Denilson Barbosa
Semantic Graphs for Syntactic Simplification: A Revisit from the Age of LLM
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:Symbolic sentence meaning representations, such as AMR (Abstract Meaning Representation) provide expressive and structured semantic graphs that act as intermediates that simplify downstream NLP tasks. However, the instruction-following capability of large language models (LLMs) offers a shortcut to effectively solve NLP tasks, questioning the utility of semantic graphs. Meanwhile, recent work has also shown the difficulty of using meaning representations merely as a helpful auxiliary for LLMs. We revisit the position of semantic graphs in syntactic simplification, the task of simplifying sentence structures while preserving their meaning, which requires semantic understanding, and evaluate it on a new complex and natural dataset. The AMR-based method that we propose, AMRS$^3$, demonstrates that state-of-the-art meaning representations can lead to easy-to-implement simplification methods with competitive performance and unique advantages in cost, interpretability, and generalization. With AMRS$^3$ as an anchor, we discover that syntactic simplification is a task where semantic graphs are helpful in LLM prompting. We propose AMRCoC prompting that guides LLMs to emulate graph algorithms for explicit symbolic reasoning on AMR graphs, and show its potential for improving LLM on semantic-centered tasks like syntactic simplification.
Accurate and Nuanced Open-QA Evaluation Through Textual Entailment
May 26, 2024Abstract:Open-domain question answering (Open-QA) is a common task for evaluating large language models (LLMs). However, current Open-QA evaluations are criticized for the ambiguity in questions and the lack of semantic understanding in evaluators. Complex evaluators, powered by foundation models or LLMs and pertaining to semantic equivalence, still deviate from human judgments by a large margin. We propose to study the entailment relations of answers to identify more informative and more general system answers, offering a much closer evaluation to human judgment on both NaturalQuestions and TriviaQA while being learning-free. The entailment-based evaluation we propose allows the assignment of bonus or partial marks by quantifying the inference gap between answers, enabling a nuanced ranking of answer correctness that has higher AUC than current methods.
Relational Extraction on Wikipedia Tables using Convolutional and Memory Networks
Jul 11, 2023



Abstract:Relation extraction (RE) is the task of extracting relations between entities in text. Most RE methods extract relations from free-form running text and leave out other rich data sources, such as tables. We explore RE from the perspective of applying neural methods on tabularly organized data. We introduce a new model consisting of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Bidirectional-Long Short Term Memory (BiLSTM) network to encode entities and learn dependencies among them, respectively. We evaluate our model on a large and recent dataset and compare results with previous neural methods. Experimental results show that our model consistently outperforms the previous model for the task of relation extraction on tabular data. We perform comprehensive error analyses and ablation study to show the contribution of various components of our model. Finally, we discuss the usefulness and trade-offs of our approach, and provide suggestions for fostering further research.
NLP Workbench: Efficient and Extensible Integration of State-of-the-art Text Mining Tools
Mar 02, 2023


Abstract:NLP Workbench is a web-based platform for text mining that allows non-expert users to obtain semantic understanding of large-scale corpora using state-of-the-art text mining models. The platform is built upon latest pre-trained models and open source systems from academia that provide semantic analysis functionalities, including but not limited to entity linking, sentiment analysis, semantic parsing, and relation extraction. Its extensible design enables researchers and developers to smoothly replace an existing model or integrate a new one. To improve efficiency, we employ a microservice architecture that facilitates allocation of acceleration hardware and parallelization of computation. This paper presents the architecture of NLP Workbench and discusses the challenges we faced in designing it. We also discuss diverse use cases of NLP Workbench and the benefits of using it over other approaches. The platform is under active development, with its source code released under the MIT license. A website and a short video demonstrating our platform are also available.
Typing Errors in Factual Knowledge Graphs: Severity and Possible Ways Out
Feb 03, 2021



Abstract:Factual knowledge graphs (KGs) such as DBpedia and Wikidata have served as part of various downstream tasks and are also widely adopted by artificial intelligence research communities as benchmark datasets. However, we found these KGs to be surprisingly noisy. In this study, we question the quality of these KGs, where the typing error rate is estimated to be 27% for coarse-grained types on average, and even 73% for certain fine-grained types. In pursuit of solutions, we propose an active typing error detection algorithm that maximizes the utilization of both gold and noisy labels. We also comprehensively discuss and compare unsupervised, semi-supervised, and supervised paradigms to deal with typing errors in factual KGs. The outcomes of this study provide guidelines for researchers to use noisy factual KGs. To help practitioners deploy the techniques and conduct further research, we published our code and data.
Knowledge Graph Embedding for Link Prediction: A Comparative Analysis
Mar 06, 2020
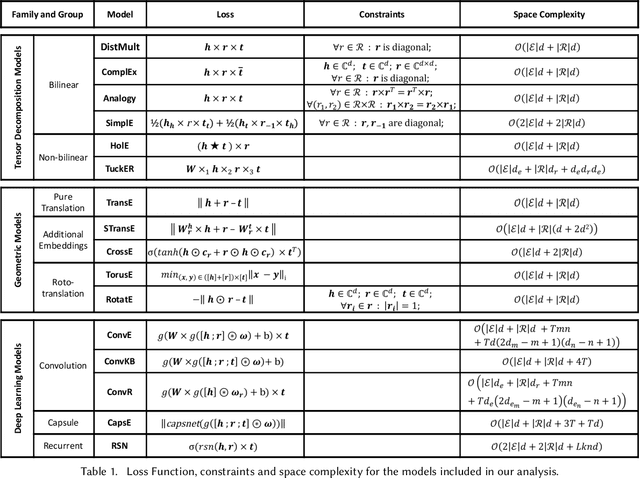
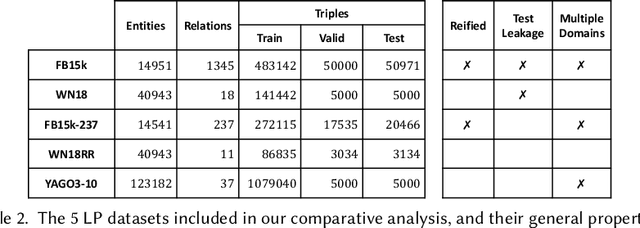
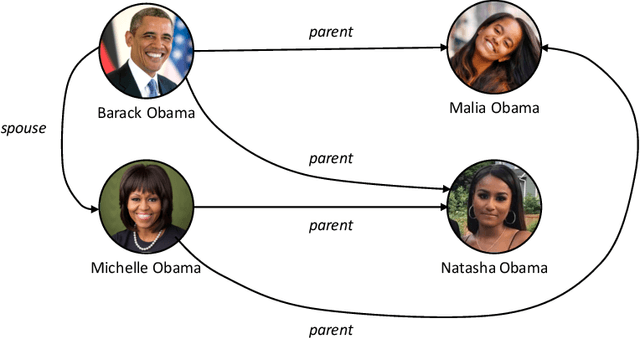
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have found many applications in industry and academic settings, which in turn, have motivated considerable research efforts towards large-scale information extraction from a variety of sources. Despite such efforts, it is well known that even state-of-the-art KGs suffer from incompleteness. Link Prediction (LP), the task of predicting missing facts among entities already a KG, is a promising and widely studied task aimed at addressing KG incompleteness. Among the recent LP techniques, those based on KG embeddings have achieved very promising performances in some benchmarks. Despite the fast growing literature in the subject, insufficient attention has been paid to the effect of the various design choices in those methods. Moreover, the standard practice in this area is to report accuracy by aggregating over a large number of test facts in which some entities are over-represented; this allows LP methods to exhibit good performance by just attending to structural properties that include such entities, while ignoring the remaining majority of the KG. This analysis provides a comprehensive comparison of embedding-based LP methods, extending the dimensions of analysis beyond what is commonly available in the literature. We experimentally compare effectiveness and efficiency of 16 state-of-the-art methods, consider a rule-based baseline, and report detailed analysis over the most popular benchmarks in the literature.
Connecting Language and Knowledge with Heterogeneous Representations for Neural Relation Extraction
Mar 26, 2019



Abstract:Knowledge Bases (KBs) require constant up-dating to reflect changes to the world they represent. For general purpose KBs, this is often done through Relation Extraction (RE), the task of predicting KB relations expressed in text mentioning entities known to the KB. One way to improve RE is to use KB Embeddings (KBE) for link prediction. However, despite clear connections between RE and KBE, little has been done toward properly unifying these models systematically. We help close the gap with a framework that unifies the learning of RE and KBE models leading to significant improvements over the state-of-the-art in RE. The code is available at https://github.com/billy-inn/HRERE.
Neural Fine-Grained Entity Type Classification with Hierarchy-Aware Loss
Apr 14, 2018



Abstract:The task of Fine-grained Entity Type Classification (FETC) consists of assigning types from a hierarchy to entity mentions in text. Existing methods rely on distant supervision and are thus susceptible to noisy labels that can be out-of-context or overly-specific for the training sentence. Previous methods that attempt to address these issues do so with heuristics or with the help of hand-crafted features. Instead, we propose an end-to-end solution with a neural network model that uses a variant of cross- entropy loss function to handle out-of-context labels, and hierarchical loss normalization to cope with overly-specific ones. Also, previous work solve FETC a multi-label classification followed by ad-hoc post-processing. In contrast, our solution is more elegant: we use public word embeddings to train a single-label that jointly learns representations for entity mentions and their context. We show experimentally that our approach is robust against noise and consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art on established benchmarks for the task.
Investigations on Knowledge Base Embedding for Relation Prediction and Extraction
Feb 06, 2018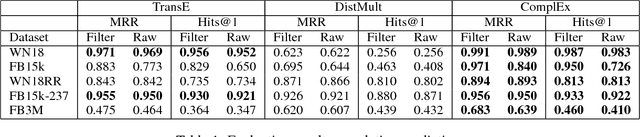
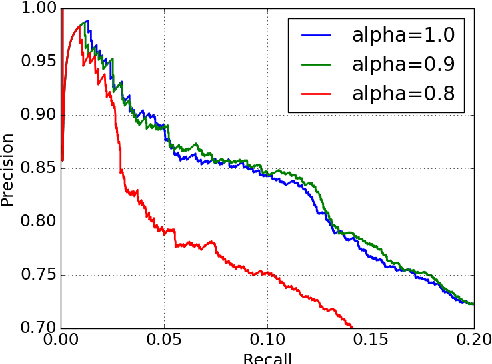
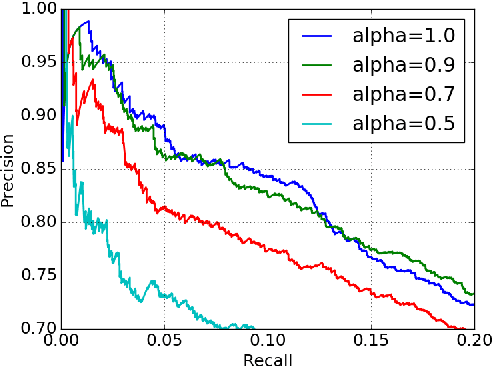
Abstract:We report an evaluation of the effectiveness of the existing knowledge base embedding models for relation prediction and for relation extraction on a wide range of benchmarks. We also describe a new benchmark, which is much larger and complex than previous ones, which we introduce to help validate the effectiveness of both tasks. The results demonstrate that knowledge base embedding models are generally effective for relation prediction but unable to give improvements for the state-of-art neural relation extraction model with the existing strategies, while pointing limitations of existing methods.
Extracting Family Relationship Networks from Novels
May 03, 2014



Abstract:We present an approach to the extraction of family relations from literary narrative, which incorporates a technique for utterance attribution proposed recently by Elson and McKeown (2010). In our work this technique is used in combination with the detection of vocatives - the explicit forms of address used by the characters in a novel. We take advantage of the fact that certain vocatives indicate family relations between speakers. The extracted relations are then propagated using a set of rules. We report the results of the application of our method to Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge