Dongmyoung Lee
A Backbone for Long-Horizon Robot Task Understanding
Aug 07, 2024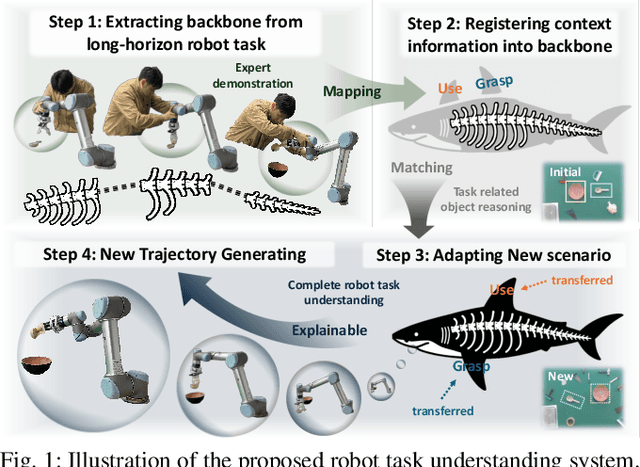
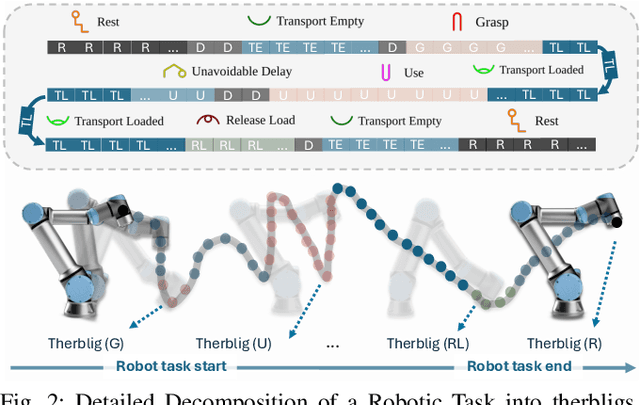
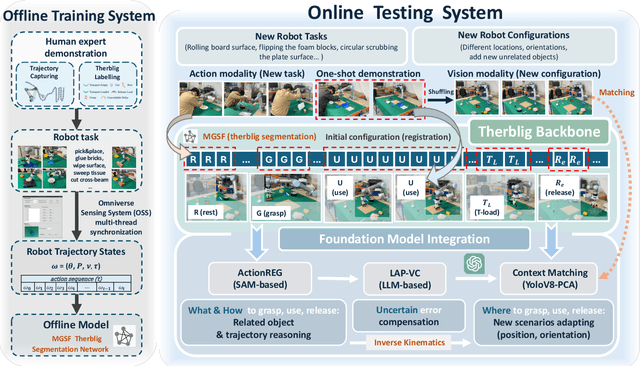
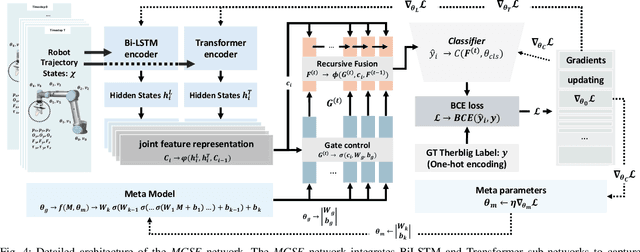
Abstract:End-to-end robot learning, particularly for long-horizon tasks, often results in unpredictable outcomes and poor generalization. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Therblig-based Backbone Framework (TBBF) to enhance robot task understanding and transferability. This framework uses therbligs (basic action elements) as the backbone to decompose high-level robot tasks into elemental robot configurations, which are then integrated with current foundation models to improve task understanding. The approach consists of two stages: offline training and online testing. During the offline training stage, we developed the Meta-RGate SynerFusion (MGSF) network for accurate therblig segmentation across various tasks. In the online testing stage, after a one-shot demonstration of a new task is collected, our MGSF network extracts high-level knowledge, which is then encoded into the image using Action Registration (ActionREG). Additionally, the Large Language Model (LLM)-Alignment Policy for Visual Correction (LAP-VC) is employed to ensure precise action execution, facilitating trajectory transfer in novel robot scenarios. Experimental results validate these methods, achieving 94.37% recall in therblig segmentation and success rates of 94.4% and 80% in real-world online robot testing for simple and complex scenarios, respectively. Supplementary material is available at: https://sites.google.com/view/therbligsbasedbackbone/home
Synthetic data enables faster annotation and robust segmentation for multi-object grasping in clutter
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:Object recognition and object pose estimation in robotic grasping continue to be significant challenges, since building a labelled dataset can be time consuming and financially costly in terms of data collection and annotation. In this work, we propose a synthetic data generation method that minimizes human intervention and makes downstream image segmentation algorithms more robust by combining a generated synthetic dataset with a smaller real-world dataset (hybrid dataset). Annotation experiments show that the proposed synthetic scene generation can diminish labelling time dramatically. RGB image segmentation is trained with hybrid dataset and combined with depth information to produce pixel-to-point correspondence of individual segmented objects. The object to grasp is then determined by the confidence score of the segmentation algorithm. Pick-and-place experiments demonstrate that segmentation trained on our hybrid dataset (98.9%, 70%) outperforms the real dataset and a publicly available dataset by (6.7%, 18.8%) and (2.8%, 10%) in terms of labelling and grasping success rate, respectively. Supplementary material is available at https://sites.google.com/view/synthetic-dataset-generation.
G.O.G: A Versatile Gripper-On-Gripper Design for Bimanual Cloth Manipulation with a Single Robotic Arm
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:The manipulation of garments poses research challenges due to their deformable nature and the extensive variability in shapes and sizes. Despite numerous attempts by researchers to address these via approaches involving robot perception and control, there has been a relatively limited interest in resolving it through the co-development of robot hardware. Consequently, the majority of studies employ off-the-shelf grippers in conjunction with dual robot arms to enable bimanual manipulation and high dexterity. However, this dual-arm system increases the overall cost of the robotic system as well as its control complexity in order to tackle robot collisions and other robot coordination issues. As an alternative approach, we propose to enable bimanual cloth manipulation using a single robot arm via novel end effector design -- sharing dexterity skills between manipulator and gripper rather than relying entirely on robot arm coordination. To this end, we introduce a new gripper, called G.O.G., based on a gripper-on-gripper structure where the first gripper independently regulates the span, up to 500mm, between its fingers which are in turn also grippers. These finger grippers consist of a variable friction module that enables two grasping modes: firm and sliding grasps. Household item and cloth object benchmarks are employed to evaluate the performance of the proposed design, encompassing both experiments on the gripper design itself and on cloth manipulation. Experimental results demonstrate the potential of the introduced ideas to undertake a range of bimanual cloth manipulation tasks with a single robot arm. Supplementary material is available at https://sites.google.com/view/gripperongripper.
* Accepted for IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters in January 2024. Dongmyoung Lee and Wei Chen contributed equally to this research
A Soft Continuum Robot with Self-Controllable Variable Curvature
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a new type of soft continuum robot, called SCoReS, which is capable of self-controlling continuously its curvature at the segment level; in contrast to previous designs which either require external forces or machine elements, or whose variable curvature capabilities are discrete -- depending on the number of locking mechanisms and segments. The ability to have a variable curvature, whose control is continuous and independent from external factors, makes a soft continuum robot more adaptive in constrained environments, similar to what is observed in nature in the elephant's trunk or ostrich's neck for instance which exhibit multiple curvatures. To this end, our soft continuum robot enables reconfigurable variable curvatures utilizing a variable stiffness growing spine based on micro-particle granular jamming for the first time. We detail the design of the proposed robot, presenting its modeling through beam theory and FEA simulation -- which is validated through experiments. The robot's versatile bending profiles are then explored in experiments and an application to grasp fruits at different configurations is demonstrated.
Learning to Grasp Clothing Structural Regions for Garment Manipulation Tasks
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:When performing cloth-related tasks, such as garment hanging, it is often important to identify and grasp certain structural regions -- a shirt's collar as opposed to its sleeve, for instance. However, due to cloth deformability, these manipulation activities, which are essential in domestic, health care, and industrial contexts, remain challenging for robots. In this paper, we focus on how to segment and grasp structural regions of clothes to enable manipulation tasks, using hanging tasks as case study. To this end, a neural network-based perception system is proposed to segment a shirt's collar from areas that represent the rest of the scene in a depth image. With a 10-minute video of a human manipulating shirts to train it, our perception system is capable of generalizing to other shirts regardless of texture as well as to other types of collared garments. A novel grasping strategy is then proposed based on the segmentation to determine grasping pose. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed grasping strategy achieves 92\%, 80\%, and 50\% grasping success rates with one folded garment, one crumpled garment and three crumpled garments, respectively. Our grasping strategy performs considerably better than tested baselines that do not take into account the structural nature of the garments. With the proposed region segmentation and grasping strategy, challenging garment hanging tasks are successfully implemented using an open-loop control policy. Supplementary material is available at https://sites.google.com/view/garment-hanging
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge