Davor Golac
Learning LLM Preference over Intra-Dialogue Pairs: A Framework for Utterance-level Understandings
Mar 07, 2025

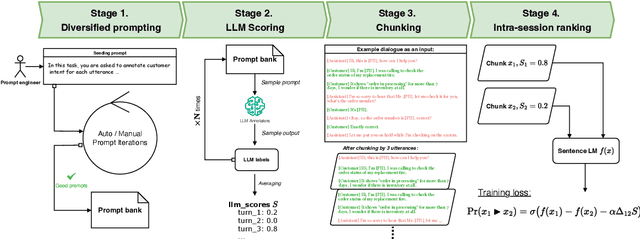

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling complex dialogue tasks without requiring use case-specific fine-tuning. However, analyzing live dialogues in real-time necessitates low-latency processing systems, making it impractical to deploy models with billions of parameters due to latency constraints. As a result, practitioners often prefer smaller models with millions of parameters, trained on high-quality, human-annotated datasets. Yet, curating such datasets is both time-consuming and costly. Consequently, there is a growing need to combine the scalability of LLM-generated labels with the precision of human annotations, enabling fine-tuned smaller models to achieve both higher speed and accuracy comparable to larger models. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective framework to address this challenge. Our approach is specifically designed for per-utterance classification problems, which encompass tasks such as intent detection, dialogue state tracking, and more. To mitigate the impact of labeling errors from LLMs -- the primary source of inaccuracies in student models -- we propose a noise-reduced preference learning loss. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves accuracy across utterance-level dialogue tasks, including sentiment detection (over $2\%$), dialogue act classification (over $1.5\%$), etc.
CSR-Bench: Benchmarking LLM Agents in Deployment of Computer Science Research Repositories
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:The increasing complexity of computer science research projects demands more effective tools for deploying code repositories. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Anthropic Claude and Meta Llama, have demonstrated significant advancements across various fields of computer science research, including the automation of diverse software engineering tasks. To evaluate the effectiveness of LLMs in handling complex code development tasks of research projects, particularly for NLP/CV/AI/ML/DM topics, we introduce CSR-Bench, a benchmark for Computer Science Research projects. This benchmark assesses LLMs from various aspects including accuracy, efficiency, and deployment script quality, aiming to explore their potential in conducting computer science research autonomously. We also introduce a novel framework, CSR-Agents, that utilizes multiple LLM agents to automate the deployment of GitHub code repositories of computer science research projects. Specifically, by checking instructions from markdown files and interpreting repository structures, the model generates and iteratively improves bash commands that set up the experimental environments and deploy the code to conduct research tasks. Preliminary results from CSR-Bench indicate that LLM agents can significantly enhance the workflow of repository deployment, thereby boosting developer productivity and improving the management of developmental workflows.
GRAM: Generative Retrieval Augmented Matching of Data Schemas in the Context of Data Security
Jun 04, 2024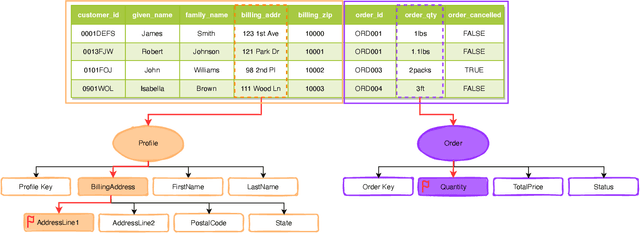
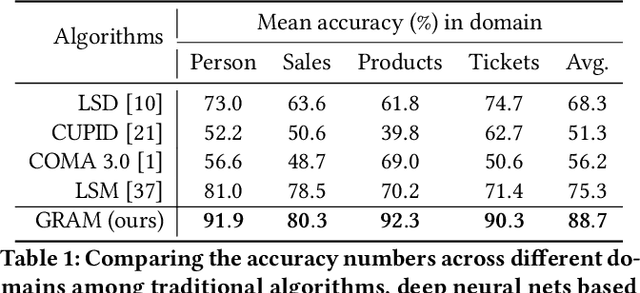
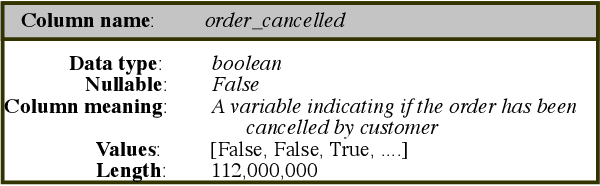
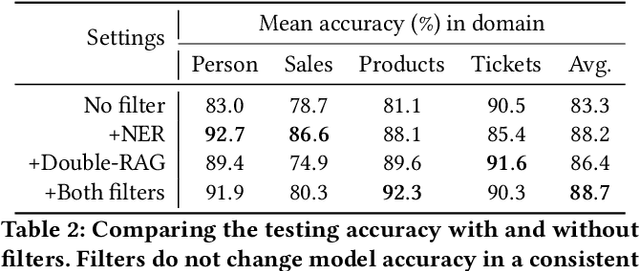
Abstract:Schema matching constitutes a pivotal phase in the data ingestion process for contemporary database systems. Its objective is to discern pairwise similarities between two sets of attributes, each associated with a distinct data table. This challenge emerges at the initial stages of data analytics, such as when incorporating a third-party table into existing databases to inform business insights. Given its significance in the realm of database systems, schema matching has been under investigation since the 2000s. This study revisits this foundational problem within the context of large language models. Adhering to increasingly stringent data security policies, our focus lies on the zero-shot and few-shot scenarios: the model should analyze only a minimal amount of customer data to execute the matching task, contrasting with the conventional approach of scrutinizing the entire data table. We emphasize that the zero-shot or few-shot assumption is imperative to safeguard the identity and privacy of customer data, even at the potential cost of accuracy. The capability to accurately match attributes under such stringent requirements distinguishes our work from previous literature in this domain.
Neural Locality Sensitive Hashing for Entity Blocking
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) is a fundamental algorithmic technique widely employed in large-scale data processing applications, such as nearest-neighbor search, entity resolution, and clustering. However, its applicability in some real-world scenarios is limited due to the need for careful design of hashing functions that align with specific metrics. Existing LSH-based Entity Blocking solutions primarily rely on generic similarity metrics such as Jaccard similarity, whereas practical use cases often demand complex and customized similarity rules surpassing the capabilities of generic similarity metrics. Consequently, designing LSH functions for these customized similarity rules presents considerable challenges. In this research, we propose a neuralization approach to enhance locality-sensitive hashing by training deep neural networks to serve as hashing functions for complex metrics. We assess the effectiveness of this approach within the context of the entity resolution problem, which frequently involves the use of task-specific metrics in real-world applications. Specifically, we introduce NLSHBlock (Neural-LSH Block), a novel blocking methodology that leverages pre-trained language models, fine-tuned with a novel LSH-based loss function. Through extensive evaluations conducted on a diverse range of real-world datasets, we demonstrate the superiority of NLSHBlock over existing methods, exhibiting significant performance improvements. Furthermore, we showcase the efficacy of NLSHBlock in enhancing the performance of the entity matching phase, particularly within the semi-supervised setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge