Dong H. Jeong
Active Learning on Neural Networks through Interactive Generation of Digit Patterns and Visual Representation
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:Artificial neural networks (ANNs) have been broadly utilized to analyze various data and solve different domain problems. However, neural networks (NNs) have been considered a black box operation for years because their underlying computation and meaning are hidden. Due to this nature, users often face difficulties in interpreting the underlying mechanism of the NNs and the benefits of using them. In this paper, to improve users' learning and understanding of NNs, an interactive learning system is designed to create digit patterns and recognize them in real time. To help users clearly understand the visual differences of digit patterns (i.e., 0 ~ 9) and their results with an NN, integrating visualization is considered to present all digit patterns in a two-dimensional display space with supporting multiple user interactions. An evaluation with multiple datasets is conducted to determine its usability for active learning. In addition, informal user testing is managed during a summer workshop by asking the workshop participants to use the system.
Uncertainty-Aware Reward-based Deep Reinforcement Learning for Intent Analysis of Social Media Information
Feb 19, 2023Abstract:Due to various and serious adverse impacts of spreading fake news, it is often known that only people with malicious intent would propagate fake news. However, it is not necessarily true based on social science studies. Distinguishing the types of fake news spreaders based on their intent is critical because it will effectively guide how to intervene to mitigate the spread of fake news with different approaches. To this end, we propose an intent classification framework that can best identify the correct intent of fake news. We will leverage deep reinforcement learning (DRL) that can optimize the structural representation of each tweet by removing noisy words from the input sequence when appending an actor to the long short-term memory (LSTM) intent classifier. Policy gradient DRL model (e.g., REINFORCE) can lead the actor to a higher delayed reward. We also devise a new uncertainty-aware immediate reward using a subjective opinion that can explicitly deal with multidimensional uncertainty for effective decision-making. Via 600K training episodes from a fake news tweets dataset with an annotated intent class, we evaluate the performance of uncertainty-aware reward in DRL. Evaluation results demonstrate that our proposed framework efficiently reduces the number of selected words to maintain a high 95\% multi-class accuracy.
PPO-UE: Proximal Policy Optimization via Uncertainty-Aware Exploration
Dec 13, 2022Abstract:Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is a highly popular policy-based deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach. However, we observe that the homogeneous exploration process in PPO could cause an unexpected stability issue in the training phase. To address this issue, we propose PPO-UE, a PPO variant equipped with self-adaptive uncertainty-aware explorations (UEs) based on a ratio uncertainty level. The proposed PPO-UE is designed to improve convergence speed and performance with an optimized ratio uncertainty level. Through extensive sensitivity analysis by varying the ratio uncertainty level, our proposed PPO-UE considerably outperforms the baseline PPO in Roboschool continuous control tasks.
A Survey on Uncertainty Reasoning and Quantification for Decision Making: Belief Theory Meets Deep Learning
Jun 14, 2022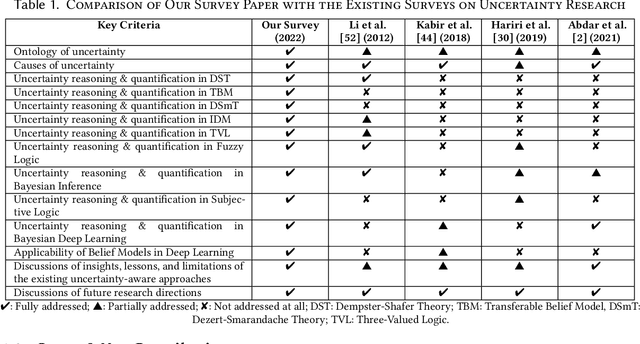
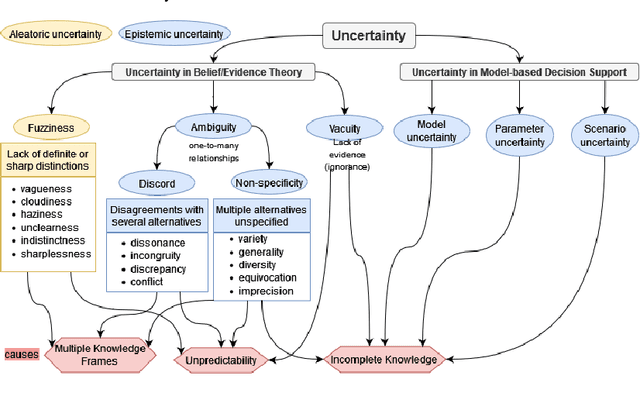
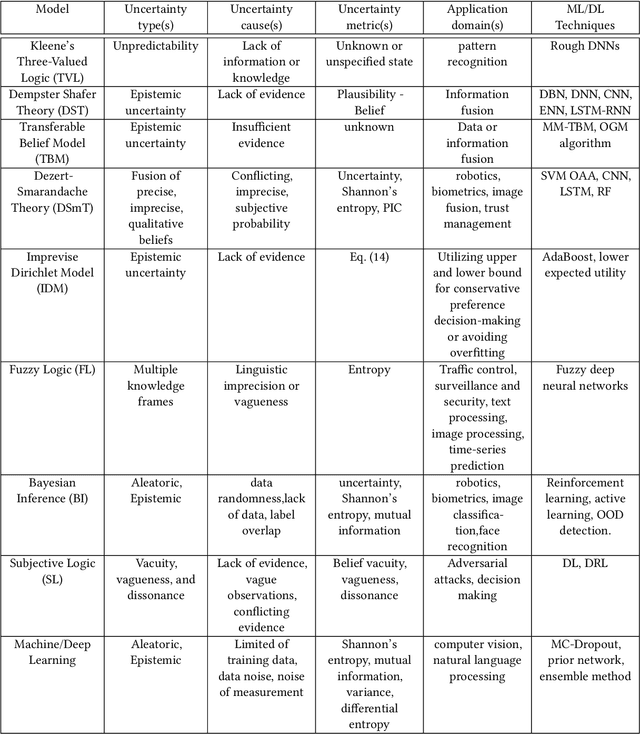
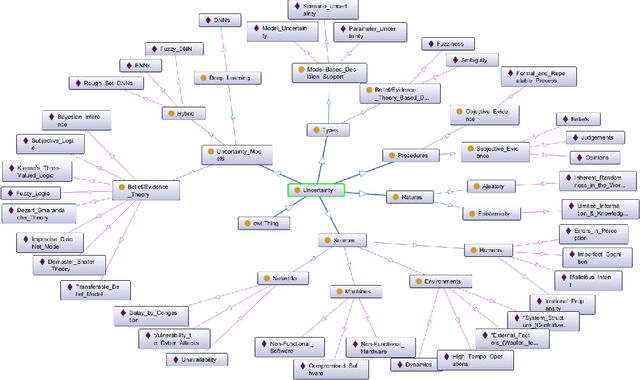
Abstract:An in-depth understanding of uncertainty is the first step to making effective decisions under uncertainty. Deep/machine learning (ML/DL) has been hugely leveraged to solve complex problems involved with processing high-dimensional data. However, reasoning and quantifying different types of uncertainties to achieve effective decision-making have been much less explored in ML/DL than in other Artificial Intelligence (AI) domains. In particular, belief/evidence theories have been studied in KRR since the 1960s to reason and measure uncertainties to enhance decision-making effectiveness. We found that only a few studies have leveraged the mature uncertainty research in belief/evidence theories in ML/DL to tackle complex problems under different types of uncertainty. In this survey paper, we discuss several popular belief theories and their core ideas dealing with uncertainty causes and types and quantifying them, along with the discussions of their applicability in ML/DL. In addition, we discuss three main approaches that leverage belief theories in Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), including Evidential DNNs, Fuzzy DNNs, and Rough DNNs, in terms of their uncertainty causes, types, and quantification methods along with their applicability in diverse problem domains. Based on our in-depth survey, we discuss insights, lessons learned, limitations of the current state-of-the-art bridging belief theories and ML/DL, and finally, future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge