Denis Kukushkin
SmartPortraits: Depth Powered Handheld Smartphone Dataset of Human Portraits for State Estimation, Reconstruction and Synthesis
Apr 21, 2022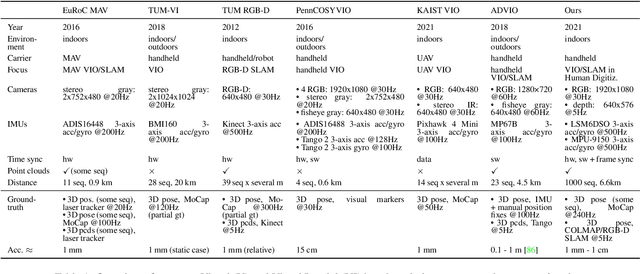
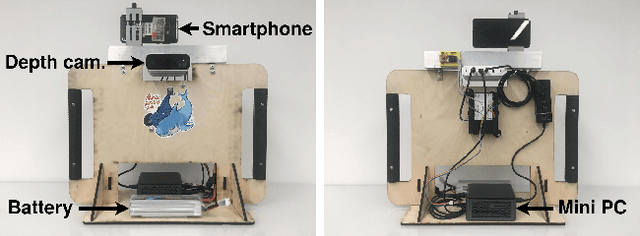
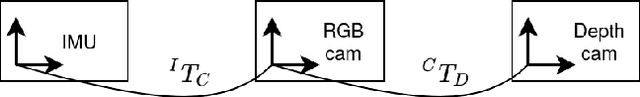
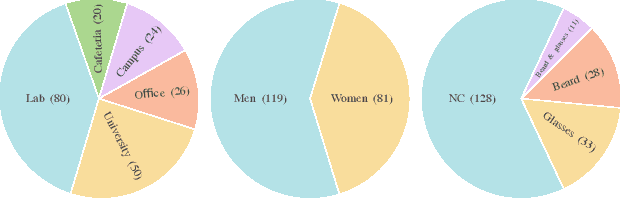
Abstract:We present a dataset of 1000 video sequences of human portraits recorded in real and uncontrolled conditions by using a handheld smartphone accompanied by an external high-quality depth camera. The collected dataset contains 200 people captured in different poses and locations and its main purpose is to bridge the gap between raw measurements obtained from a smartphone and downstream applications, such as state estimation, 3D reconstruction, view synthesis, etc. The sensors employed in data collection are the smartphone's camera and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), and an external Azure Kinect DK depth camera software synchronized with sub-millisecond precision to the smartphone system. During the recording, the smartphone flash is used to provide a periodic secondary source of lightning. Accurate mask of the foremost person is provided as well as its impact on the camera alignment accuracy. For evaluation purposes, we compare multiple state-of-the-art camera alignment methods by using a Motion Capture system. We provide a smartphone visual-inertial benchmark for portrait capturing, where we report results for multiple methods and motivate further use of the provided trajectories, available in the dataset, in view synthesis and 3D reconstruction tasks.
EVOPS Benchmark: Evaluation of Plane Segmentation from RGBD and LiDAR Data
Apr 12, 2022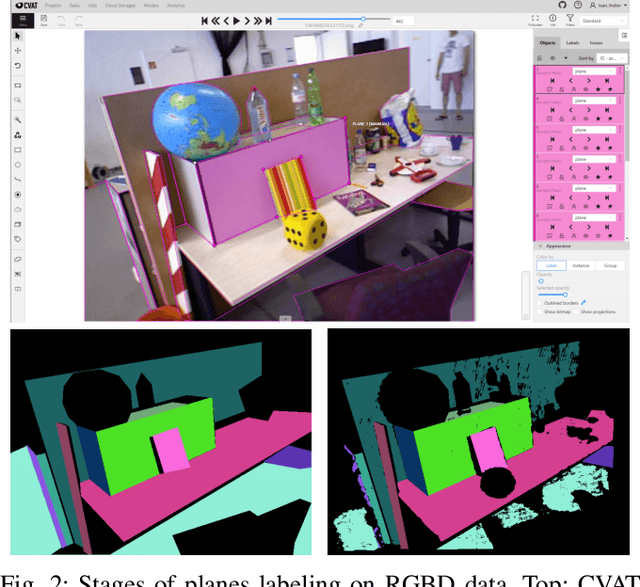
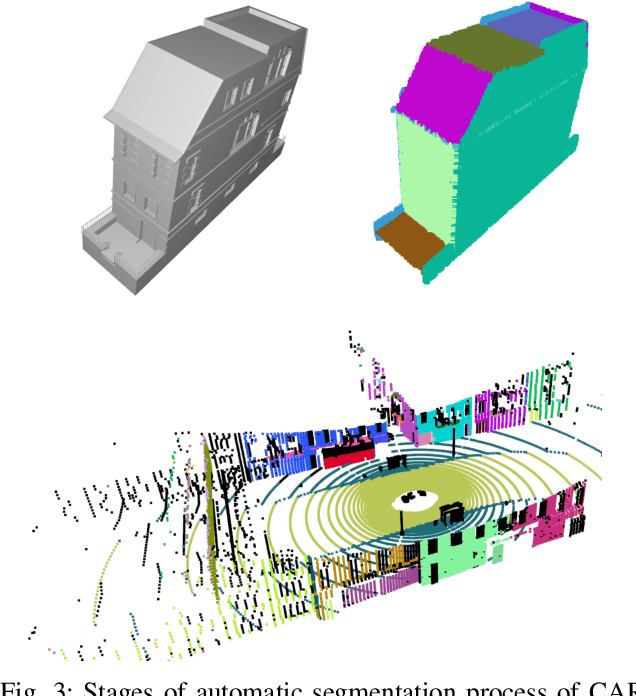
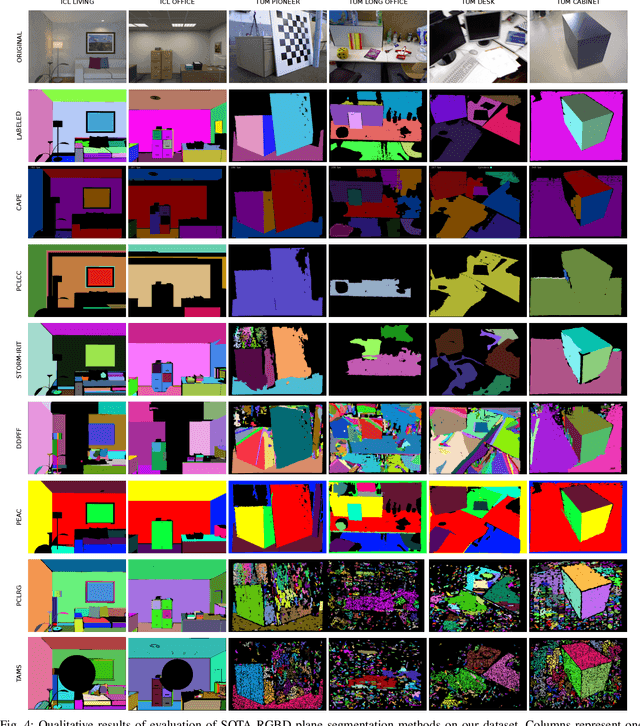
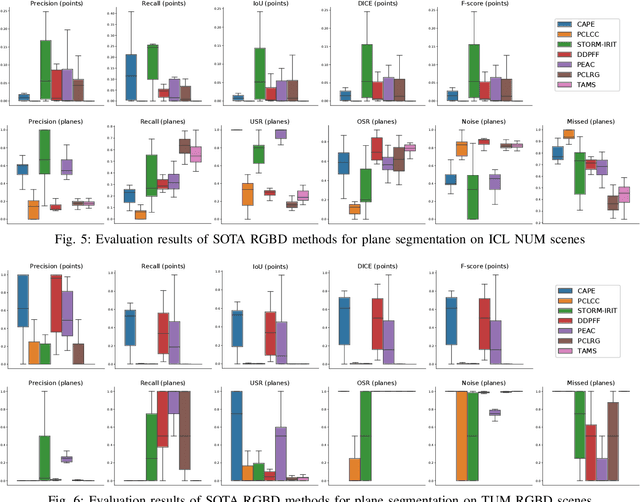
Abstract:This paper provides the EVOPS dataset for plane segmentation from 3D data, both from RGBD images and LiDAR point clouds (PC). We have designed two annotation methodologies (RGBD and LiDAR) running on well-known and widely-used datasets and we have provided a complete set of benchmarking tools including point, planes and segmentation metrics. The data includes a total number of 10k RGBD and 7K LiDAR frames over different selected scenes which consist of high quality segmented planes. The experiments report quality of SOTA methods for RGBD plane segmentation on our annotated data. All labeled data and benchmark tools used have been made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge