Dillon Davis
Transforming Location Retrieval at Airbnb: A Journey from Heuristics to Reinforcement Learning
Aug 23, 2024
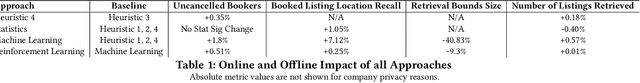


Abstract:The Airbnb search system grapples with many unique challenges as it continues to evolve. We oversee a marketplace that is nuanced by geography, diversity of homes, and guests with a variety of preferences. Crafting an efficient search system that can accommodate diverse guest needs, while showcasing relevant homes lies at the heart of Airbnb's success. Airbnb search has many challenges that parallel other recommendation and search systems but it has a unique information retrieval problem, upstream of ranking, called location retrieval. It requires defining a topological map area that is relevant to the searched query for homes listing retrieval. The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the methodology, challenges, and impact of building a machine learning based location retrieval product from the ground up. Despite the lack of suitable, prevalent machine learning based approaches, we tackle cold start, generalization, differentiation and algorithmic bias. We detail the efficacy of heuristics, statistics, machine learning, and reinforcement learning approaches to solve these challenges, particularly for systems that are often unexplored by current literature.
Piggyback: Adapting a Single Network to Multiple Tasks by Learning to Mask Weights
Mar 16, 2018



Abstract:This work presents a method for adapting a single, fixed deep neural network to multiple tasks without affecting performance on already learned tasks. By building upon ideas from network quantization and pruning, we learn binary masks that piggyback on an existing network, or are applied to unmodified weights of that network to provide good performance on a new task. These masks are learned in an end-to-end differentiable fashion, and incur a low overhead of 1 bit per network parameter, per task. Even though the underlying network is fixed, the ability to mask individual weights allows for the learning of a large number of filters. We show performance comparable to dedicated fine-tuned networks for a variety of classification tasks, including those with large domain shifts from the initial task (ImageNet), and a variety of network architectures. Unlike prior work, we do not suffer from catastrophic forgetting or competition between tasks, and our performance is agnostic to task ordering. Code available at https://github.com/arunmallya/piggyback.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge