Davide Ettori
Intel Labs, Oregon
Spectral Geometry for Deep Learning: Compression and Hallucination Detection via Random Matrix Theory
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large language models and deep neural networks achieve strong performance but suffer from reliability issues and high computational cost. This thesis proposes a unified framework based on spectral geometry and random matrix theory to address both problems by analyzing the eigenvalue structure of hidden activations. The first contribution, EigenTrack, is a real-time method for detecting hallucinations and out-of-distribution behavior in language and vision-language models using spectral features and their temporal dynamics. The second contribution, RMT-KD, is a principled compression method that identifies informative spectral components and applies iterative knowledge distillation to produce compact and efficient models while preserving accuracy. Together, these results show that spectral statistics provide interpretable and robust signals for monitoring uncertainty and guiding compression in large-scale neural networks.
EigenTrack: Spectral Activation Feature Tracking for Hallucination and Out-of-Distribution Detection in LLMs and VLMs
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer broad utility but remain prone to hallucination and out-of-distribution (OOD) errors. We propose EigenTrack, an interpretable real-time detector that uses the spectral geometry of hidden activations, a compact global signature of model dynamics. By streaming covariance-spectrum statistics such as entropy, eigenvalue gaps, and KL divergence from random baselines into a lightweight recurrent classifier, EigenTrack tracks temporal shifts in representation structure that signal hallucination and OOD drift before surface errors appear. Unlike black- and grey-box methods, it needs only a single forward pass without resampling. Unlike existing white-box detectors, it preserves temporal context, aggregates global signals, and offers interpretable accuracy-latency trade-offs.
RMT-KD: Random Matrix Theoretic Causal Knowledge Distillation
Sep 19, 2025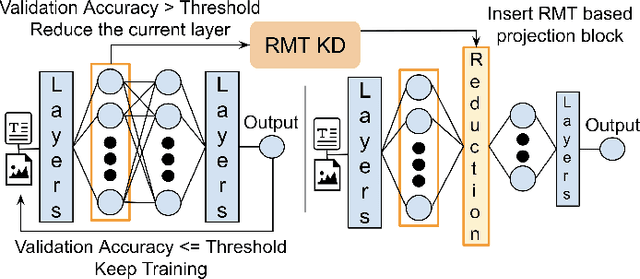
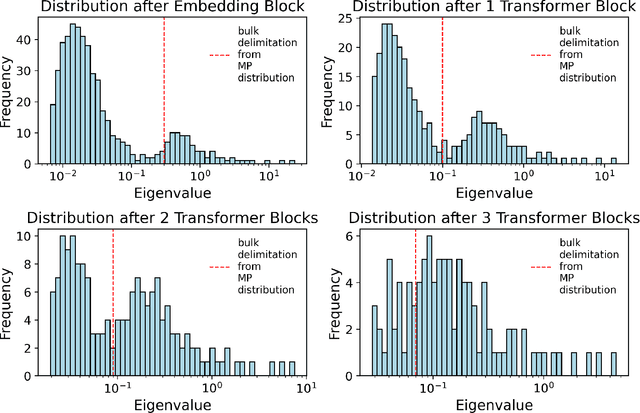
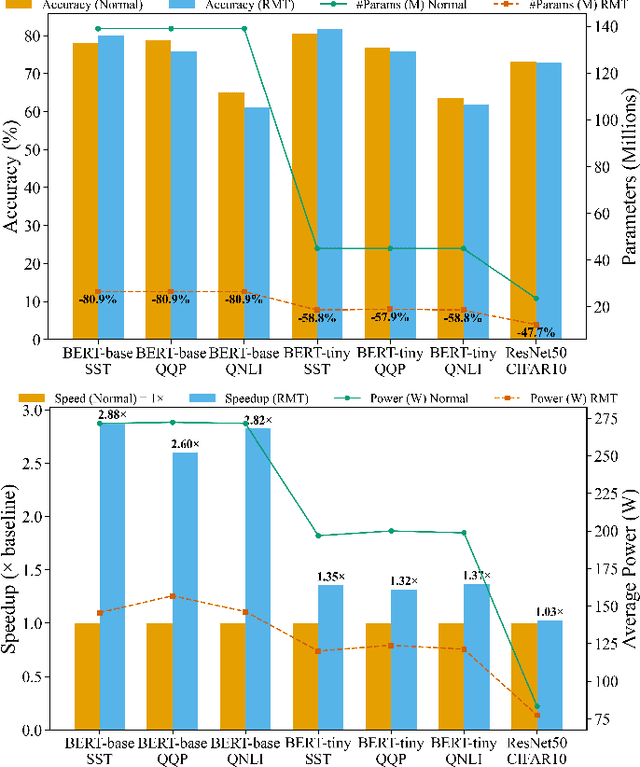
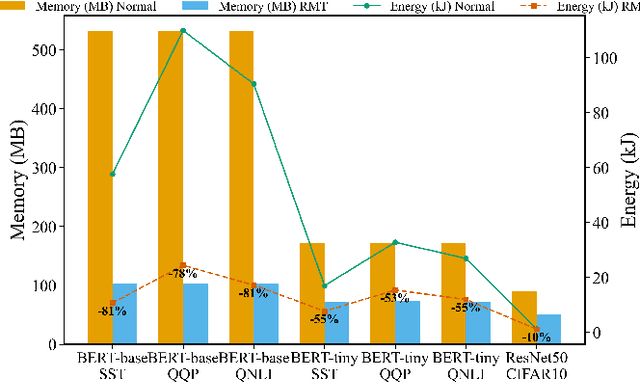
Abstract:Large deep learning models such as BERT and ResNet achieve state-of-the-art performance but are costly to deploy at the edge due to their size and compute demands. We present RMT-KD, a compression method that leverages Random Matrix Theory (RMT) for knowledge distillation to iteratively reduce network size. Instead of pruning or heuristic rank selection, RMT-KD preserves only informative directions identified via the spectral properties of hidden representations. RMT-based causal reduction is applied layer by layer with self-distillation to maintain stability and accuracy. On GLUE, AG News, and CIFAR-10, RMT-KD achieves up to 80% parameter reduction with only 2% accuracy loss, delivering 2.8x faster inference and nearly halved power consumption. These results establish RMT-KD as a mathematically grounded approach to network distillation.
SPARC: Subspace-Aware Prompt Adaptation for Robust Continual Learning in LLMs
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:We propose SPARC, a lightweight continual learning framework for large language models (LLMs) that enables efficient task adaptation through prompt tuning in a lower-dimensional space. By leveraging principal component analysis (PCA), we identify a compact subspace of the training data. Optimizing prompts in this lower-dimensional space enhances training efficiency, as it focuses updates on the most relevant features while reducing computational overhead. Furthermore, since the model's internal structure remains unaltered, the extensive knowledge gained from pretraining is fully preserved, ensuring that previously learned information is not compromised during adaptation. Our method achieves high knowledge retention in both task-incremental and domain-incremental continual learning setups while fine-tuning only 0.04% of the model's parameters. Additionally, by integrating LoRA, we enhance adaptability to computational constraints, allowing for a tradeoff between accuracy and training cost. Experiments on the SuperGLUE benchmark demonstrate that our PCA-based prompt tuning combined with LoRA maintains full knowledge retention while improving accuracy, utilizing only 1% of the model's parameters. These results establish our approach as a scalable and resource-efficient solution for continual learning in LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge