Divyagna Bavikadi
Sea-cret Agents: Maritime Abduction for Region Generation to Expose Dark Vessel Trajectories
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Bad actors in the maritime industry engage in illegal behaviors after disabling their vessel's automatic identification system (AIS) - which makes finding such vessels difficult for analysts. Machine learning approaches only succeed in identifying the locations of these ``dark vessels'' in the immediate future. This work leverages ideas from the literature on abductive inference applied to locating adversarial agents to solve the problem. Specifically, we combine concepts from abduction, logic programming, and rule learning to create an efficient method that approaches full recall of dark vessels while requiring less search area than machine learning methods. We provide a logic-based paradigm for reasoning about maritime vessels, an abductive inference query method, an automatically extracted rule-based behavior model methodology, and a thorough suite of experiments.
Geospatial Trajectory Generation via Efficient Abduction: Deployment for Independent Testing
Jul 08, 2024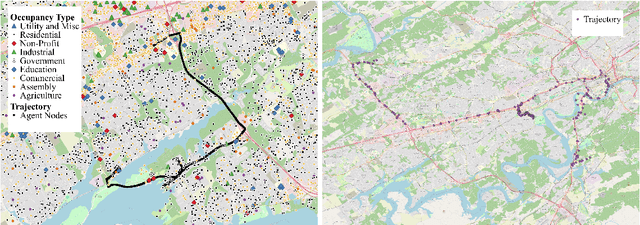
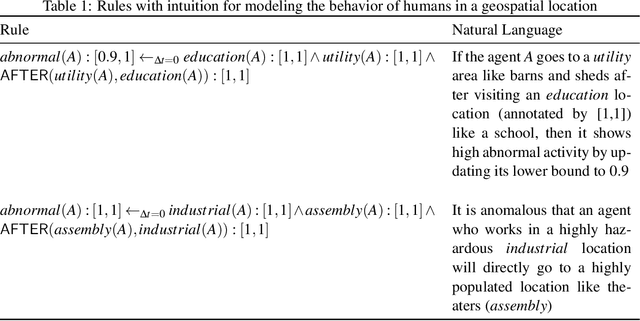
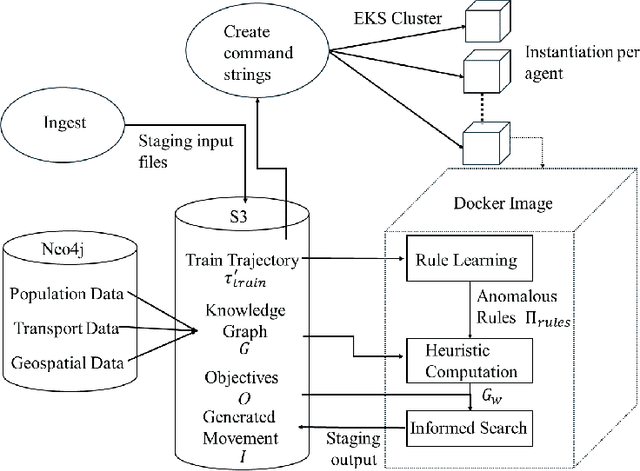
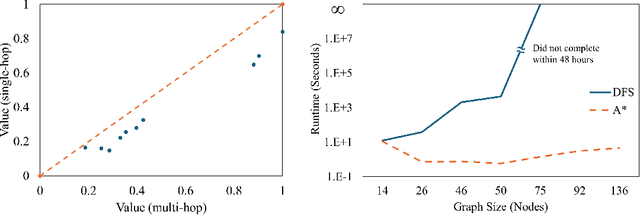
Abstract:The ability to generate artificial human movement patterns while meeting location and time constraints is an important problem in the security community, particularly as it enables the study of the analog problem of detecting such patterns while maintaining privacy. We frame this problem as an instance of abduction guided by a novel parsimony function represented as an aggregate truth value over an annotated logic program. This approach has the added benefit of affording explainability to an analyst user. By showing that any subset of such a program can provide a lower bound on this parsimony requirement, we are able to abduce movement trajectories efficiently through an informed (i.e., A*) search. We describe how our implementation was enhanced with the application of multiple techniques in order to be scaled and integrated with a cloud-based software stack that included bottom-up rule learning, geolocated knowledge graph retrieval/management, and interfaces with government systems for independently conducted government-run tests for which we provide results. We also report on our own experiments showing that we not only provide exact results but also scale to very large scenarios and provide realistic agent trajectories that can go undetected by machine learning anomaly detectors.
Machine Learning Driven Biomarker Selection for Medical Diagnosis
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in experimental methods have enabled researchers to collect data on thousands of analytes simultaneously. This has led to correlational studies that associated molecular measurements with diseases such as Alzheimer's, Liver, and Gastric Cancer. However, the use of thousands of biomarkers selected from the analytes is not practical for real-world medical diagnosis and is likely undesirable due to potentially formed spurious correlations. In this study, we evaluate 4 different methods for biomarker selection and 4 different machine learning (ML) classifiers for identifying correlations, evaluating 16 approaches in all. We found that contemporary methods outperform previously reported logistic regression in cases where 3 and 10 biomarkers are permitted. When specificity is fixed at 0.9, ML approaches produced a sensitivity of 0.240 (3 biomarkers) and 0.520 (10 biomarkers), while standard logistic regression provided a sensitivity of 0.000 (3 biomarkers) and 0.040 (10 biomarkers). We also noted that causal-based methods for biomarker selection proved to be the most performant when fewer biomarkers were permitted, while univariate feature selection was the most performant when a greater number of biomarkers were permitted.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge