Dominika Woszczyk
DiDOTS: Knowledge Distillation from Large-Language-Models for Dementia Obfuscation in Transcribed Speech
Oct 05, 2024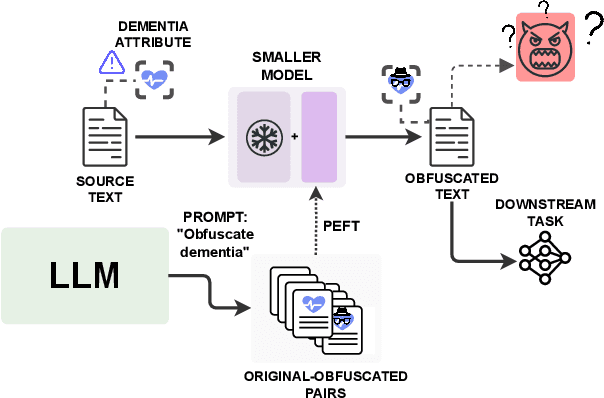
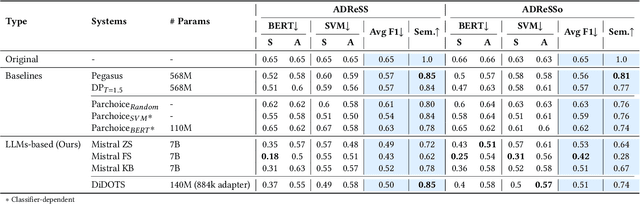
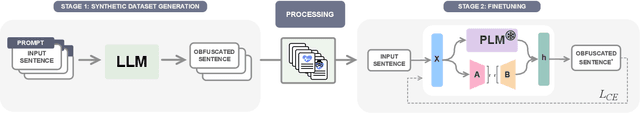
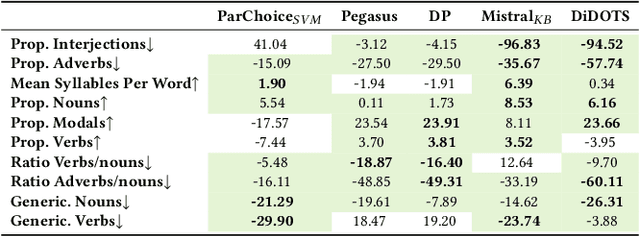
Abstract:Dementia is a sensitive neurocognitive disorder affecting tens of millions of people worldwide and its cases are expected to triple by 2050. Alarmingly, recent advancements in dementia classification make it possible for adversaries to violate affected individuals' privacy and infer their sensitive condition from speech transcriptions. Existing obfuscation methods in text have never been applied for dementia and depend on the availability of large labeled datasets which are challenging to collect for sensitive medical attributes. In this work, we bridge this research gap and tackle the above issues by leveraging Large-Language-Models (LLMs) with diverse prompt designs (zero-shot, few-shot, and knowledge-based) to obfuscate dementia in speech transcripts. Our evaluation shows that LLMs are more effective dementia obfuscators compared to competing methods. However, they have billions of parameters which renders them hard to train, store and share, and they are also fragile suffering from hallucination, refusal and contradiction effects among others. To further mitigate these, we propose a novel method, DiDOTS. DiDOTS distills knowledge from LLMs using a teacher-student paradigm and parameter-efficient fine-tuning. DiDOTS has one order of magnitude fewer parameters compared to its teacher LLM and can be fine-tuned using three orders of magnitude less parameters compared to full fine-tuning. Our evaluation shows that compared to prior work DiDOTS retains the performance of LLMs achieving 1.3x and 2.2x improvement in privacy performance on two datasets, while humans rate it as better in preserving utility even when compared to state-of-the-art paraphrasing models.
Prosody-Driven Privacy-Preserving Dementia Detection
Jul 03, 2024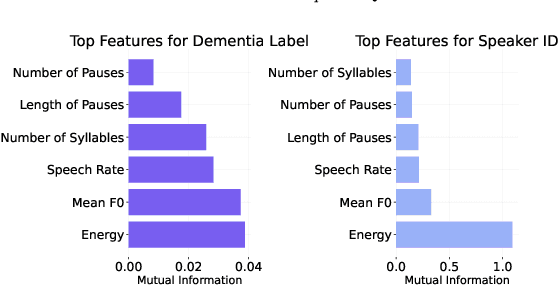
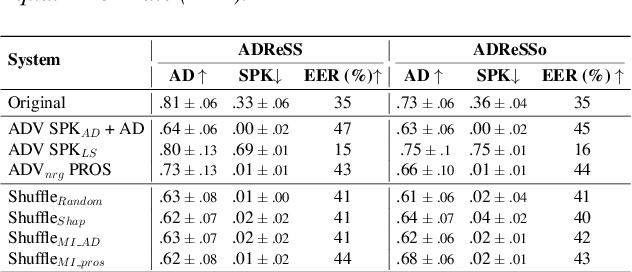
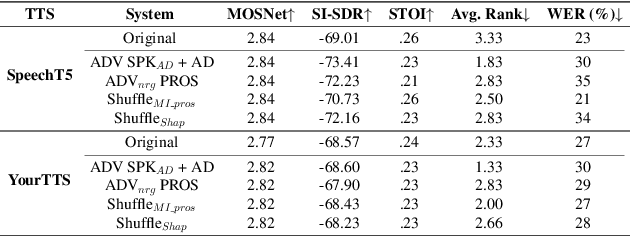
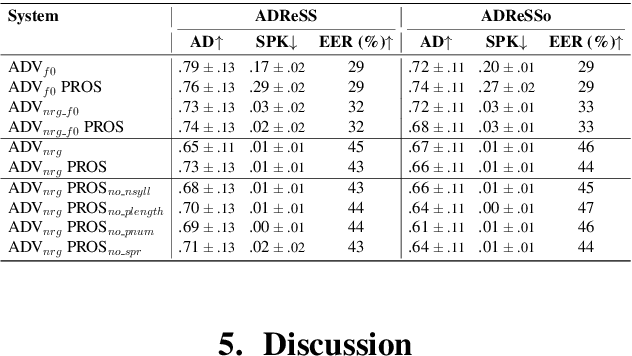
Abstract:Speaker embeddings extracted from voice recordings have been proven valuable for dementia detection. However, by their nature, these embeddings contain identifiable information which raises privacy concerns. In this work, we aim to anonymize embeddings while preserving the diagnostic utility for dementia detection. Previous studies rely on adversarial learning and models trained on the target attribute and struggle in limited-resource settings. We propose a novel approach that leverages domain knowledge to disentangle prosody features relevant to dementia from speaker embeddings without relying on a dementia classifier. Our experiments show the effectiveness of our approach in preserving speaker privacy (speaker recognition F1-score .01%) while maintaining high dementia detection score F1-score of 74% on the ADReSS dataset. Our results are also on par with a more constrained classifier-dependent system on ADReSSo (.01% and .66%), and have no impact on synthesized speech naturalness.
Data Augmentation for Dementia Detection in Spoken Language
Jun 26, 2022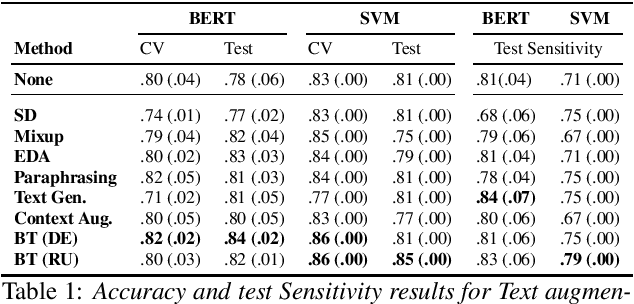
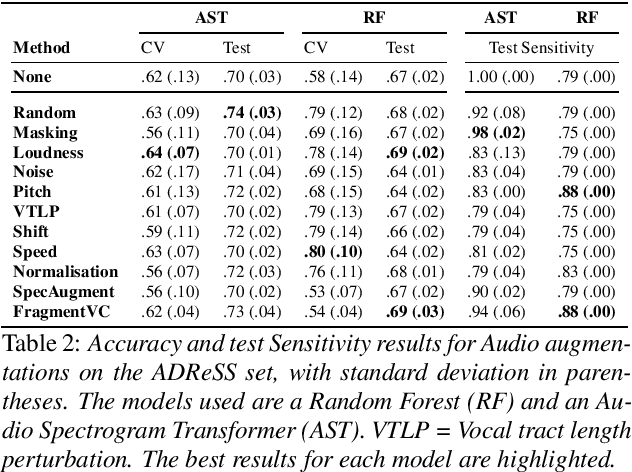
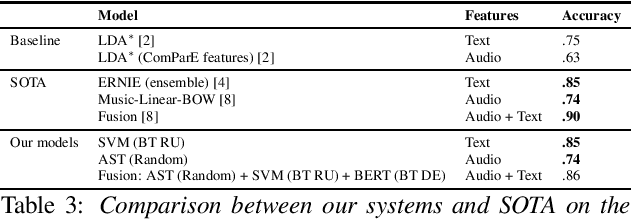
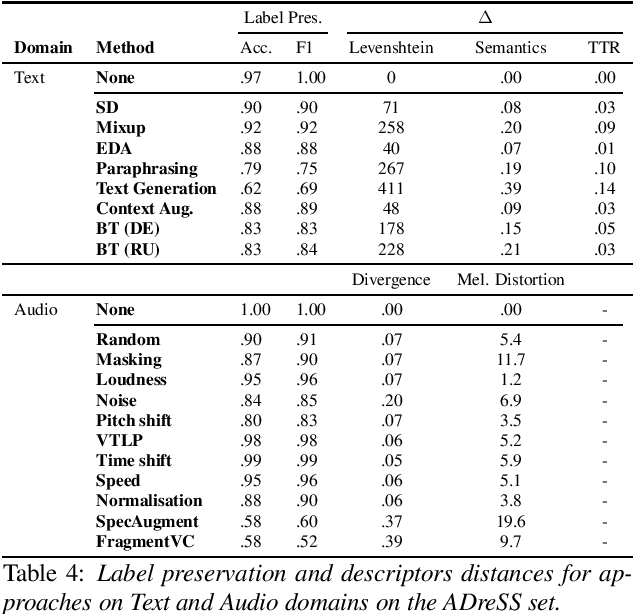
Abstract:Dementia is a growing problem as our society ages, and detection methods are often invasive and expensive. Recent deep-learning techniques can offer a faster diagnosis and have shown promising results. However, they require large amounts of labelled data which is not easily available for the task of dementia detection. One effective solution to sparse data problems is data augmentation, though the exact methods need to be selected carefully. To date, there has been no empirical study of data augmentation on Alzheimer's disease (AD) datasets for NLP and speech processing. In this work, we investigate data augmentation techniques for the task of AD detection and perform an empirical evaluation of the different approaches on two kinds of models for both the text and audio domains. We use a transformer-based model for both domains, and SVM and Random Forest models for the text and audio domains, respectively. We generate additional samples using traditional as well as deep learning based methods and show that data augmentation improves performance for both the text- and audio-based models and that such results are comparable to state-of-the-art results on the popular ADReSS set, with carefully crafted architectures and features.
Domain Adversarial Neural Networks for Dysarthric Speech Recognition
Oct 07, 2020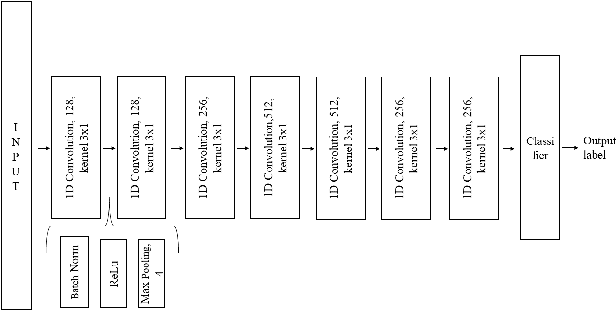
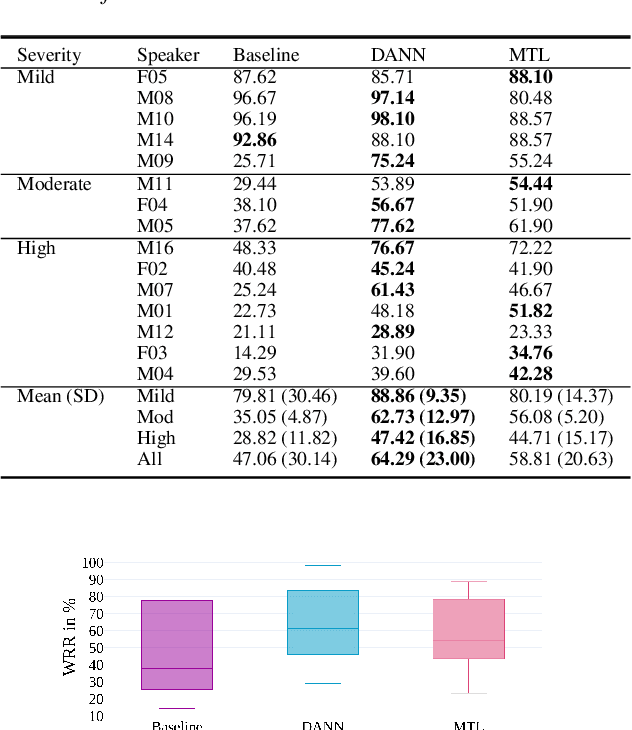
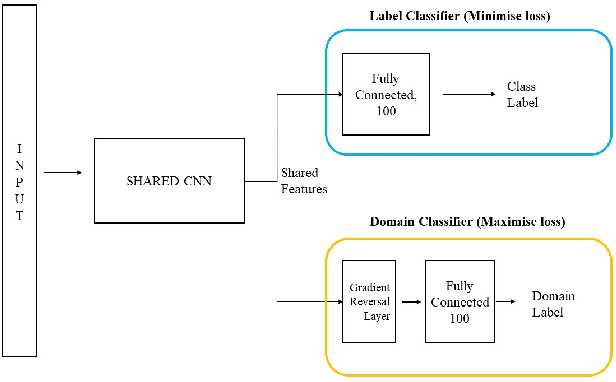
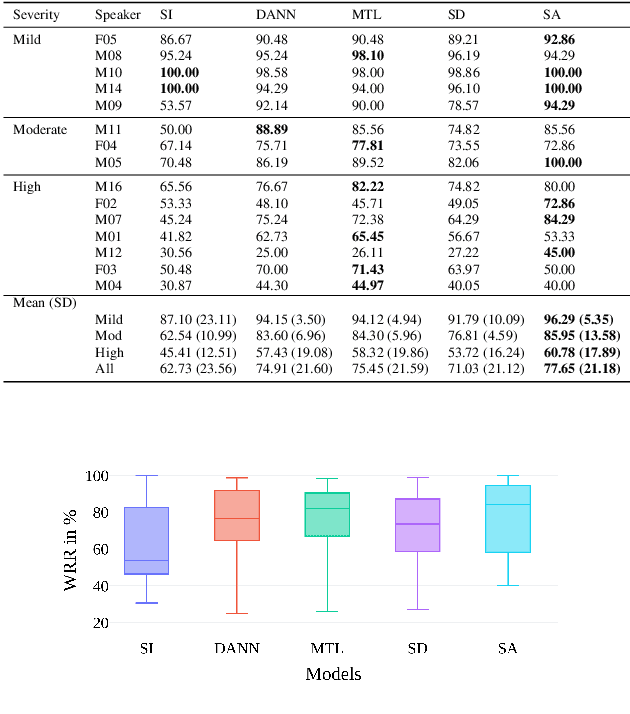
Abstract:Speech recognition systems have improved dramatically over the last few years, however, their performance is significantly degraded for the cases of accented or impaired speech. This work explores domain adversarial neural networks (DANN) for speaker-independent speech recognition on the UAS dataset of dysarthric speech. The classification task on 10 spoken digits is performed using an end-to-end CNN taking raw audio as input. The results are compared to a speaker-adaptive (SA) model as well as speaker-dependent (SD) and multi-task learning models (MTL). The experiments conducted in this paper show that DANN achieves an absolute recognition rate of 74.91% and outperforms the baseline by 12.18%. Additionally, the DANN model achieves comparable results to the SA model's recognition rate of 77.65%. We also observe that when labelled dysarthric speech data is available DANN and MTL perform similarly, but when they are not DANN performs better than MTL.
MaaSim: A Liveability Simulation for Improving the Quality of Life in Cities
Oct 13, 2018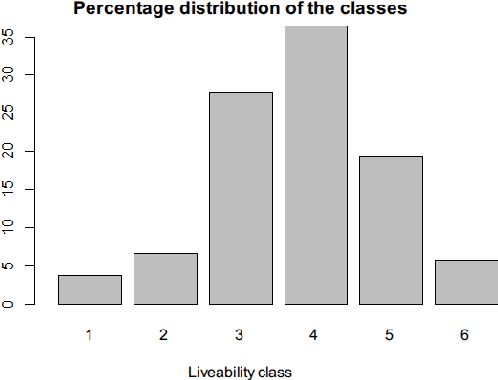
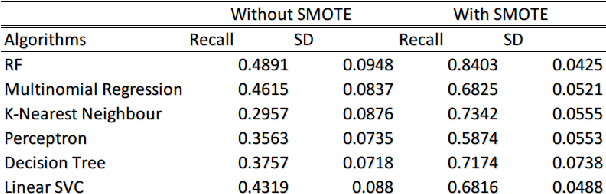
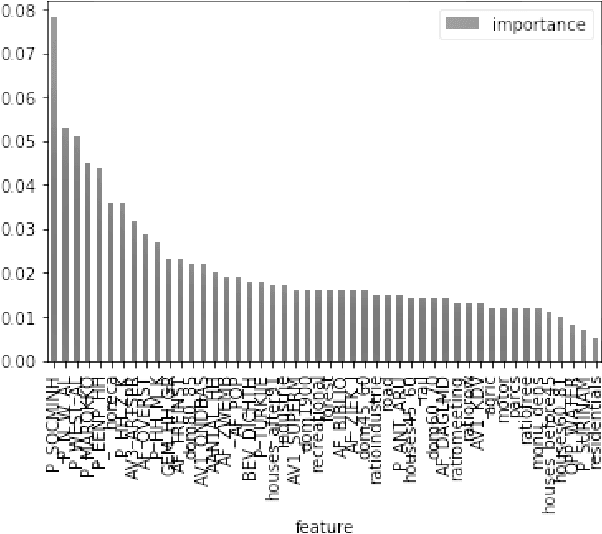
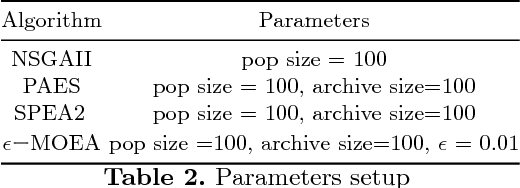
Abstract:Urbanism is no longer planned on paper thanks to powerful models and 3D simulation platforms. However, current work is not open to the public and lacks an optimisation agent that could help in decision making. This paper describes the creation of an open-source simulation based on an existing Dutch liveability score with a built-in AI module. Features are selected using feature engineering and Random Forests. Then, a modified scoring function is built based on the former liveability classes. The score is predicted using Random Forest for regression and achieved a recall of 0.83 with 10-fold cross-validation. Afterwards, Exploratory Factor Analysis is applied to select the actions present in the model. The resulting indicators are divided into 5 groups, and 12 actions are generated. The performance of four optimisation algorithms is compared, namely NSGA-II, PAES, SPEA2 and eps-MOEA, on three established criteria of quality: cardinality, the spread of the solutions, spacing, and the resulting score and number of turns. Although all four algorithms show different strengths, eps-MOEA is selected to be the most suitable for this problem. Ultimately, the simulation incorporates the model and the selected AI module in a GUI written in the Kivy framework for Python. Tests performed on users show positive responses and encourage further initiatives towards joining technology and public applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge