Desheng Cai
Cross-Modal Attention Network with Dual Graph Learning in Multimodal Recommendation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Multimedia recommendation systems leverage user-item interactions and multimodal information to capture user preferences, enabling more accurate and personalized recommendations. Despite notable advancements, existing approaches still face two critical limitations: first, shallow modality fusion often relies on simple concatenation, failing to exploit rich synergic intra- and inter-modal relationships; second, asymmetric feature treatment-where users are only characterized by interaction IDs while items benefit from rich multimodal content-hinders the learning of a shared semantic space. To address these issues, we propose a Cross-modal Recursive Attention Network with dual graph Embedding (CRANE). To tackle shallow fusion, we design a core Recursive Cross-Modal Attention (RCA) mechanism that iteratively refines modality features based on cross-correlations in a joint latent space, effectively capturing high-order intra- and inter-modal dependencies. For symmetric multimodal learning, we explicitly construct users' multimodal profiles by aggregating features of their interacted items. Furthermore, CRANE integrates a symmetric dual-graph framework-comprising a heterogeneous user-item interaction graph and a homogeneous item-item semantic graph-unified by a self-supervised contrastive learning objective to fuse behavioral and semantic signals. Despite these complex modeling capabilities, CRANE maintains high computational efficiency. Theoretical and empirical analyses confirm its scalability and high practical efficiency, achieving faster convergence on small datasets and superior performance ceilings on large-scale ones. Comprehensive experiments on four public real-world datasets validate an average 5% improvement in key metrics over state-of-the-art baselines.
GRecX: An Efficient and Unified Benchmark for GNN-based Recommendation
Dec 03, 2021
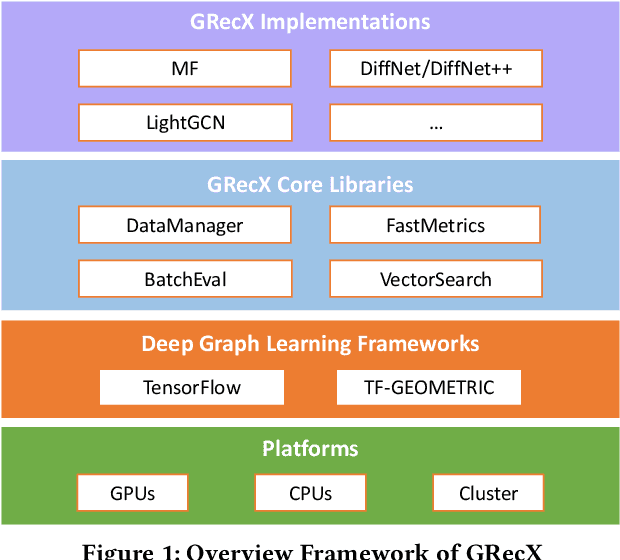
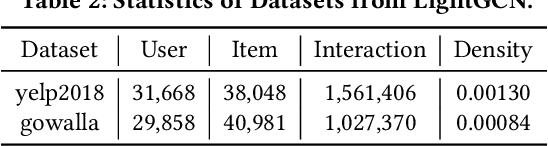
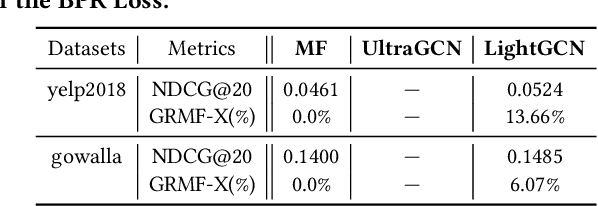
Abstract:In this paper, we present GRecX, an open-source TensorFlow framework for benchmarking GNN-based recommendation models in an efficient and unified way. GRecX consists of core libraries for building GNN-based recommendation benchmarks, as well as the implementations of popular GNN-based recommendation models. The core libraries provide essential components for building efficient and unified benchmarks, including FastMetrics (efficient metrics computation libraries), VectorSearch (efficient similarity search libraries for dense vectors), BatchEval (efficient mini-batch evaluation libraries), and DataManager (unified dataset management libraries). Especially, to provide a unified benchmark for the fair comparison of different complex GNN-based recommendation models, we design a new metric GRMF-X and integrate it into the FastMetrics component. Based on a TensorFlow GNN library tf_geometric, GRecX carefully implements a variety of popular GNN-based recommendation models. We carefully implement these baseline models to reproduce the performance reported in the literature, and our implementations are usually more efficient and friendly. In conclusion, GRecX enables uses to train and benchmark GNN-based recommendation baselines in an efficient and unified way. We conduct experiments with GRecX, and the experimental results show that GRecX allows us to train and benchmark GNN-based recommendation baselines in an efficient and unified way. The source code of GRecX is available at https://github.com/maenzhier/GRecX.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge