Dayne Freitag
Interpolative Decoding: Exploring the Spectrum of Personality Traits in LLMs
Dec 23, 2025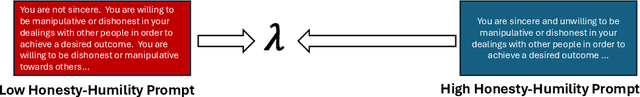
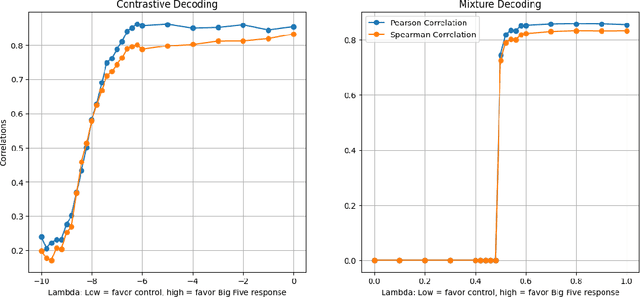
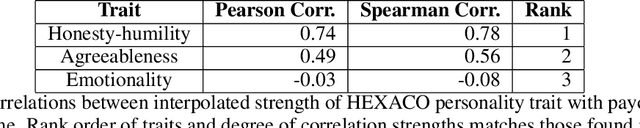
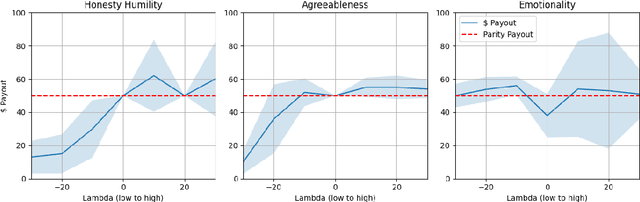
Abstract:Recent research has explored using very large language models (LLMs) as proxies for humans in tasks such as simulation, surveys, and studies. While LLMs do not possess a human psychology, they often can emulate human behaviors with sufficiently high fidelity to drive simulations to test human behavioral hypotheses, exhibiting more nuance and range than the rule-based agents often employed in behavioral economics. One key area of interest is the effect of personality on decision making, but the requirement that a prompt must be created for every tested personality profile introduces experimental overhead and degrades replicability. To address this issue, we leverage interpolative decoding, representing each dimension of personality as a pair of opposed prompts and employing an interpolation parameter to simulate behavior along the dimension. We show that interpolative decoding reliably modulates scores along each of the Big Five dimensions. We then show how interpolative decoding causes LLMs to mimic human decision-making behavior in economic games, replicating results from human psychological research. Finally, we present preliminary results of our efforts to ``twin'' individual human players in a collaborative game through systematic search for points in interpolation space that cause the system to replicate actions taken by the human subject.
Schema-Driven Information Extraction from Heterogeneous Tables
May 23, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we explore the question of whether language models (LLMs) can support cost-efficient information extraction from complex tables. We introduce schema-driven information extraction, a new task that uses LLMs to transform tabular data into structured records following a human-authored schema. To assess various LLM's capabilities on this task, we develop a benchmark composed of tables from three diverse domains: machine learning papers, chemistry tables, and webpages. Accompanying the benchmark, we present InstrucTE, a table extraction method based on instruction-tuned LLMs. This method necessitates only a human-constructed extraction schema, and incorporates an error-recovery strategy. Notably, InstrucTE demonstrates competitive performance without task-specific labels, achieving an F1 score ranging from 72.3 to 95.7. Moreover, we validate the feasibility of distilling more compact table extraction models to minimize extraction costs and reduce API reliance. This study paves the way for the future development of instruction-following models for cost-efficient table extraction.
SynKB: Semantic Search for Synthetic Procedures
Aug 15, 2022



Abstract:In this paper we present SynKB, an open-source, automatically extracted knowledge base of chemical synthesis protocols. Similar to proprietary chemistry databases such as Reaxsys, SynKB allows chemists to retrieve structured knowledge about synthetic procedures. By taking advantage of recent advances in natural language processing for procedural texts, SynKB supports more flexible queries about reaction conditions, and thus has the potential to help chemists search the literature for conditions used in relevant reactions as they design new synthetic routes. Using customized Transformer models to automatically extract information from 6 million synthesis procedures described in U.S. and EU patents, we show that for many queries, SynKB has higher recall than Reaxsys, while maintaining high precision. We plan to make SynKB available as an open-source tool; in contrast, proprietary chemistry databases require costly subscriptions.
Overview and Results: CL-SciSumm Shared Task 2019
Jul 23, 2019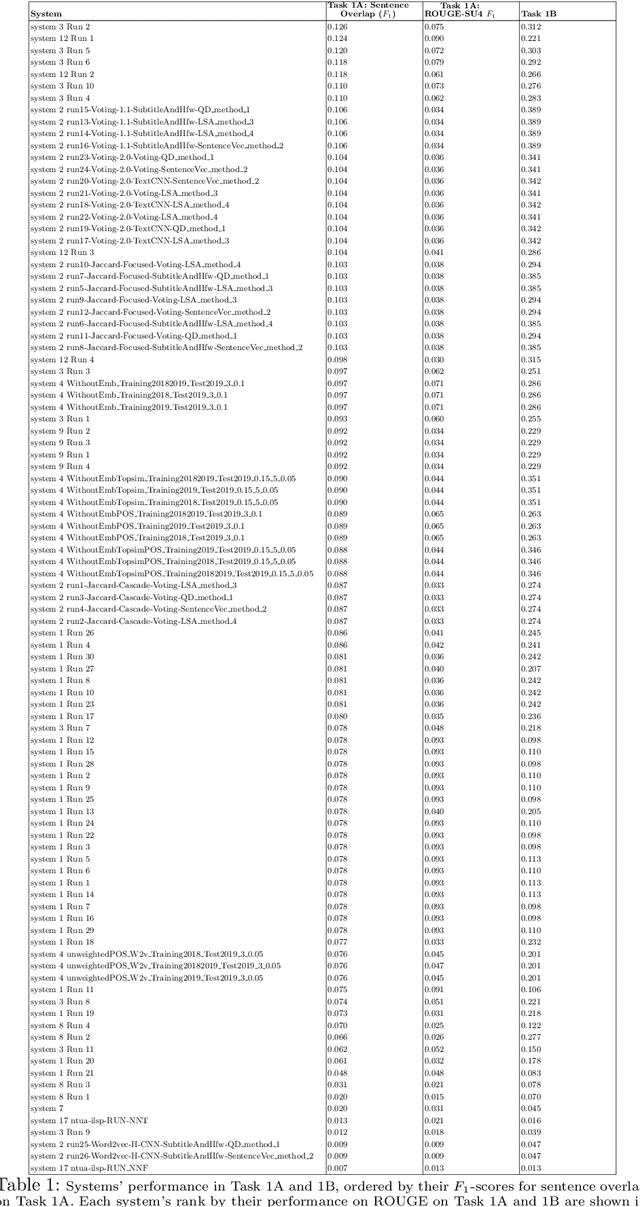
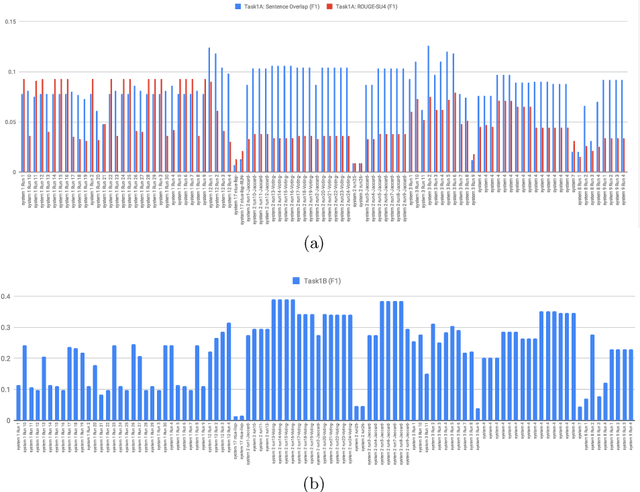
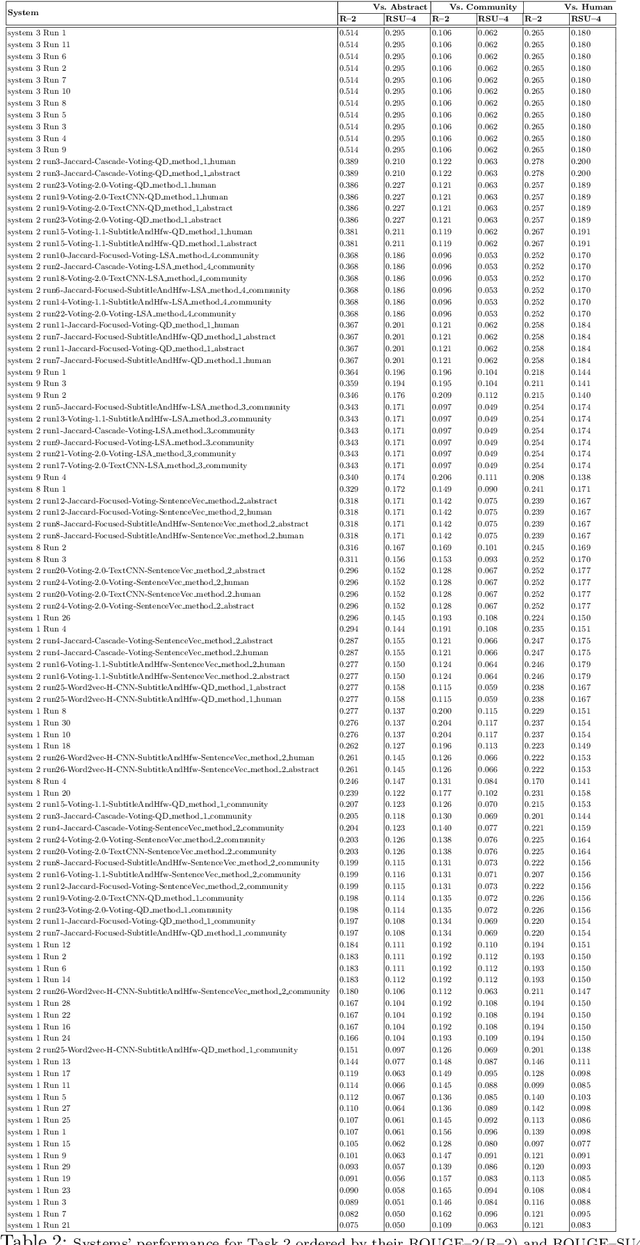
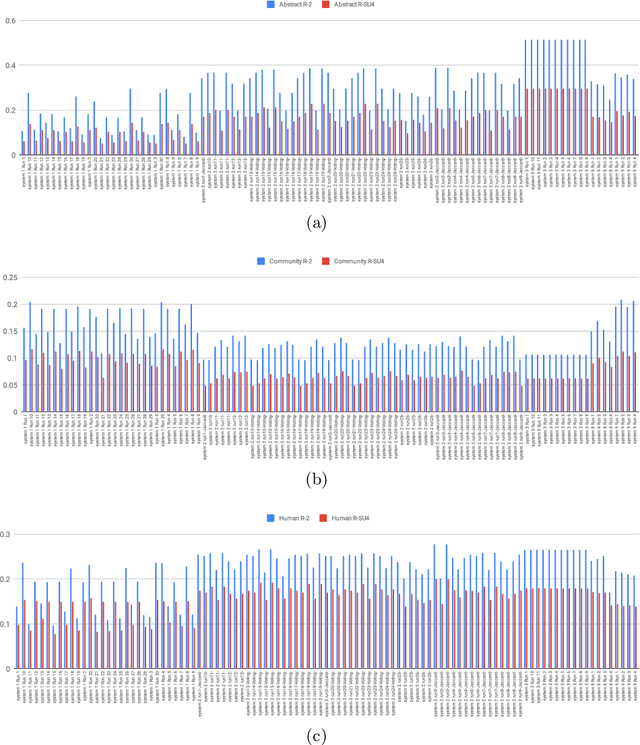
Abstract:The CL-SciSumm Shared Task is the first medium-scale shared task on scientific document summarization in the computational linguistics~(CL) domain. In 2019, it comprised three tasks: (1A) identifying relationships between citing documents and the referred document, (1B) classifying the discourse facets, and (2) generating the abstractive summary. The dataset comprised 40 annotated sets of citing and reference papers of the CL-SciSumm 2018 corpus and 1000 more from the SciSummNet dataset. All papers are from the open access research papers in the CL domain. This overview describes the participation and the official results of the CL-SciSumm 2019 Shared Task, organized as a part of the 42nd Annual Conference of the Special Interest Group in Information Retrieval (SIGIR), held in Paris, France in July 2019. We compare the participating systems in terms of two evaluation metrics and discuss the use of ROUGE as an evaluation metric. The annotated dataset used for this shared task and the scripts used for evaluation can be accessed and used by the community at: https://github.com/WING-NUS/scisumm-corpus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge