Dongshuo Yin
DAPE: Dual-Stage Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Consistent Video Editing with Diffusion Models
May 11, 2025Abstract:Video generation based on diffusion models presents a challenging multimodal task, with video editing emerging as a pivotal direction in this field. Recent video editing approaches primarily fall into two categories: training-required and training-free methods. While training-based methods incur high computational costs, training-free alternatives often yield suboptimal performance. To address these limitations, we propose DAPE, a high-quality yet cost-effective two-stage parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) framework for video editing. In the first stage, we design an efficient norm-tuning method to enhance temporal consistency in generated videos. The second stage introduces a vision-friendly adapter to improve visual quality. Additionally, we identify critical shortcomings in existing benchmarks, including limited category diversity, imbalanced object distribution, and inconsistent frame counts. To mitigate these issues, we curate a large dataset benchmark comprising 232 videos with rich annotations and 6 editing prompts, enabling objective and comprehensive evaluation of advanced methods. Extensive experiments on existing datasets (BalanceCC, LOVEU-TGVE, RAVE) and our proposed benchmark demonstrate that DAPE significantly improves temporal coherence and text-video alignment while outperforming previous state-of-the-art approaches.
5%>100%: Breaking Performance Shackles of Full Fine-Tuning on Visual Recognition Tasks
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:Pre-training & fine-tuning can enhance the transferring efficiency and performance in visual tasks. Recent delta-tuning methods provide more options for visual classification tasks. Despite their success, existing visual delta-tuning art fails to exceed the upper limit of full fine-tuning on challenging tasks like object detection and segmentation. To find a competitive alternative to full fine-tuning, we propose the Multi-cognitive Visual Adapter (Mona) tuning, a novel adapter-based tuning method. First, we introduce multiple vision-friendly filters into the adapter to enhance its ability to process visual signals, while previous methods mainly rely on language-friendly linear filters. Second, we add the scaled normalization layer in the adapter to regulate the distribution of input features for visual filters. To fully demonstrate the practicality and generality of Mona, we conduct experiments on multiple representative visual tasks, including instance segmentation on COCO, semantic segmentation on ADE20K, object detection on Pascal VOC, oriented object detection on DOTA/STAR, and image classification on three common datasets. Exciting results illustrate that Mona surpasses full fine-tuning on all these tasks, and is the only delta-tuning method outperforming full fine-tuning on the above various tasks. For example, Mona achieves 1% performance gain on the COCO dataset compared to full fine-tuning. Comprehensive results suggest that Mona-tuning is more suitable for retaining and utilizing the capabilities of pre-trained models than full fine-tuning. We will make the code publicly available.
Adapter is All You Need for Tuning Visual Tasks
Nov 30, 2023
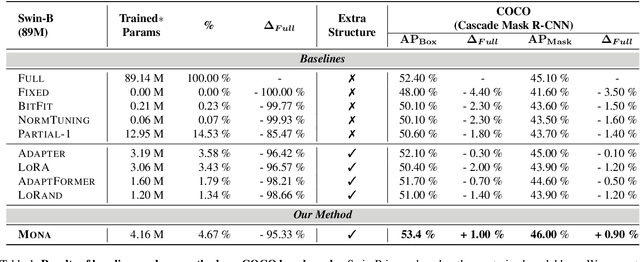
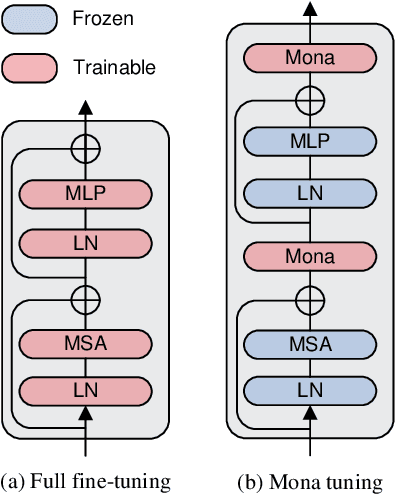
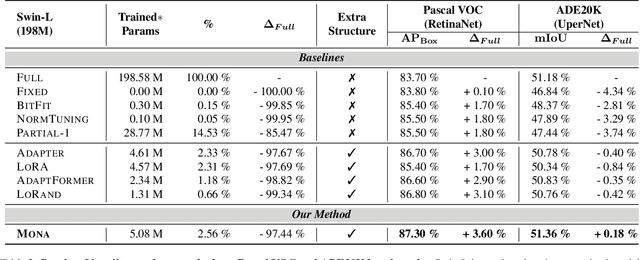
Abstract:Pre-training & fine-tuning can enhance the transferring efficiency and performance in visual tasks. Recent delta-tuning methods provide more options for visual classification tasks. Despite their success, existing visual delta-tuning art fails to exceed the upper limit of full fine-tuning on challenging tasks like instance segmentation and semantic segmentation. To find a competitive alternative to full fine-tuning, we propose the Multi-cognitive Visual Adapter (Mona) tuning, a novel adapter-based tuning method. First, we introduce multiple vision-friendly filters into the adapter to enhance its ability to process visual signals, while previous methods mainly rely on language-friendly linear filters. Second, we add the scaled normalization layer in the adapter to regulate the distribution of input features for visual filters. To fully demonstrate the practicality and generality of Mona, we conduct experiments on multiple representative visual tasks, including instance segmentation on COCO, semantic segmentation on ADE20K, object detection on Pascal VOC, and image classification on several common datasets. Exciting results illustrate that Mona surpasses full fine-tuning on all these tasks and is the only delta-tuning method outperforming full fine-tuning on instance segmentation and semantic segmentation tasks. For example, Mona achieves a 1% performance gain on the COCO dataset compared to full fine-tuning. Comprehensive results suggest that Mona-tuning is more suitable for retaining and utilizing the capabilities of pre-trained models than full fine-tuning. The code will be released at https://github.com/Leiyi-Hu/mona.
Parameter-efficient is not sufficient: Exploring Parameter, Memory, and Time Efficient Adapter Tuning for Dense Predictions
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Pre-training & fine-tuning is a prevalent paradigm in computer vision (CV). Recently, parameter-efficient transfer learning (PETL) methods have shown promising performance in transferring knowledge from pre-trained models with only a few trainable parameters. Despite their success, the existing PETL methods in CV can be computationally expensive and require large amounts of memory and time cost during training, which limits low-resource users from conducting research and applications on large models. In this work, we propose Parameter, Memory, and Time Efficient Visual Adapter ($\mathrm{E^3VA}$) tuning to address this issue. We provide a gradient backpropagation highway for low-rank adapters which removes large gradient computations for the frozen pre-trained parameters, resulting in substantial savings of training memory and training time. Furthermore, we optimise the $\mathrm{E^3VA}$ structure for dense predictions tasks to promote model performance. Extensive experiments on COCO, ADE20K, and Pascal VOC benchmarks show that $\mathrm{E^3VA}$ can save up to 62.2% training memory and 26.2% training time on average, while achieving comparable performance to full fine-tuning and better performance than most PETL methods. Note that we can even train the Swin-Large-based Cascade Mask RCNN on GTX 1080Ti GPUs with less than 1.5% trainable parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge