Doganay Sirintuna
Human-Robot Interfaces and Interaction, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Genoa, Italy, Dept. of Informatics, Bioengineering, Robotics, and System Engineering, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy
A Machine Learning Approach to Sensor Substitution for Non-Prehensile Manipulation
Feb 13, 2025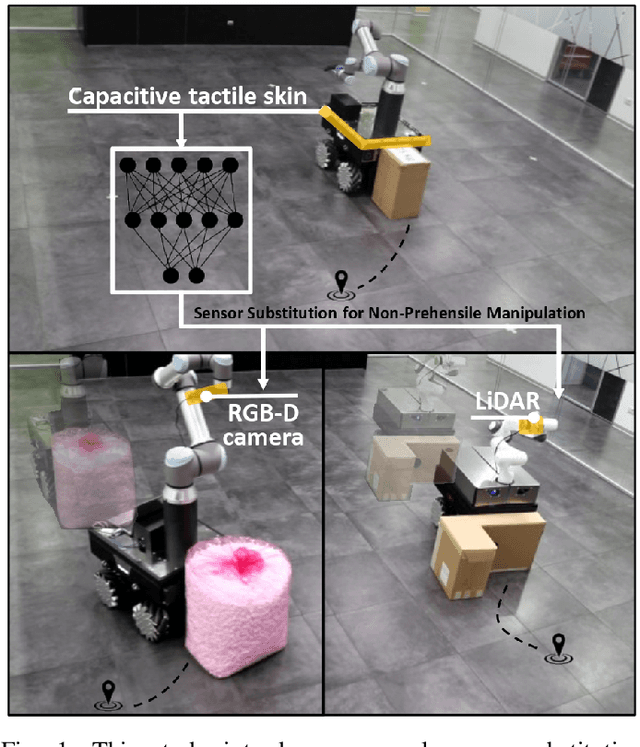
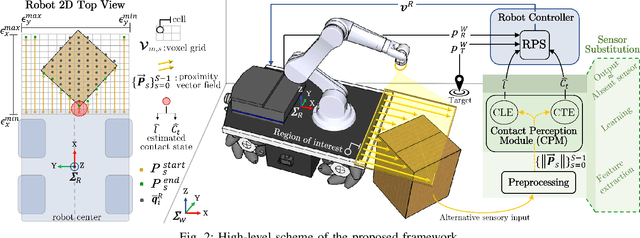
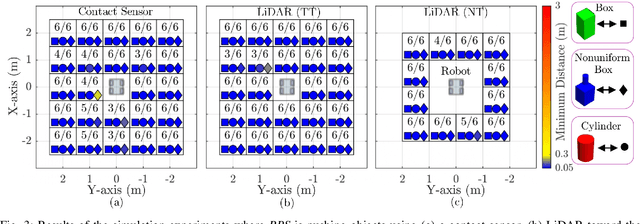
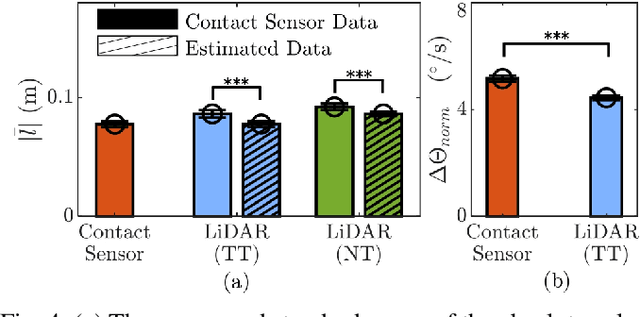
Abstract:Mobile manipulators are increasingly deployed in complex environments, requiring diverse sensors to perceive and interact with their surroundings. However, equipping every robot with every possible sensor is often impractical due to cost and physical constraints. A critical challenge arises when robots with differing sensor capabilities need to collaborate or perform similar tasks. For example, consider a scenario where a mobile manipulator equipped with high-resolution tactile skin is skilled at non-prehensile manipulation tasks like pushing. If this robot needs to be replaced or augmented by a robot lacking such tactile sensing, the learned manipulation policies become inapplicable. This paper addresses the problem of sensor substitution in non-prehensile manipulation. We propose a novel machine learning-based framework that enables a robot with a limited sensor set (e.g., LiDAR or RGB-D camera) to effectively perform tasks previously reliant on a richer sensor suite (e.g., tactile skin). Our approach learns a mapping between the available sensor data and the information provided by the substituted sensor, effectively synthesizing the missing sensory input. Specifically, we demonstrate the efficacy of our framework by training a model to substitute tactile skin data for the task of non-prehensile pushing using a mobile manipulator. We show that a manipulator equipped only with LiDAR or RGB-D can, after training, achieve comparable and sometimes even better pushing performance to a mobile base utilizing direct tactile feedback.
Pushing in the Dark: A Reactive Pushing Strategy for Mobile Robots Using Tactile Feedback
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:For mobile robots, navigating cluttered or dynamic environments often necessitates non-prehensile manipulation, particularly when faced with objects that are too large, irregular, or fragile to grasp. The unpredictable behavior and varying physical properties of these objects significantly complicate manipulation tasks. To address this challenge, this manuscript proposes a novel Reactive Pushing Strategy. This strategy allows a mobile robot to dynamically adjust its base movements in real-time to achieve successful pushing maneuvers towards a target location. Notably, our strategy adapts the robot motion based on changes in contact location obtained through the tactile sensor covering the base, avoiding dependence on object-related assumptions and its modeled behavior. The effectiveness of the Reactive Pushing Strategy was initially evaluated in the simulation environment, where it significantly outperformed the compared baseline approaches. Following this, we validated the proposed strategy through real-world experiments, demonstrating the robot capability to push objects to the target points located in the entire vicinity of the robot. In both simulation and real-world experiments, the object-specific properties (shape, mass, friction, inertia) were altered along with the changes in target locations to assess the robustness of the proposed method comprehensively.
Robot-Assisted Navigation for Visually Impaired through Adaptive Impedance and Path Planning
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a framework to navigate visually impaired people through unfamiliar environments by means of a mobile manipulator. The Human-Robot system consists of three key components: a mobile base, a robotic arm, and the human subject who gets guided by the robotic arm via physically coupling their hand with the cobot's end-effector. These components, receiving a goal from the user, traverse a collision-free set of waypoints in a coordinated manner, while avoiding static and dynamic obstacles through an obstacle avoidance unit and a novel human guidance planner. With this aim, we also present a legs tracking algorithm that utilizes 2D LiDAR sensors integrated into the mobile base to monitor the human pose. Additionally, we introduce an adaptive pulling planner responsible for guiding the individual back to the intended path if they veer off course. This is achieved by establishing a target arm end-effector position and dynamically adjusting the impedance parameters in real-time through a impedance tuning unit. To validate the framework we present a set of experiments both in laboratory settings with 12 healthy blindfolded subjects and a proof-of-concept demonstration in a real-world scenario.
Enhancing Human-Robot Collaboration Transportation through Obstacle-Aware Vibrotactile Feedback
Feb 06, 2023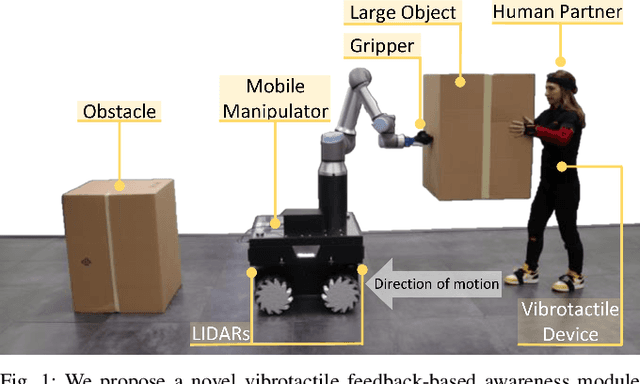
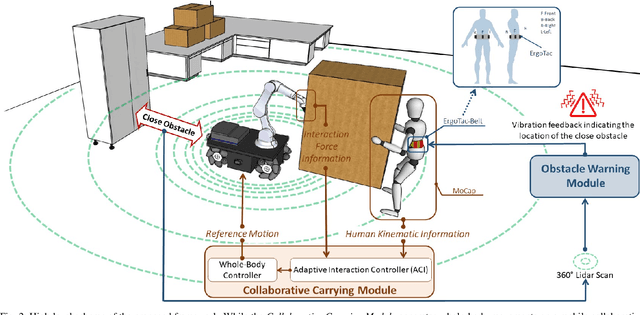
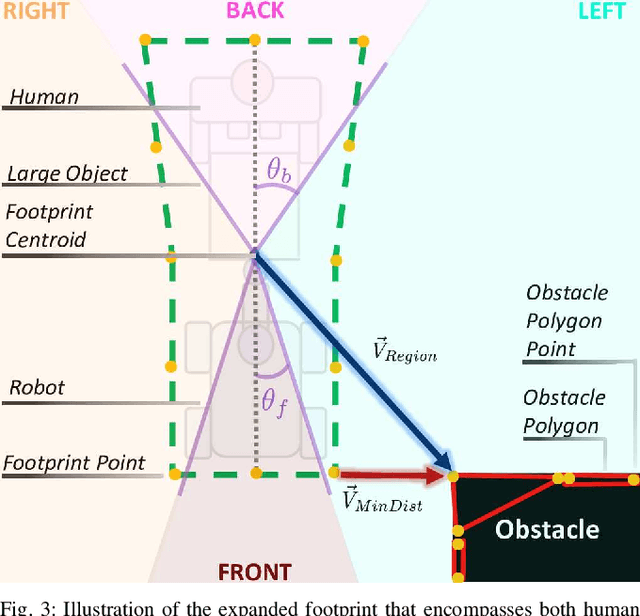
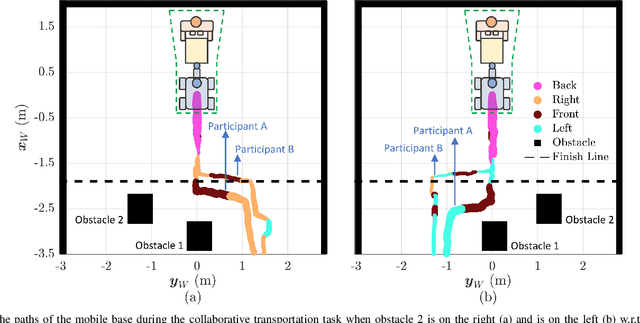
Abstract:Transporting large and heavy objects can benefit from Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC), increasing the contribution of robots to our daily tasks and reducing the risk of injuries to the human operator. This approach usually posits the human collaborator as the leader, while the robot has the follower role. Hence, it is essential for the leader to be aware of the environmental situation. However, when transporting a large object, the operator's situational awareness can be compromised as the object may occlude different parts of the environment. This paper proposes a novel haptic-based environmental awareness module for a collaborative transportation framework that informs the human operator about surrounding obstacles. The robot uses two LIDARs to detect the obstacles in the surroundings. The warning module alerts the operator through a haptic belt with four vibrotactile devices that provide feedback about the location and proximity of the obstacles. By enhancing the operator's awareness of the surroundings, the proposed module improves the safety of the human-robot team in co-carrying scenarios by preventing collisions. Experiments with two non-expert subjects in two different situations are conducted. The results show that the human partner can successfully lead the co-transportation system in an unknown environment with hidden obstacles thanks to the haptic feedback.
Carrying the uncarriable: a deformation-agnostic and human-cooperative framework for unwieldy objects using multiple robots
Sep 28, 2022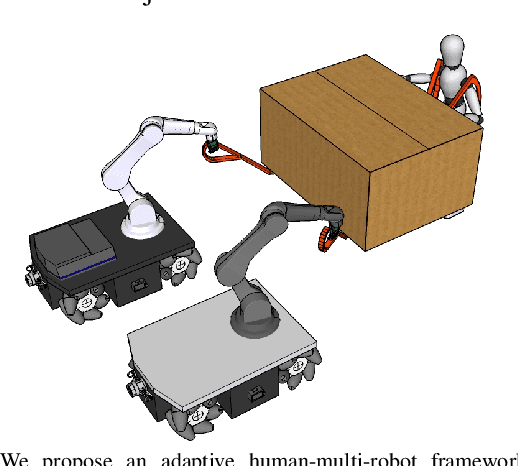
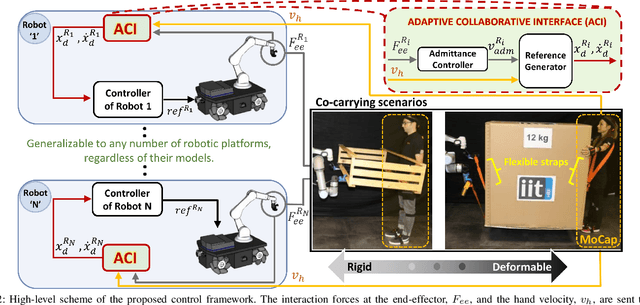
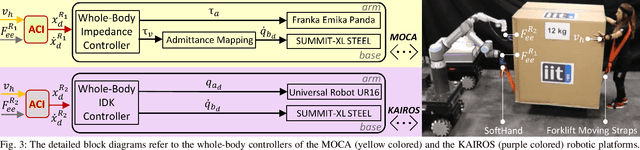
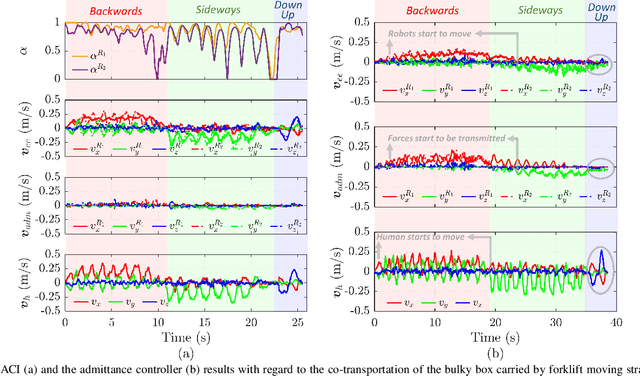
Abstract:This manuscript introduces an object deformability-agnostic framework for co-carrying tasks that are shared between a person and multiple robots. Our approach allows the full control of the co-carrying trajectories by the person while sharing the load with multiple robots depending on the size and the weight of the object. This is achieved by merging the haptic information transferred through the object and the human motion information obtained from a motion capture system. One important advantage of the framework is that no strict internal communication is required between the robots, regardless of the object size and deformation characteristics. We validate the framework with two challenging real-world scenarios: co-transportation of a wooden rigid closet and a bulky box on top of forklift moving straps, with the latter characterizing deformable objects. In order to evaluate the generalizability of the proposed framework, a heterogenous team of two mobile manipulators that consist of an Omni-directional mobile base and a collaborative robotic arm with different DoFs is chosen for the experiments. The qualitative comparison between our controller and the baseline controller (i.e., an admittance controller) during these experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed framework especially when co-carrying deformable objects. Furthermore, we believe that the performance of our framework during the experiment with the lifting straps offers a promising solution for the co-transportation of bulky and ungraspable objects.
An Object Deformation-Agnostic Framework for Human-Robot Collaborative Transportation
Jul 27, 2022



Abstract:In this study, an adaptive object deformability-agnostic human-robot collaborative transportation framework is presented. The proposed framework enables to combine the haptic information transferred through the object with the human kinematic information obtained from a motion capture system to generate reactive whole-body motions on a mobile collaborative robot. Furthermore, it allows rotating the objects in an intuitive and accurate way during co-transportation based on an algorithm that detects the human rotation intention using the torso and hand movements. First, we validate the framework with the two extremities of the object deformability range (i.e, purely rigid aluminum rod and highly deformable rope) by utilizing a mobile manipulator which consists of an Omni-directional mobile base and a collaborative robotic arm. Next, its performance is compared with an admittance controller during a co-carry task of a partially deformable object in a 12-subjects user study. Quantitative and qualitative results of this experiment show that the proposed framework can effectively handle the transportation of objects regardless of their deformability and provides intuitive assistance to human partners. Finally, we have demonstrated the potential of our framework in a different scenario, where the human and the robot co-transport a manikin using a deformable sheet.
Human-Robot Collaborative Carrying of Objects with Unknown Deformation Characteristics
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:In this work, we introduce an adaptive control framework for human-robot collaborative transportation of objects with unknown deformation behaviour. The proposed framework takes as input the haptic information transmitted through the object, and the kinematic information of the human body obtained from a motion capture system to create reactive whole-body motions on a mobile collaborative robot. Moreover, the designed framework delivers an intuitive way to rotate the object by processing the human torso and hand movements. In order to validate our framework experimentally, we compared its performance with an admittance controller during a co-transportation task of a partially deformable object. We additionally demonstrate the potential of the framework while co-transporting rigid (aluminum rod) and deformable (rope) objects. A mobile manipulator which consists of an Omni-directional mobile base, a collaborative robotic arm, and a robotic hand is used as the robotic partner in the experiments. Quantitative and qualitative results of a 12-subjects experiment show that the proposed framework can effectively deal with objects of unknown deformability and provides intuitive assistance to human partners.
Towards Collaborative Drilling with a Cobot Using Admittance Controller
Jul 28, 2020

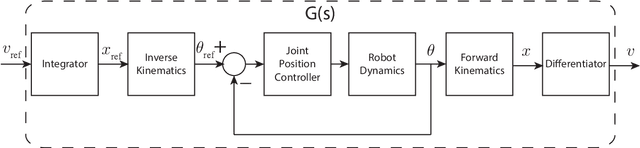

Abstract:In the near future, collaborative robots (cobots) are expected to play a vital role in the manufacturing and automation sectors. It is predicted that workers will work side by side in collaboration with cobots to surpass fully automated factories. In this regard, physical human-robot interaction (pHRI) aims to develop natural communication between the partners to bring speed, flexibility, and ergonomics to the execution of complex manufacturing tasks. One challenge in pHRI is to design an optimal interaction controller to balance the limitations introduced by the contradicting nature of transparency and stability requirements. In this paper, a general methodology to design an admittance controller for a pHRI system is developed by considering the stability and transparency objectives. In our approach, collaborative robot constrains the movement of human operator to help with a pHRI task while an augmented reality (AR) interface informs the operator about its phases. To this end, dynamical characterization of the collaborative robot (LBR IIWA 7 R800, KUKA Inc.) is presented first. Then, the stability and transparency analyses for our pHRI task involving collaborative drilling with this robot are reported. A range of allowable parameters for the admittance controller is determined by superimposing the stability and transparency graphs. Finally, three different sets of parameters are selected from the allowable range and the effect of admittance controllers utilizing these parameter sets on the task performance is investigated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge