Dongjie Liu
Wavelet-Aware Anomaly Detection in Multi-Channel User Logs via Deviation Modulation and Resolution-Adaptive Attention
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Insider threat detection is a key challenge in enterprise security, relying on user activity logs that capture rich and complex behavioral patterns. These logs are often multi-channel, non-stationary, and anomalies are rare, making anomaly detection challenging. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework that integrates wavelet-aware modulation, multi-resolution wavelet decomposition, and resolution-adaptive attention for robust anomaly detection. Our approach first applies a deviation-aware modulation scheme to suppress routine behaviors while amplifying anomalous deviations. Next, discrete wavelet transform (DWT) decomposes the log signals into multi-resolution representations, capturing both long-term trends and short-term anomalies. Finally, a learnable attention mechanism dynamically reweights the most discriminative frequency bands for detection. On the CERT r4.2 benchmark, our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines in precision, recall, and F1 score across various time granularities and scenarios.
From ORAN to Cell-Free RAN: Architecture, Performance Analysis, Testbeds and Trials
Feb 07, 2023Abstract:Open radio access network (ORAN) provides an open architecture to implement radio access network (RAN) of the fifth generation (5G) and beyond mobile communications. As a key technology for the evolution to the sixth generation (6G) systems, cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (CF-mMIMO) can effectively improve the spectrum efficiency, peak rate and reliability of wireless communication systems. Starting from scalable implementation of CF-mMIMO, we study a cell-free RAN (CF-RAN) under the ORAN architecture. Through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, we investigate the uplink and downlink spectral efficiencies of CF-mMIMO with the new architecture. We then discuss the implementation issues of CF-RAN under ORAN architecture, including time-frequency synchronization and over-the-air reciprocity calibration, low layer splitting, deployment of ORAN radio units (O-RU), artificial intelligent based user associations. Finally, we present some representative experimental results for the uplink distributed reception and downlink coherent joint transmission of CF-RAN with commercial off-the-shelf O-RUs.
Service Delay Minimization for Federated Learning over Mobile Devices
May 19, 2022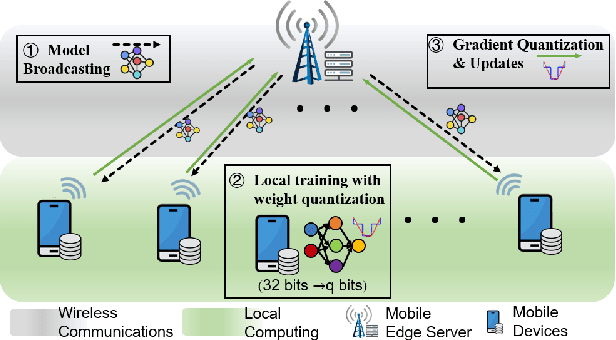
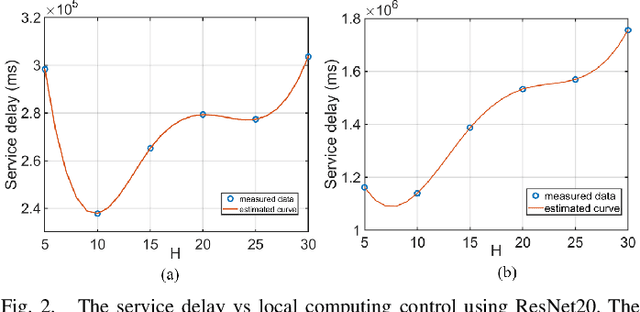
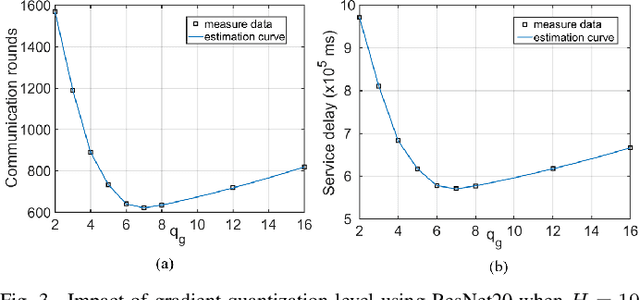
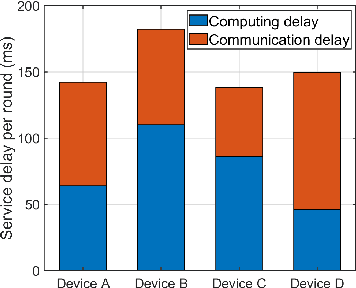
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) over mobile devices has fostered numerous intriguing applications/services, many of which are delay-sensitive. In this paper, we propose a service delay efficient FL (SDEFL) scheme over mobile devices. Unlike traditional communication efficient FL, which regards wireless communications as the bottleneck, we find that under many situations, the local computing delay is comparable to the communication delay during the FL training process, given the development of high-speed wireless transmission techniques. Thus, the service delay in FL should be computing delay + communication delay over training rounds. To minimize the service delay of FL, simply reducing local computing/communication delay independently is not enough. The delay trade-off between local computing and wireless communications must be considered. Besides, we empirically study the impacts of local computing control and compression strategies (i.e., the number of local updates, weight quantization, and gradient quantization) on computing, communication and service delays. Based on those trade-off observation and empirical studies, we develop an optimization scheme to minimize the service delay of FL over heterogeneous devices. We establish testbeds and conduct extensive emulations/experiments to verify our theoretical analysis. The results show that SDEFL reduces notable service delay with a small accuracy drop compared to peer designs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge