Cooperative Motion Planning for Non-Holonomic Agents with Value Iteration Networks
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2017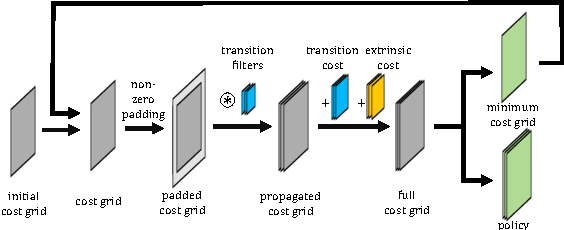
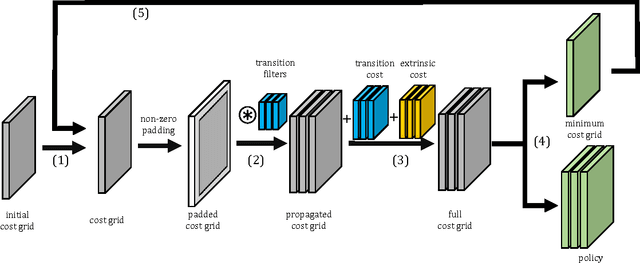
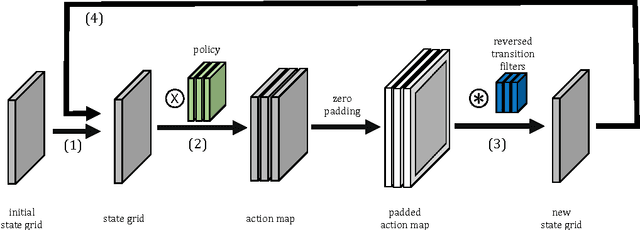
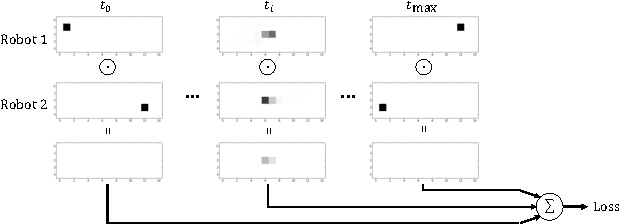
Cooperative motion planning is still a challenging task for robots. Recently, Value Iteration Networks (VINs) were proposed to model motion planning tasks as Neural Networks. In this work, we extend VINs to solve cooperative planning tasks under non-holonomic constraints. For this, we interconnect multiple VINs to pay respect to each other's outputs. Policies for cooperation are generated via iterative gradient descend. Validation in simulation shows that the resulting networks can resolve non-holonomic motion planning problems that require cooperation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge