches face the problem of adapting the training to the online setting, leading to inevitable distribution mismatch between training and inference as well as suboptimal performance. In this work, we propose 3DMOTFormer, a learned geometry-based 3D MOT framework building upon the transformer architecture. We use an Edge-Augmented Graph Transformer to reason on the track-detection bipartite graph frame-by-frame and conduct data association via edge classification. To reduce the distribution mismatch between training and inference, we propose a novel online training strategy with an autoregressive and recurrent forward pass as well as sequential batch optimization. Using CenterPoint detections, our approach achieves 71.2% and 68.2% AMOTA on the nuScenes validation and test split, respectively. In addition, a trained 3DMOTFormer model generalizes well across different object detectors. Code is available at: https://github.com/dsx0511/3DMOTFormer.
Cooperative Motion Planning for Non-Holonomic Agents with Value Iteration Networks
Sep 15, 2017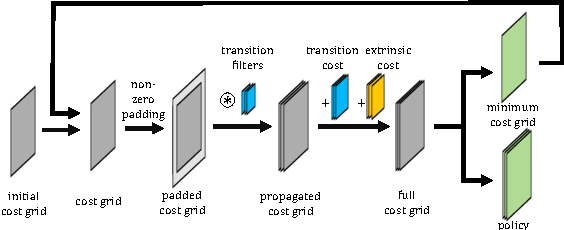
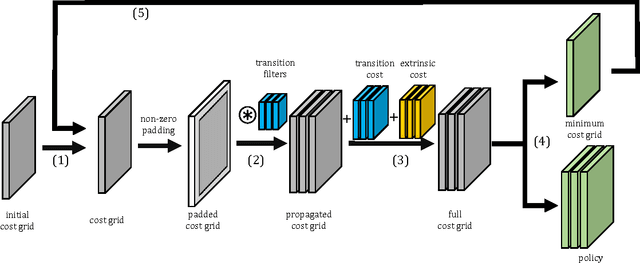
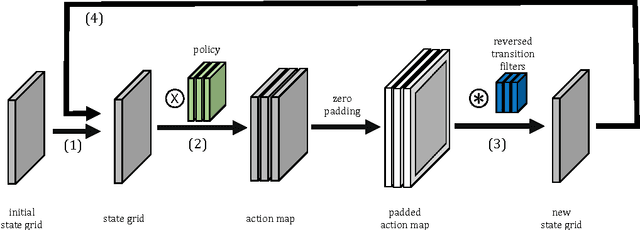
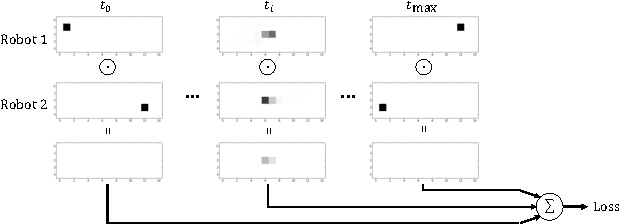
Abstract:Cooperative motion planning is still a challenging task for robots. Recently, Value Iteration Networks (VINs) were proposed to model motion planning tasks as Neural Networks. In this work, we extend VINs to solve cooperative planning tasks under non-holonomic constraints. For this, we interconnect multiple VINs to pay respect to each other's outputs. Policies for cooperation are generated via iterative gradient descend. Validation in simulation shows that the resulting networks can resolve non-holonomic motion planning problems that require cooperation.
Pedestrian Prediction by Planning using Deep Neural Networks
Jun 20, 2017



Abstract:Accurate traffic participant prediction is the prerequisite for collision avoidance of autonomous vehicles. In this work, we predict pedestrians by emulating their own motion planning. From online observations, we infer a mixture density function for possible destinations. We use this result as the goal states of a planning stage that performs motion prediction based on common behavior patterns. The entire system is modeled as one monolithic neural network and trained via inverse reinforcement learning. Experimental validation on real world data shows the system's ability to predict both, destinations and trajectories accurately.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge