Dawei Xu
Qibo: A Large Language Model for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Mar 24, 2024



Abstract:In the field of Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant advances in user intent understanding and response in a number of specialized domains, including medicine, law, and finance. However, in the unique domain of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), the performance enhancement of LLMs is challenged by the essential differences between its theories and modern medicine, as well as the lack of specialized corpus resources. In this paper, we aim to construct and organize a professional corpus in the field of TCM, to endow the large model with professional knowledge that is characteristic of TCM theory, and to successfully develop the Qibo model based on LLaMA, which is the first LLM in the field of TCM to undergo a complete training process from pre-training to Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). Furthermore, we develop the Qibo-benchmark, a specialized tool for evaluating the performance of LLMs, which is a specialized tool for evaluating the performance of LLMs in the TCM domain. This tool will provide an important basis for quantifying and comparing the understanding and application capabilities of different models in the field of traditional Chinese medicine, and provide guidance for future research directions and practical applications of intelligent assistants for traditional Chinese medicine. Finally, we conducted sufficient experiments to prove that Qibo has good performance in the field of traditional Chinese medicine.
Being Automated or Not? Risk Identification of Occupations with Graph Neural Networks
Sep 06, 2022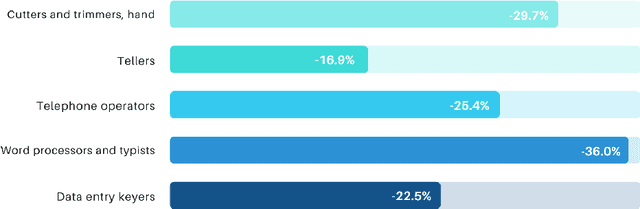
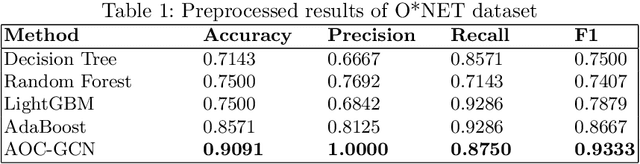
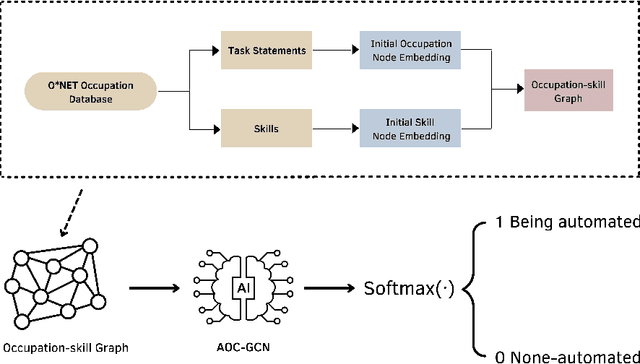
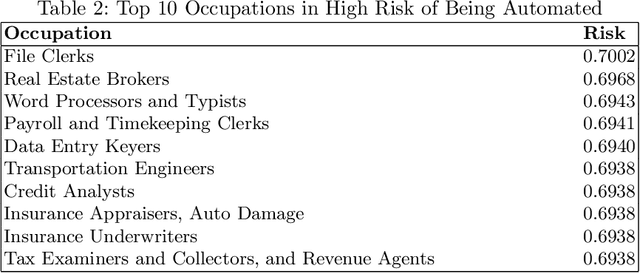
Abstract:The rapid advances in automation technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics, pose an increasing risk of automation for occupations, with a likely significant impact on the labour market. Recent social-economic studies suggest that nearly 50\% of occupations are at high risk of being automated in the next decade. However, the lack of granular data and empirically informed models have limited the accuracy of these studies and made it challenging to predict which jobs will be automated. In this paper, we study the automation risk of occupations by performing a classification task between automated and non-automated occupations. The available information is 910 occupations' task statements, skills and interactions categorised by Standard Occupational Classification (SOC). To fully utilize this information, we propose a graph-based semi-supervised classification method named \textbf{A}utomated \textbf{O}ccupation \textbf{C}lassification based on \textbf{G}raph \textbf{C}onvolutional \textbf{N}etworks (\textbf{AOC-GCN}) to identify the automated risk for occupations. This model integrates a heterogeneous graph to capture occupations' local and global contexts. The results show that our proposed method outperforms the baseline models by considering the information of both internal features of occupations and their external interactions. This study could help policymakers identify potential automated occupations and support individuals' decision-making before entering the job market.
Challenge report:VIPriors Action Recognition Challenge
Jul 16, 2020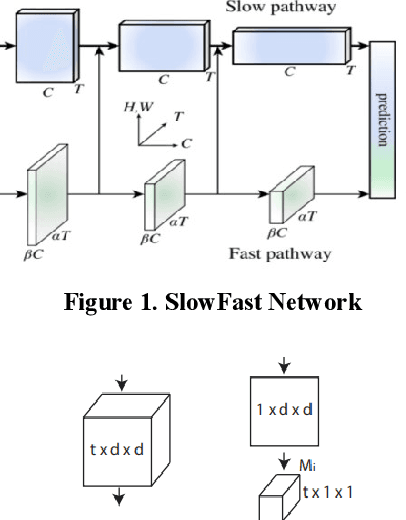
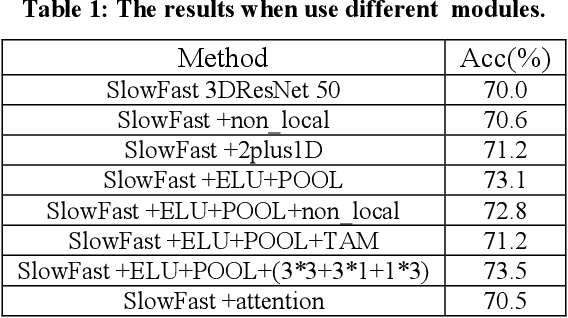
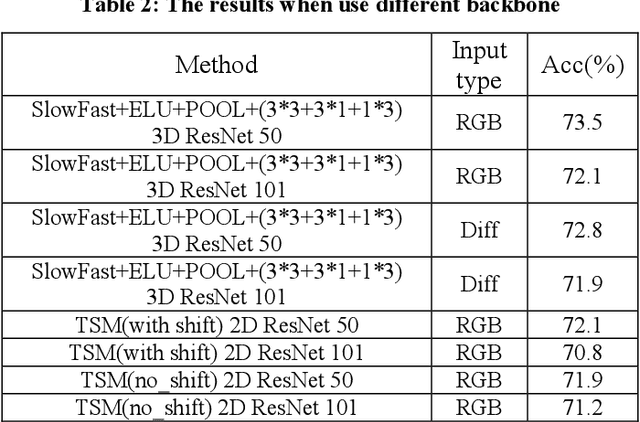
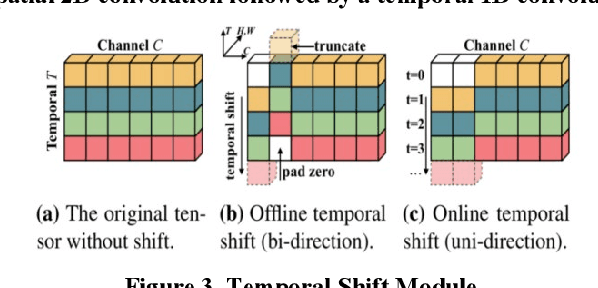
Abstract:This paper is a brief report to our submission to the VIPriors Action Recognition Challenge. Action recognition has attracted many researchers attention for its full application, but it is still challenging. In this paper, we study previous methods and propose our method. In our method, we are primarily making improvements on the SlowFast Network and fusing with TSM to make further breakthroughs. Also, we use a fast but effective way to extract motion features from videos by using residual frames as input. Better motion features can be extracted using residual frames with SlowFast, and the residual-frame-input path is an excellent supplement for existing RGB-frame-input models. And better performance obtained by combining 3D convolution(SlowFast) with 2D convolution(TSM). The above experiments were all trained from scratch on UCF101.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge