Dustin Klebe
GeRA: Label-Efficient Geometrically Regularized Alignment
Oct 07, 2023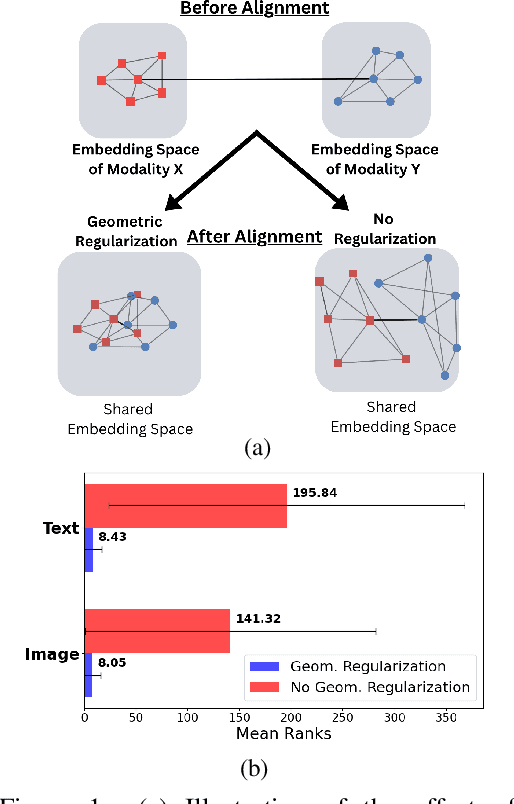
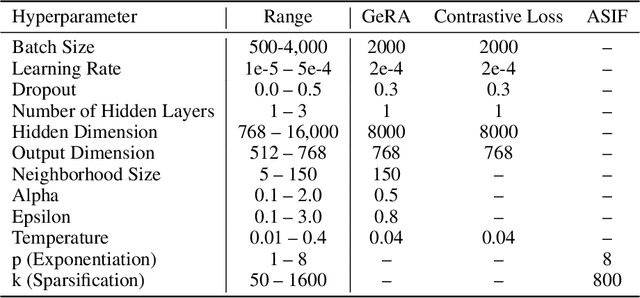
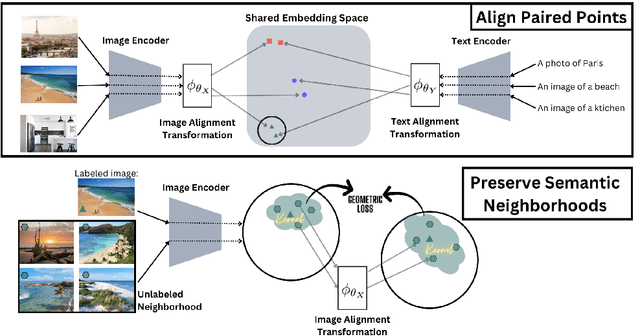
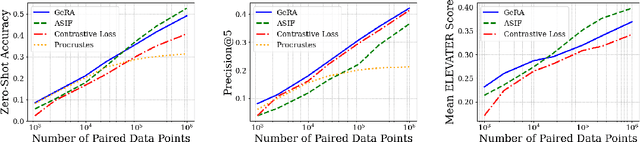
Abstract:Pretrained unimodal encoders incorporate rich semantic information into embedding space structures. To be similarly informative, multi-modal encoders typically require massive amounts of paired data for alignment and training. We introduce a semi-supervised Geometrically Regularized Alignment (GeRA) method to align the embedding spaces of pretrained unimodal encoders in a label-efficient way. Our method leverages the manifold geometry of unpaired (unlabeled) data to improve alignment performance. To prevent distortions to local geometry during the alignment process, potentially disrupting semantic neighborhood structures and causing misalignment of unobserved pairs, we introduce a geometric loss term. This term is built upon a diffusion operator that captures the local manifold geometry of the unimodal pretrained encoders. GeRA is modality-agnostic and thus can be used to align pretrained encoders from any data modalities. We provide empirical evidence to the effectiveness of our method in the domains of speech-text and image-text alignment. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvement in alignment quality compared to a variaty of leading baselines, especially with a small amount of paired data, using our proposed geometric regularization.
A Deep Learning Approach for the Segmentation of Electroencephalography Data in Eye Tracking Applications
Jun 17, 2022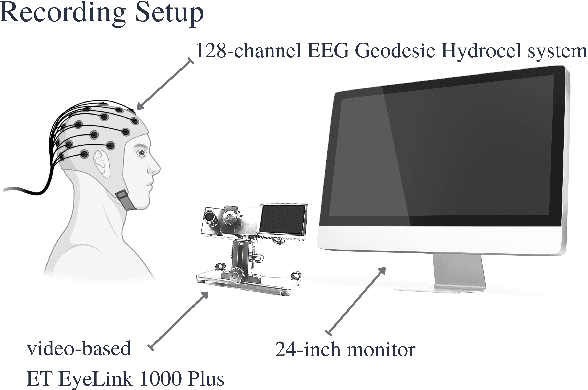
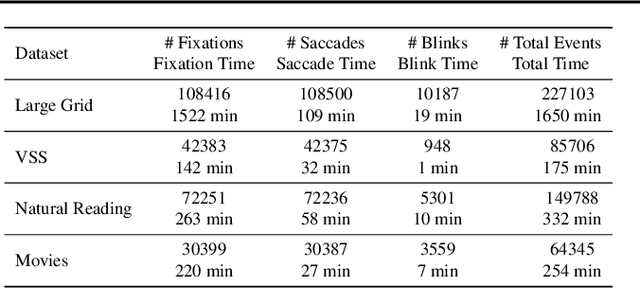
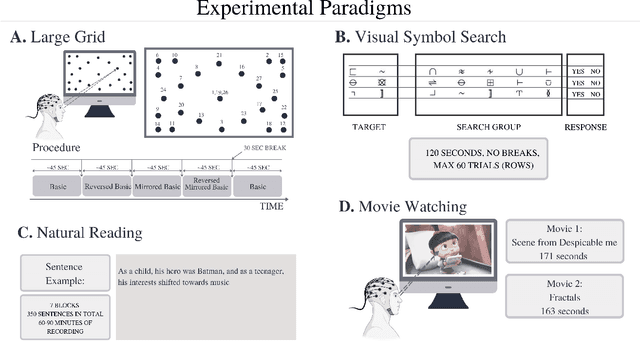
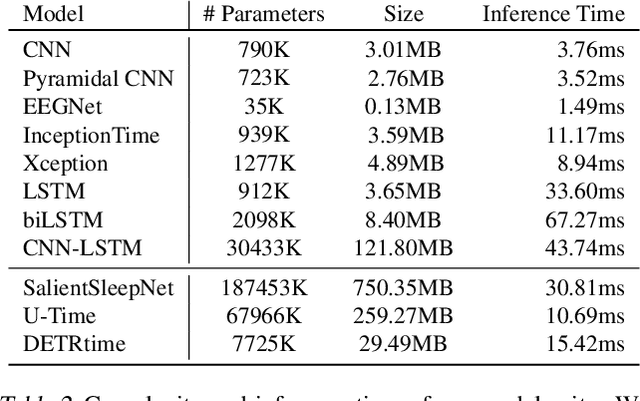
Abstract:The collection of eye gaze information provides a window into many critical aspects of human cognition, health and behaviour. Additionally, many neuroscientific studies complement the behavioural information gained from eye tracking with the high temporal resolution and neurophysiological markers provided by electroencephalography (EEG). One of the essential eye-tracking software processing steps is the segmentation of the continuous data stream into events relevant to eye-tracking applications, such as saccades, fixations, and blinks. Here, we introduce DETRtime, a novel framework for time-series segmentation that creates ocular event detectors that do not require additionally recorded eye-tracking modality and rely solely on EEG data. Our end-to-end deep learning-based framework brings recent advances in Computer Vision to the forefront of the times series segmentation of EEG data. DETRtime achieves state-of-the-art performance in ocular event detection across diverse eye-tracking experiment paradigms. In addition to that, we provide evidence that our model generalizes well in the task of EEG sleep stage segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge