David Choi
AlphaStar Unplugged: Large-Scale Offline Reinforcement Learning
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:StarCraft II is one of the most challenging simulated reinforcement learning environments; it is partially observable, stochastic, multi-agent, and mastering StarCraft II requires strategic planning over long time horizons with real-time low-level execution. It also has an active professional competitive scene. StarCraft II is uniquely suited for advancing offline RL algorithms, both because of its challenging nature and because Blizzard has released a massive dataset of millions of StarCraft II games played by human players. This paper leverages that and establishes a benchmark, called AlphaStar Unplugged, introducing unprecedented challenges for offline reinforcement learning. We define a dataset (a subset of Blizzard's release), tools standardizing an API for machine learning methods, and an evaluation protocol. We also present baseline agents, including behavior cloning, offline variants of actor-critic and MuZero. We improve the state of the art of agents using only offline data, and we achieve 90% win rate against previously published AlphaStar behavior cloning agent.
A Semidefinite Program for Structured Blockmodels
Nov 16, 2016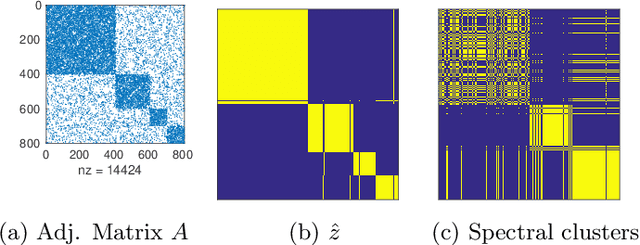



Abstract:Semidefinite programs have recently been developed for the problem of community detection, which may be viewed as a special case of the stochastic blockmodel. Here, we develop a semidefinite program that can be tailored to other instances of the blockmodel, such as non-assortative networks and overlapping communities. We establish label recovery in sparse settings, with conditions that are analogous to recent results for community detection. In settings where the data is not generated by a blockmodel, we give an oracle inequality that bounds excess risk relative to the best blockmodel approximation. Simulations are presented for community detection, for overlapping communities, and for latent space models.
Co-clustering separately exchangeable network data
Jan 16, 2014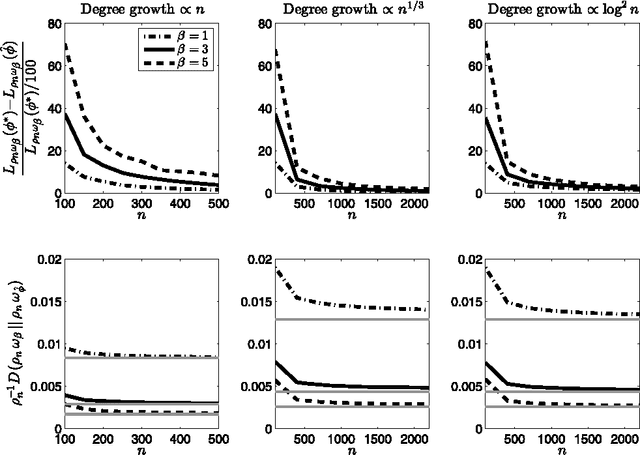
Abstract:This article establishes the performance of stochastic blockmodels in addressing the co-clustering problem of partitioning a binary array into subsets, assuming only that the data are generated by a nonparametric process satisfying the condition of separate exchangeability. We provide oracle inequalities with rate of convergence $\mathcal{O}_P(n^{-1/4})$ corresponding to profile likelihood maximization and mean-square error minimization, and show that the blockmodel can be interpreted in this setting as an optimal piecewise-constant approximation to the generative nonparametric model. We also show for large sample sizes that the detection of co-clusters in such data indicates with high probability the existence of co-clusters of equal size and asymptotically equivalent connectivity in the underlying generative process.
* Published in at http://dx.doi.org/10.1214/13-AOS1173 the Annals of Statistics (http://www.imstat.org/aos/) by the Institute of Mathematical Statistics (http://www.imstat.org)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge