David Solans
Non-IID data in Federated Learning: A Systematic Review with Taxonomy, Metrics, Methods, Frameworks and Future Directions
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in machine learning have highlighted Federated Learning (FL) as a promising approach that enables multiple distributed users (so-called clients) to collectively train ML models without sharing their private data. While this privacy-preserving method shows potential, it struggles when data across clients is not independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data. The latter remains an unsolved challenge that can result in poorer model performance and slower training times. Despite the significance of non-IID data in FL, there is a lack of consensus among researchers about its classification and quantification. This systematic review aims to fill that gap by providing a detailed taxonomy for non-IID data, partition protocols, and metrics to quantify data heterogeneity. Additionally, we describe popular solutions to address non-IID data and standardized frameworks employed in FL with heterogeneous data. Based on our state-of-the-art review, we present key lessons learned and suggest promising future research directions.
Human Response to an AI-Based Decision Support System: A User Study on the Effects of Accuracy and Bias
Mar 24, 2022
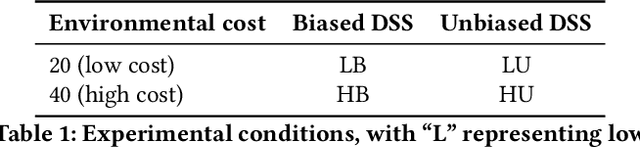
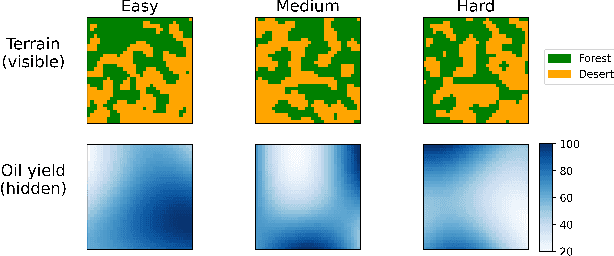
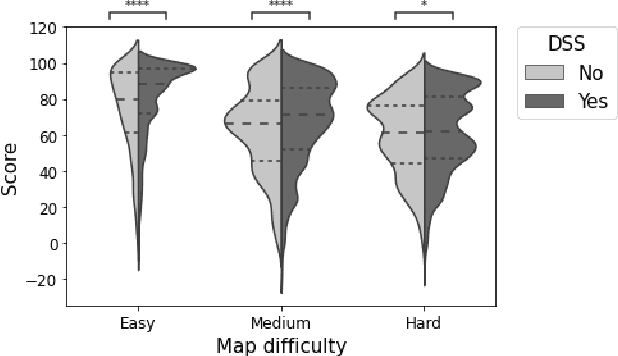
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly used to build Decision Support Systems (DSS) across many domains. This paper describes a series of experiments designed to observe human response to different characteristics of a DSS such as accuracy and bias, particularly the extent to which participants rely on the DSS, and the performance they achieve. In our experiments, participants play a simple online game inspired by so-called "wildcat" (i.e., exploratory) drilling for oil. The landscape has two layers: a visible layer describing the costs (terrain), and a hidden layer describing the reward (oil yield). Participants in the control group play the game without receiving any assistance, while in treatment groups they are assisted by a DSS suggesting places to drill. For certain treatments, the DSS does not consider costs, but only rewards, which introduces a bias that is observable by users. Between subjects, we vary the accuracy and bias of the DSS, and observe the participants' total score, time to completion, the extent to which they follow or ignore suggestions. We also measure the acceptability of the DSS in an exit survey. Our results show that participants tend to score better with the DSS, that the score increase is due to users following the DSS advice, and related to the difficulty of the game and the accuracy of the DSS. We observe that this setting elicits mostly rational behavior from participants, who place a moderate amount of trust in the DSS and show neither algorithmic aversion (under-reliance) nor automation bias (over-reliance).However, their stated willingness to accept the DSS in the exit survey seems less sensitive to the accuracy of the DSS than their behavior, suggesting that users are only partially aware of the (lack of) accuracy of the DSS.
Poisoning Attacks on Algorithmic Fairness
Apr 23, 2020



Abstract:Research in adversarial machine learning has shown how the performance of machine learning models can be seriously compromised by injecting even a small fraction of poisoning points into the training data. While the effects on model accuracy of such poisoning attacks have been widely studied, their potential effects on other model performance metrics remain to be evaluated. In this work, we introduce an optimization framework for poisoning attacks against algorithmic fairness, and develop a gradient-based poisoning attack aimed at introducing classification disparities among different groups in the data. We empirically show that our attack is effective not only in the white-box setting, in which the attacker has full access to the target model, but also in a more challenging black-box scenario in which the attacks are optimized against a substitute model and then transferred to the target model. We believe that our findings pave the way towards the definition of an entirely novel set of adversarial attacks targeting algorithmic fairness in different scenarios, and that investigating such vulnerabilities will help design more robust algorithms and countermeasures in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge